Innovation Strategy: 9-Step Strategy Framework for Innovation
Published: 30 November, 2023
Innovation
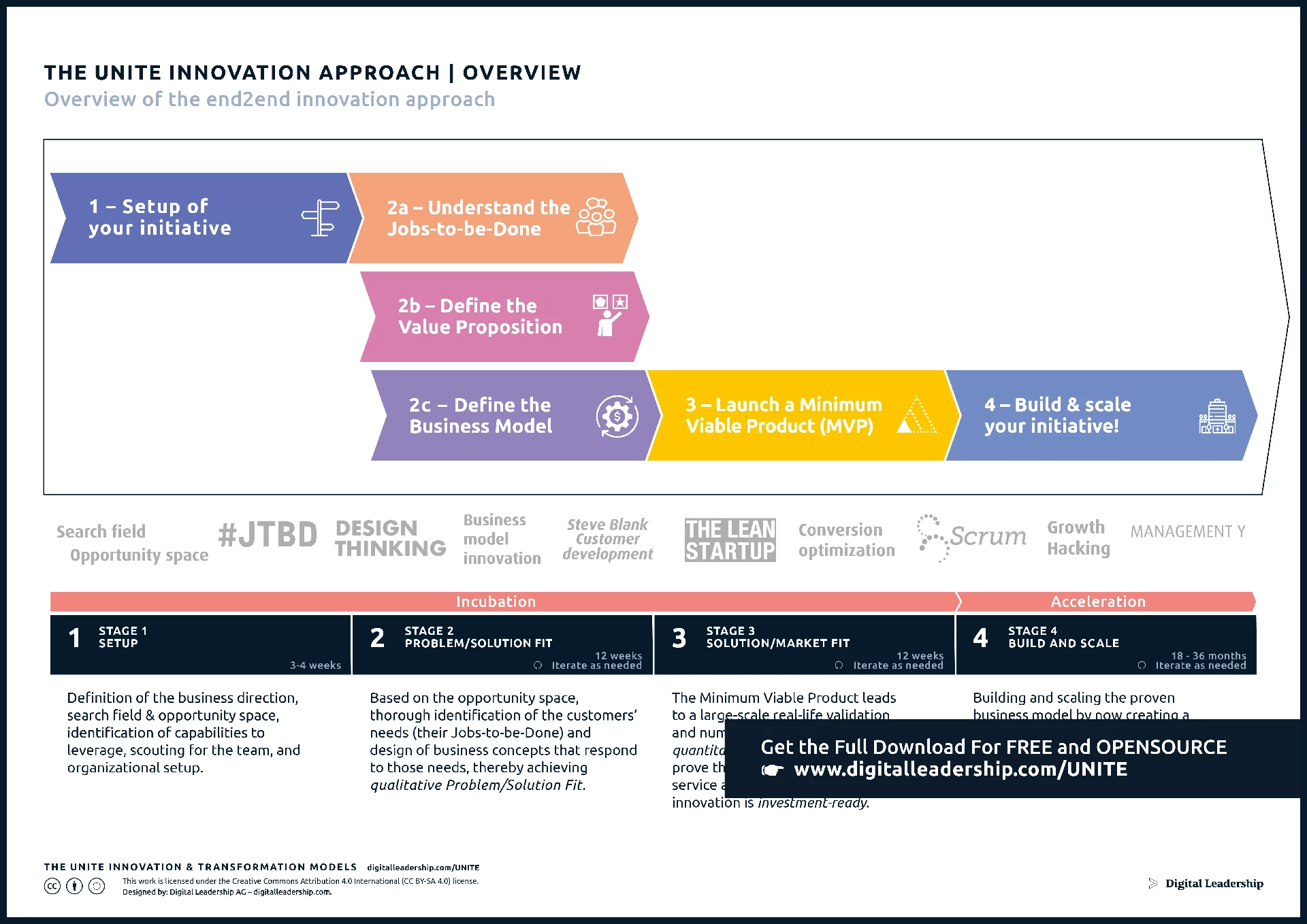
Table of Contents
Innovation is the art of turning ideas into impactful solutions, the engine driving progress, and the key differentiator in a competitive marketplace, It is the force that propels organizations forward and creates value. Innovative strategies play a key role in how products are created, It is the deliberate and strategic plan to harness creative energies toward defined business goals, and gain a competitive advantage. Digital Leadership leverages a wealth of experience and a commitment to staying at the forefront of Innovation and digital transformation strategy.
Recognizing the crucial significance of innovation in shaping the success of modern businesses is essential in the business environment, At Digital Leadership, we understand the pivotal role of innovation Strategy specializing in Innovation and Leadership Consulting services, we empower organizations to navigate the challenges and opportunities in their digital transformation journey. Our Innovation blueprint service serves as the starting point, conducting a meticulous evaluation of current innovation practices and integrating them into the overall business plan. This sets the foundation for businesses to choose tailored services aligned with their specific needs and innovation objectives.
This article delves into the intricacies of innovation strategy, dissecting its dimensions and unveiling a strategic framework comprising seven pivotal steps. From understanding the essence of innovation strategy to dissecting real-world innovation examples, each section is meticulously crafted to provide you with actionable insights that transcend theoretical concepts.
Innovation Strategy Definition In Business: What is an Innovation Strategy?
An innovation strategy directs decisions on the allocation of resources to meet a business’s innovation objectives, deliver and create value, and establish a competitive advantage. This strategic framework encompasses an analysis of the business’s competitive and technological environment, considering both external challenges and opportunities.
By addressing external challenges and opportunities, an innovation strategy becomes a dynamic tool for organizations aiming not only to adapt but to proactively shape their future A flexible and dynamic organizational structure that encourages cross-functional collaboration and communication is vital. This strategic approach encompasses a range of considerations, including the identification of emerging trends, the assessment of market demands, and the evaluation of potential disruptive forces. It serves as a proactive and forward-thinking guide, aligning the organization’s innovation efforts with broader business goals and ensuring resilience in the face of evolving market dynamics.
It extends beyond a mere roadmap; it serves as a blueprint for decision-making, resource allocation, and risk management. It involves a strategic plan for harnessing creativity, fostering collaboration, and implementing new ideas to drive meaningful change within the organization. As businesses navigate the complexities of today’s fast-paced and technology-driven landscape, an effective innovation strategy becomes a key differentiator, enabling them to stay ahead of the curve.
One crucial aspect of an innovation strategy is its alignment with the “Jobs-to-be-Done” framework. This framework recognizes that customers “hire” a product or service to get a job done in their lives. Understanding these jobs and designing solutions that address them is integral to successful innovation. It shifts the focus from merely improving products to solving specific customer problems, providing a more targeted and customer-centric approach. You can download it now.
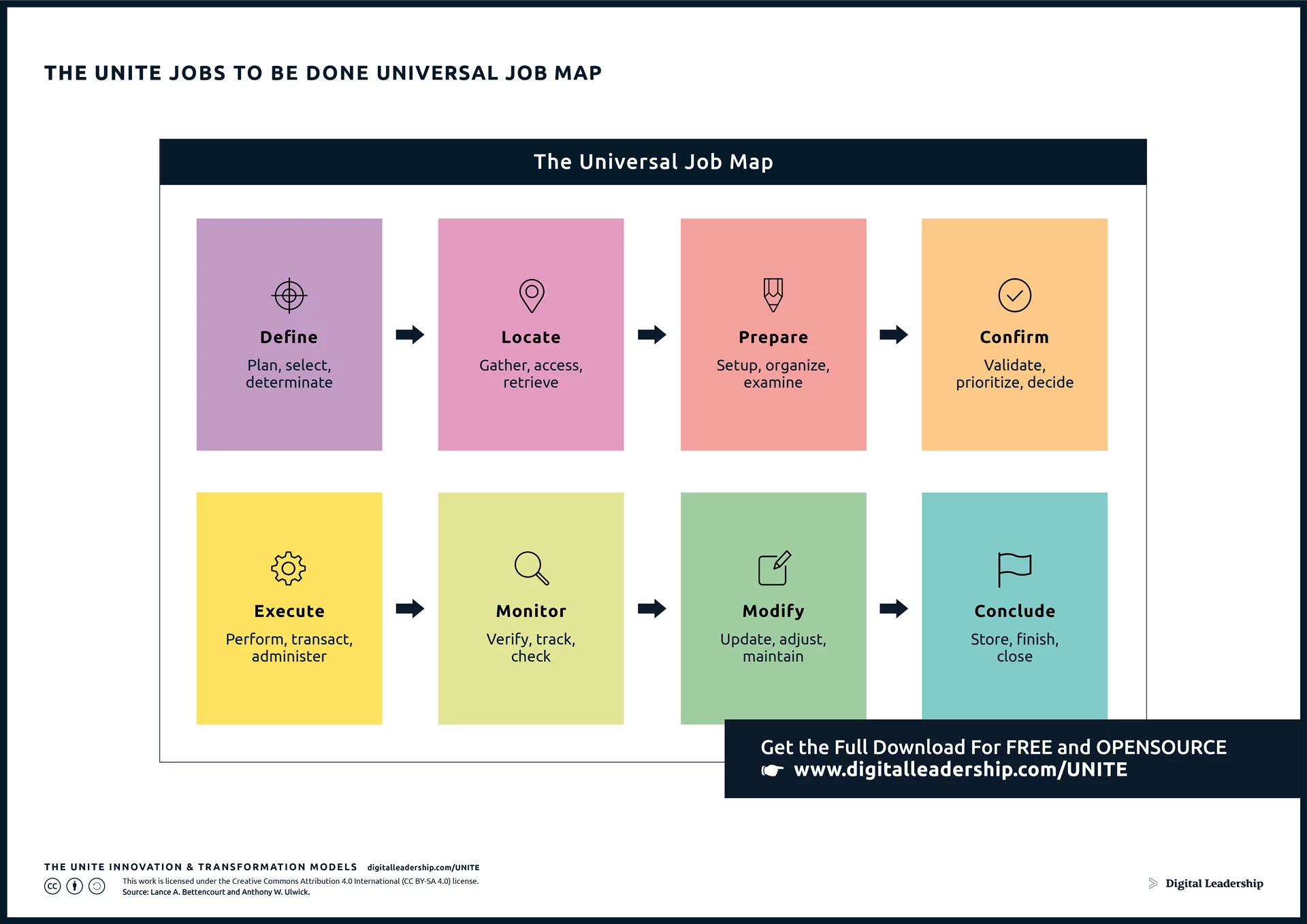
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Source: Lance A. Bettencourt and Anthony W. Ulwick.
Much more about Jobs to be done and other approaches to innovation strategy you will find in our book “How to Create Innovation”. Recognizing that innovation is a dynamic process, this guide emphasizes adaptability. Stay ahead of the curve by understanding how innovation strategies evolve with market dynamics, ensuring sustained relevance and competitiveness.
Benefits of Innovation Strategy for Business
The adoption of a well-crafted Innovation Strategy brings forth a myriad of benefits for businesses. From fostering a culture of creativity to staying competitive in the market, innovation serves as the lifeblood of growth and resilience. Innovation strategy is a crucial component when a new brand identifies gaps in the industry or overlooked segments. Our expertise lies in developing customized strategies, launching new ventures, and cultivating positive relationships, all aimed at driving innovation, business transformation, and business growth.
1) Competitive Advantage:
An innovation strategy is a cornerstone for businesses aiming to secure and maintain a competitive edge. In a rapidly evolving market, where consumer preferences and technological landscapes constantly shift, businesses must proactively introduce novel and improved products, services, or processes. This ongoing commitment to innovation not only differentiates organizations from competitors but positions them as leaders in their respective industries. By staying at the forefront of advancements, businesses can anticipate market trends, meet evolving customer needs, and consistently outperform competitors. This sustained effort to innovate not only attracts customers but also fosters brand loyalty, making it a pivotal factor in long-term success.
2) Market Relevance:
The ability to dynamically adapt to changes, whether driven by technology, economics, or societal shifts, is a hallmark of businesses with a robust innovation strategy. Beyond survival, innovation enhances customer engagement, fosters brand resonance, and positions businesses as agile responders to disruptions. It opens avenues to compete in emerging markets, build a reputation for forward-thinking, and establish a legacy of success. Ultimately, the benefits of innovation extend beyond product features; they shape the very essence of a business, ensuring its relevance, resonance, and enduring impact on the market it serves.
3) Increased Efficiency:
Businesses that actively embrace innovation find themselves at the forefront of streamlined processes, empowered by the integration of cutting-edge technologies and the optimization of workflows. Automation, a cornerstone of innovation, replaces manual tasks with precision, leading to significant time savings and reduced errors. The strategic adoption of new technologies, from artificial intelligence to the Internet of Things, propels organizations into a realm of real-time insights and predictive analytics, fostering proactive decision-making.
This commitment to innovation not only reduces operational costs through optimized resource utilization but also paves the way for scalable and customer-centric processes. By continually refining and reimagining their operational frameworks, businesses position themselves to not only meet the demands of the present but also to navigate the complexities of an ever-evolving future with resilience and excellence.
4) Enhanced Customer Satisfaction:
Enhanced customer satisfaction is a pivotal outcome of addressing customer needs through innovative products or services. It transcends conventional approaches by creating memorable and meaningful experiences that resonate deeply with customers. The key to achieving enhanced satisfaction lies in a multifaceted approach. Businesses can leverage innovation to personalize their offerings based on individual preferences, respond to inquiries swiftly through advanced communication channels, and design user-friendly interfaces for seamless interactions.
Anticipating customer needs through data-driven insights, fostering continuous improvement, and implementing innovative loyalty programs contribute to building strong emotional connections. Transparent communication, innovative feedback mechanisms, and the provision of multichannel experiences further enhance customer satisfaction. Ultimately, businesses that prioritize innovation in these areas not only meet customer expectations but surpass them, fostering lasting loyalty and advocacy in an ever-evolving market landscape.
5) Revenue Growth:
Innovation serves as a catalyst for revenue growth. Successful innovations have the potential to open new revenue streams for organizations. By introducing novel products or services, businesses can not only attract new customers but also enhance sales to existing ones. The cumulative effect is a substantial increase in overall revenue.
This aspect of innovation underscores its strategic importance, positioning it not only as a driver of creativity but as a direct contributor to the financial success and sustainability of the organization. Embracing innovative practices becomes a dynamic means to stay competitive, capture market share, and ultimately achieve sustained revenue growth.
6) Long-Term Sustainability:
Continuous innovation is key to long-term sustainability. Businesses that embrace innovation are better positioned to navigate challenges, thrive in evolving markets, and ensure their relevance over time. Without an effective innovation strategy in place, a company is not likely to maintain a competitive advantage and keep customers engaged over the long term.
7) Clarify goals and priorities
An effective innovation strategy serves as a compass, clearly defining the goals and priorities of an organization’s innovation activities. By articulating specific objectives, it provides a roadmap for teams to follow, ensuring alignment with broader business objectives. This clarity not only sharpens the focus on resources and energy but also establishes a cohesive direction for innovation initiatives.
The strategy becomes a guiding framework, enabling the organization to make informed decisions about where to allocate resources and efforts, fostering a more streamlined and purposeful approach to innovation. Ultimately, the articulation of goals and priorities within the innovation strategy enhances organizational efficiency and effectiveness in pursuing breakthrough innovation ideas and driving meaningful outcomes.
Types of Innovation Strategies
Businesses employ various strategies to drive change, achieve competitive advantages, and navigate the complexities of the modern market. These strategies can be broadly categorized into proactive, active, reactive, and passive approaches, each offering a distinct set of benefits and challenges. In this exploration, we delve into the intricacies of these innovation strategies and types of innovation, shedding light on their applications and implications for businesses aiming to thrive in a rapidly evolving environment.
1) Proactive Innovation Strategies
Innovative proactive strategies serve as the foundation for achieving a significant market position compared to the competition. This foundation is built on the ability to perceive signals from the external entrepreneurial environment and simultaneously evolve entrepreneurial innovative potential.
It encompasses both radical and incremental approaches, distinguishing companies that adopt them as technology market leaders with robust brand recognition and loyal customer bases. These companies prioritize extensive research, closely monitor emerging technologies, and draw insights from diverse sources. Proactive strategies are characterized by a commitment to predicting future trends, often involving high-risk initiatives.
Proactive innovation strategies in business can involve a mix of both radical and incremental approaches, and companies may also utilize other types of innovation strategies to stay competitive and meet evolving market demands. Here are several proactive innovation strategies:
1) Radical Innovation Strategy
Radical innovation is a proactive approach where businesses pursue groundbreaking and transformative changes to redefine their products, services, and overall market positioning. This strategy is driven by the recognition that to thrive in dynamic markets, companies must be willing to take bold risks and challenge industry conventions. Businesses adopt radical innovation to gain a competitive advantage, disrupt markets, future-proof their operations, reinvent their brand identity, and enhance customer engagement
Businesses strategically employ Radical Innovation Strategies within their proactive innovation strategy approach to stay at the forefront of their industries and foster long-term success. By embracing radical innovation, organizations position themselves as leaders, differentiating their products or services from competitors. This approach not only provides a competitive edge but also ensures future-proofing against industry disruptions. Radical innovation enables businesses to proactively respond to emerging trends, expand into new markets, and enhance their overall brand image.
The commitment to pushing boundaries and embracing bold ideas also makes these businesses attractive to top talent, fostering a culture of creativity and innovation. Radical innovation strategy serves as a resilience mechanism, allowing organizations to disrupt rather than be disrupted, and adapt to technological advancements. Ultimately, the integration of radical innovation into proactive strategies empowers businesses to achieve strategic growth, deliver enhanced customer value, and navigate the dynamic landscape of their industries with agility and foresight.
Case Study: Tesla’s Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Energy Products:
Tesla’s proactive innovation strategy is driven by radical innovation in its Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Energy Products. From pioneering breakthrough battery technology to leading in autonomous driving capabilities, Tesla consistently challenges industry norms. The creation of the Supercharger network addresses charging infrastructure hurdles, while energy storage solutions and solar integration showcase Tesla’s commitment to sustainability. Over-the-air software updates and a direct-to-consumer sales model further distinguish Tesla’s radical departure from traditional automotive practices. In summary, Tesla’s strategic emphasis on radical innovation not only transforms industries but also establishes new standards in technology, sustainability, and business practices.
The result of Tesla’s proactive innovation strategy is a transformative impact on industries and the establishment of new benchmarks in technology, sustainability, and business practices. Through breakthroughs in battery technology and leadership in autonomous driving, Tesla has redefined the automotive landscape. The Supercharger network addresses charging challenges, while energy storage solutions and solar integration underscore Tesla’s commitment to sustainability. Over-the-air software updates and a direct-to-consumer sales model showcase a departure from traditional practices. In essence, Tesla’s strategic emphasis on radical innovation not only sets the company apart but also shapes the future of technology and sustainable business in profound ways.
2) Incremental Innovation Strategy:
Incremental innovation, a strategy of making small, continuous improvements to existing products, processes, or services, plays a pivotal role in proactive innovation approaches. Its appeal lies in its ability to mitigate risk, as it is generally less uncertain than radical innovation. By building upon existing foundations, businesses can minimize the potential for disruptive failures associated with entirely new products.
It aligns with a mindset of continuous improvement, enabling companies to stay ahead of competitors and meet the ever-evolving needs of customers. The strategy is resource-efficient, requiring fewer resources than radical innovations, allowing for a more economical allocation of resources. This approach facilitates a steady stream of updates, contributing to customer retention by providing improved versions of familiar products and maintaining market stability through gradual changes.
Businesses opt for incremental innovation within proactive innovation strategies for various reasons:
- Firstly, it helps mitigate risk by minimizing uncertainty and avoiding large upfront investments.
- Secondly, the continuous improvement mindset enables companies to stay ahead of competitors and respond to market dynamics. Resource efficiency is another key factor, allowing for the allocation of resources in a more controlled manner.
- Additionally, incremental innovation contributes to customer retention by providing regular updates to existing products, reducing the likelihood of customer churn. Finally, it fosters market stability, as gradual changes are less likely to cause disruptions compared to radical innovations, ensuring a smoother transition for both the business and its customers.
Case Study: Apple’s iPhone Iterations:
A compelling illustration of incremental innovation within a proactive strategy is evident in Apple’s approach to the iPhone. Since the launch of the first iPhone in 2007, Apple has consistently embraced incremental improvements rather than radical changes.
- The design of the iPhone has evolved gradually with each iteration, incorporating improvements in materials, form factor, and display technology. Performance enhancements, such as upgrades in processing power, camera capabilities, and battery life, are introduced regularly, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Software updates bring new features, security enhancements, and improvements to the user interface, extending the lifespan and functionality of existing devices. Apple’s incremental innovations often focus on enhancing ecosystem integration with other Apple products and services, such as the Apple Watch, AirPods, and iCloud. This sustained approach has allowed Apple to maintain market leadership, retain a loyal customer base, and respond effectively to market trends within the competitive smartphone landscape.
3) Open Innovation Strategy:
Open Innovation is a strategy that involves collaborating with external partners, such as suppliers, customers, and competitors, to co-create and share innovative ideas. One key reason businesses opt for open innovation in proactive approaches is access to external expertise. By engaging with external partners, organizations can tap into a diverse knowledge base, bringing in fresh perspectives and specialized skills that may be lacking internally. Additionally, open innovation facilitates accelerated innovation, allowing businesses to swiftly access external solutions and ideas, thereby reducing the time required for organizational development.
Case Study: Procter & Gamble (P&G)
P&G adopted Open Innovation through its Connect + Develop program. By collaborating with external innovators, P&G successfully developed and launched numerous products, such as Swiffer and Febreze. This proactive innovation approach enabled P&G to expand its product portfolio and stay competitive in the fast-paced consumer goods industry. The company intentionally opened up its internal knowledge and resources, fostering a culture of knowledge exchange and external collaboration. This marked a strategic departure from the traditional closed innovation model, demonstrating P&G’s commitment to exploring diverse perspectives beyond its organizational boundaries.
The results of the Connect and Develop program were transformative. P&G experienced a notable surge in patent citations, underscoring the successful integration of externally sourced innovations into their product portfolio. Particularly noteworthy were the iconic products like Swiffer and Febreze, which emerged from collaborative efforts with external partners. These products not only achieved significant market success but also became synonymous with innovation in their respective categories.
4) Disruptive Innovation Strategy
Disruptive innovation involves the introduction of products or services that fundamentally alter the existing market landscape, often by addressing overlooked or underserved customer needs. Businesses adopt disruptive innovation strategies in their proactive strategies for several reasons.
- First, it allows them to attain market leadership by pioneering groundbreaking solutions and establishing a dominant position.
- Second, disruptive innovations can create entirely new markets or subvert existing ones, fostering growth and diversification.
- Third, in the face of a rapidly changing business environment, proactive adoption of disruptive innovation becomes a strategic necessity for survival and adaptation.
- Additionally, the unique value propositions offered by disruptive products can lead to differentiation from competitors, resulting in increased customer loyalty and higher profit margins.
- Lastly, embracing disruptive innovation positions businesses as industry leaders and innovators, enhancing their brand image and attracting top talent.
Case Study: Uber Company
Uber stands as a prime example of a company at the forefront of disruptive innovation, employing a proactive approach to reshape the transportation industry. Through its platform-based model, Uber has fundamentally disrupted traditional taxi services by connecting riders directly with drivers via a user-friendly mobile app. The introduction of ridesharing, where private individuals provide transportation using their own vehicles, challenged the established norms of taxi services. Uber’s dynamic pricing mechanism, responsive to real-time demand, revolutionized traditional fare structures.
Emphasizing user experience and convenience, Uber’s app, cashless transactions, and real-time tracking set new standards in the industry. What started as a disruptive force in individual cities quickly expanded globally, challenging established taxi services on an international scale. Uber’s success serves as a testament to the transformative power of disruptive innovation, illustrating how a proactive strategy can not only reshape industries but also redefine the way people approach and experience
5) Technology Innovation Strategy
Technology innovation strategy involves the deliberate use of technology to drive significant advancements in products, processes, or services. This proactive approach aims to leverage emerging technologies to gain a competitive edge and address evolving market needs. Businesses use it in proactive innovation strategies for embracing cutting-edge technologies that can differentiate a business from competitors, allowing it to offer superior products or services.
Amazon originally an e-commerce giant, strategically pursued a proactive innovation strategy, with a strong emphasis on technology innovation, to diversify its business and solidify its position as a global tech leader. As part of its technology innovation strategy, Amazon launched Amazon Web Services (AWS), recognizing the potential of cloud computing. This proactive move allowed for scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions, catering to various entities.
Amazon’s success with AWS showcases the potency of combining a proactive innovation strategy with a focus on technology innovation. By foreseeing market trends, investing in cutting-edge technology, and fostering collaboration, Amazon not only secured a competitive edge but also played a transformative role in the tech industry. This case study underscores the value of an integrated approach that merges foresight with strategic technological investments.
6) Business Innovation Strategy
In adopting a proactive innovation approach, businesses strategically harness innovation as a driving force for growth, securing a competitive edge, and successfully navigating dynamic market conditions. The core of a business innovation strategy lies in the deliberate and systematic application of diverse innovation methodologies aimed at creating new products, services, processes, or digital business models.
The Business Model Innovation, aligned with the innovation strategy, serves as a roadmap for turning imaginative ideas into tangible outcomes. By outlining the processes, structures, and frameworks essential for nurturing creativity and overseeing innovation initiatives, a well-designed business innovation model enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of innovation efforts. It also ensures alignment with overarching business goals, solidifying innovation as a fundamental and purposeful element in the organization’s growth strategy. You can download it now.
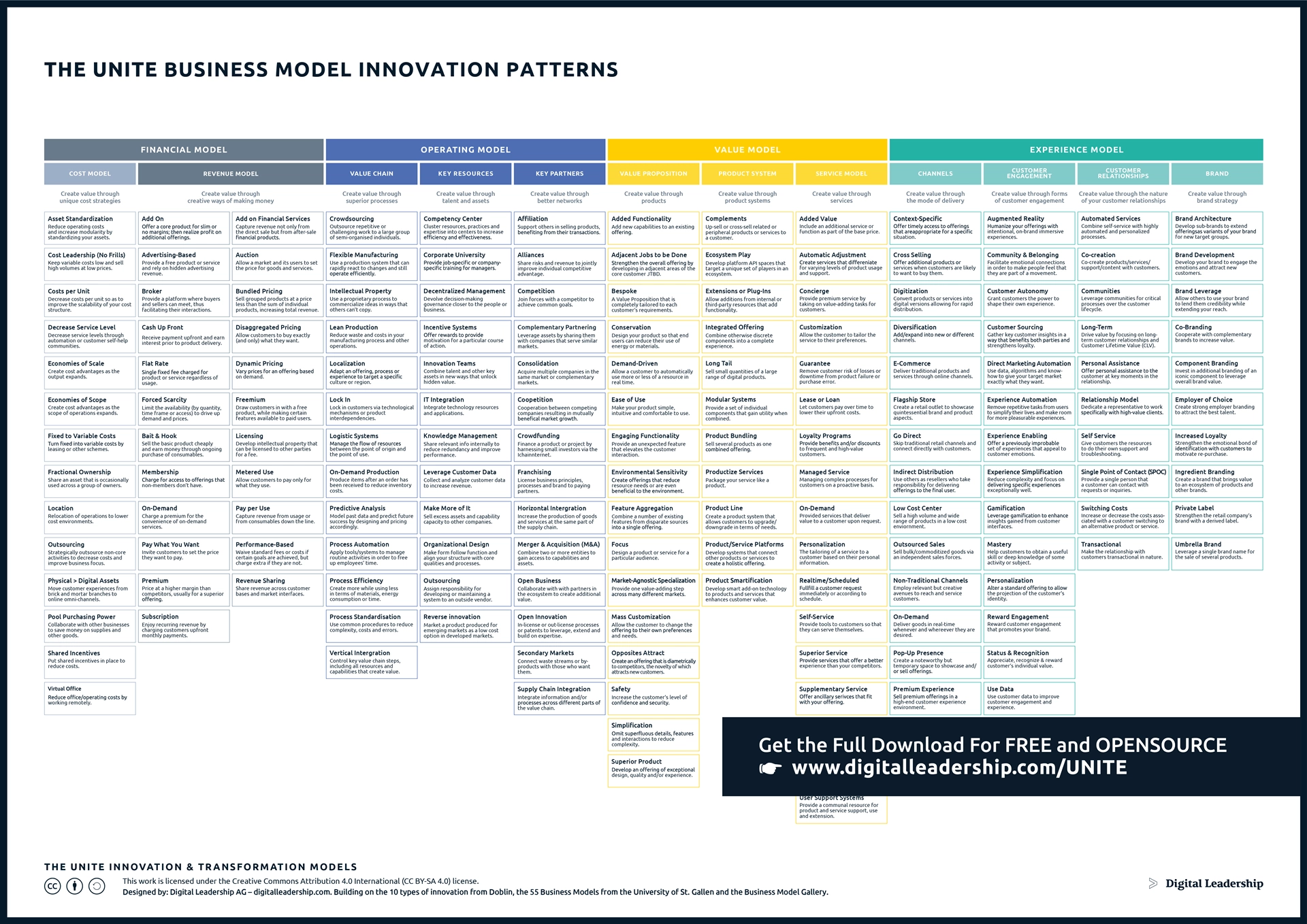
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the 10 types of innovation from Doblin, the SS Business Models from the University of St.Gallen, and the Business Model Gallery
Growth and innovation go hand in hand. The critical part is to set up a reliable innovation strategy. The UNITE Business Model Innovation Patterns summarize 95% of all business model innovations. In combination with the UNITE Innovation Approach, you have all the necessary tools at hand to systematically innovate your business model.
Case Study: Google Company
Google’s approach to business innovation extends beyond its search engine roots. Through ventures like Google X and initiatives such as “20% time” (where employees can spend a portion of their work hours on personal projects), Google fosters a culture of creativity and innovation. This proactive strategy has led to the development of products like Gmail and Google Maps, showcasing the impact of a comprehensive business innovation approach.
2) Active Innovation Strategy
Active innovation strategies involve defending existing technologies and markets while maintaining readiness to generate new ideas, products, or processes and respond promptly when markets and technologies are validated. Companies adopting this approach possess extensive sources of knowledge and operate with medium-to-low risk exposure, strategically hedging their bets.
Businesses adopt active innovation strategies to stay ahead of the competition, respond swiftly to market changes, and foster a culture of ongoing improvement. Active innovation helps organizations adapt to evolving customer needs, technological advancements, and industry trends, typically utilizing incremental innovation but may also include other types of innovation. Companies primarily rely on incremental innovation through in-house research and development.
Incremental Innovation Strategy:
Incremental innovation focuses on making small, consistent improvements to existing products, processes, or services over time. It is an evolutionary approach that builds on current capabilities to enhance and refine without radical change.
Businesses employ incremental innovation as part of an active innovation strategy, to continually refine and optimize their offerings. This strategy is less risky than radical innovation, allowing organizations to maintain market presence while steadily improving their products or processes.
Case Study of Tech Innovations Ltd.
Tech Innovations Ltd. stands out as a trailblazer by embracing an active innovation strategy approach using incremental innovation strategy. One noteworthy example is the continuous improvement in camera technology, where each new model introduces upgraded lenses, advanced image processing algorithms, and additional photography modes. Display technologies also undergo incremental enhancements, with increases in screen resolution, brightness, and colour accuracy across successive iterations. Tech Innovations prioritizes the optimization of battery life through incremental innovations in energy efficiency, incorporating advancements in battery technology and power management with each release.
3) Reactive Innovation Strategy
Reactive innovation strategies predominantly rely on incremental innovation and the emulation of proven innovations. This approach is characterized by a cautious, low-risk stance, adopting a wait-and-see attitude toward innovation. Companies adopting this strategy are often followers in their respective industries, not prioritizing innovation as a core element and aiming to manage costs effectively.
Businesses employing this strategy demonstrate the ability to adjust and thrive amid changing market conditions. By adapting to shifts in customer preferences, competitive moves, regulatory changes, and technological disruptions, businesses can maintain relevance and competitiveness. Reacting to customer feedback and addressing concerns in real time contributes to improved products and services, fostering higher levels of customer satisfaction.
1) Incremental Innovation Strategy
Businesses employing Incremental Innovation in a reactive innovation approach prioritize risk mitigation by making gradual enhancements to existing products, processes, or services. This deliberate approach allows for careful observation of market trends, aligning changes with observed patterns. It facilitates cost efficiency, as businesses can manage resources more effectively by focusing on smaller, targeted improvements.
In response to immediate competitive pressures, this strategy enables agile adjustments without the need for complete overhauls, ensuring that companies can adapt to emerging challenges while maintaining their market position. The integration of customer feedback is seamless, and resource optimization becomes a key advantage, allowing businesses to allocate resources efficiently within the constraints of a reactive strategy. Ultimately, Incremental Innovation in a reactive strategy for innovation offers businesses a practical and adaptive method to navigate change, respond to market culture and improve operations while effectively managing risk and resource constraints.
Case Study of Nokia
A prime example of a company employing incremental innovation within a reactive innovation approach is Nokia. In response to the emergence of smartphones and the shift in consumer preferences, Nokia, initially a leader in mobile phones, found itself facing challenges. In a reactive move, Nokia began to incrementally innovate its existing product lines by introducing smartphones that incorporated touchscreens, improved camera capabilities, and enhanced software features. This incremental approach aimed to adapt to the changing market dynamics and catch up with competitors who had embraced disruptive innovations.
The reactive innovation strategy employed by Nokia involved responding to the immediate challenges and trends in the industry. This reactive stance, marked by incremental improvements, allowed Nokia to navigate the evolving landscape to some extent. However, the company faced greater challenges in fully pivoting its strategy to meet the disruptive changes in the market. This experience with incremental innovation underscores the complexities of balancing reactive strategies with the imperative for more transformative changes in the face of industry shifts.
2) Outcome-Driven Innovation Strategy
Outcome-Driven Innovation (ODI) is an innovation process guided by data, introducing clarity, speed, and predictability to the initial, uncertain stages of the innovation journey. At its core is the Jobs-to-be-Done theory, which posits that customers “hire” products or services to fulfill particular jobs and accomplish desired outcomes in their lives.

Businesses leverage the Outcome-Driven Innovation (ODI) strategy as a discerning and adaptive approach to navigate unforeseen changes in the reactive innovation strategy approach. ODI’s innate customer-centricity proves instrumental in swiftly addressing evolving needs. ODI in the reactive innovation approach enables businesses to promptly identify and prioritize the outcomes that have gained significance due to environmental shifts. This strategy acts as a risk mitigation tool, aligning investments with evolving market needs, thereby enhancing the likelihood of success in reactive initiatives.
4) Passive Innovation Strategy
Companies adopting passive innovation strategies adopt a reactive approach, deferring modifications to their products or services until prompted by explicit customer demands. One notable example is seen in automotive supply companies, where the incorporation of changes to specifications is often contingent upon customer requests for particular adaptations.
In such cases, these companies may prioritize stability in their offerings, awaiting direct feedback or requests from clients before implementing alterations. While this approach allows for a level of consistency, it may also result in a slower response to emerging market trends or technological advancements. This contrasts with more proactive innovation strategies that involve anticipating customer needs and market shifts, allowing companies to stay ahead of demand and maintain a competitive edge.
Elements of a Successful Innovation Strategy
1) Innovation Culture
- Encourage a culture that celebrates diversity and inclusion, fostering a wide range of perspectives and ideas.
- Implement mechanisms for idea generation and employee collaboration, such as innovation workshops, hackathons, and suggestion programs.
- Provide training programs that enhance creative thinking and problem-solving skills among employees.
2) Digital Transformation:
- Embrace emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain to drive innovation.
- Invest in digital skills training for employees to ensure they can leverage new technologies effectively.
- Establish cross-functional teams that integrate digital expertise with domain-specific knowledge for comprehensive innovation.
3) Leadership Commitment:
- Demonstrate leadership’s commitment through consistent communication about the importance of innovation.
- Encourage leaders to actively participate in innovation initiatives, signalling its strategic value to the entire organization.
- Incorporate innovation goals and achievements into performance evaluations and recognition programs.
4) Resource Allocation:
- Implement a flexible budgeting process that allows for dynamic allocation of resources based on evolving project needs.
- Foster collaboration between departments to share resources and expertise, optimizing the overall innovation ecosystem.
- Establish clear criteria for prioritizing innovation projects to ensure alignment with strategic objectives.
5) Customer-Centric Approach:
- Utilize design thinking methodologies to deeply understand customer pain points and desires.
- Implement customer feedback loops that involve customers in the co-creation process, ensuring solutions meet their evolving needs.
- Leverage advanced analytics and market research to anticipate future customer trends and preferences.
6) Agile Methodologies:
- Promote cross-functional collaboration and iterative development cycles to enhance adaptability.
- Implement agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban to streamline project management and encourage continuous improvement.
- Foster a culture that values quick experimentation, rapid prototyping, and the ability to pivot based on feedback.
7) Metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Define clear and measurable KPIs aligned with strategic innovation goals.
- Regularly assess both quantitative and qualitative data to gauge the impact of innovation efforts.
- Adjust KPIs over time to reflect evolving business priorities and market dynamics.
8) Investment in Research and Development:
- Establish dedicated teams focused on exploring emerging technologies and market trends.
- Collaborate with external research institutions, startups, or industry partners to access a broader innovation ecosystem.
- Encourage a balance between short-term and long-term research initiatives to drive both immediate and sustained innovation.
9) Risk Tolerance and Learning from Failure:
- Foster a psychologically safe environment where employees feel empowered to take calculated risks.
- Celebrate instances of learning from failure, emphasizing the importance of resilience and adaptation.
- Incorporate post-mortem analyses into the innovation process, extracting valuable insights from unsuccessful endeavors to inform future strategies.
10) Business Environment
The business environment stands as a pivotal element intricately woven into the fabric of innovation strategy. This dynamic interplay recognizes that the success of innovation initiatives is not solely an internal affair but is profoundly influenced by external factors. Market dynamics, comprising trends, demands, and the competitive landscape, guide the development of innovations that resonate with consumers and outpace rivals. A keen awareness of the competitive landscape informs strategic decisions, allowing businesses to carve out unique value propositions and differentiate themselves.
Frameworks, technological trends, economic conditions, and cultural dynamics each imprint their signature on the innovation landscape, shaping the feasibility, acceptance, and impact of innovative endeavors. In a globalized context, businesses navigate international markets, considering global trends and competition. As sustainability becomes paramount, aligning innovation strategies with environmental goals reflects a conscientious approach. Thus, a holistic understanding of the business environment becomes an indispensable compass, steering innovation strategies toward relevance, competitiveness, and ethical practices in an ever-evolving marketplace.
The Business Environment Canvas holds paramount importance in the realm of innovation strategy as it acts as a comprehensive and dynamic guide for organizations navigating the intricacies of their operating landscapes. By offering a structured framework for analyzing internal and external factors, this canvas empowers businesses to align their innovation strategies strategically with organizational goals. It serves as a proactive risk management tool, enabling the identification and mitigation of potential challenges. You can download it now.
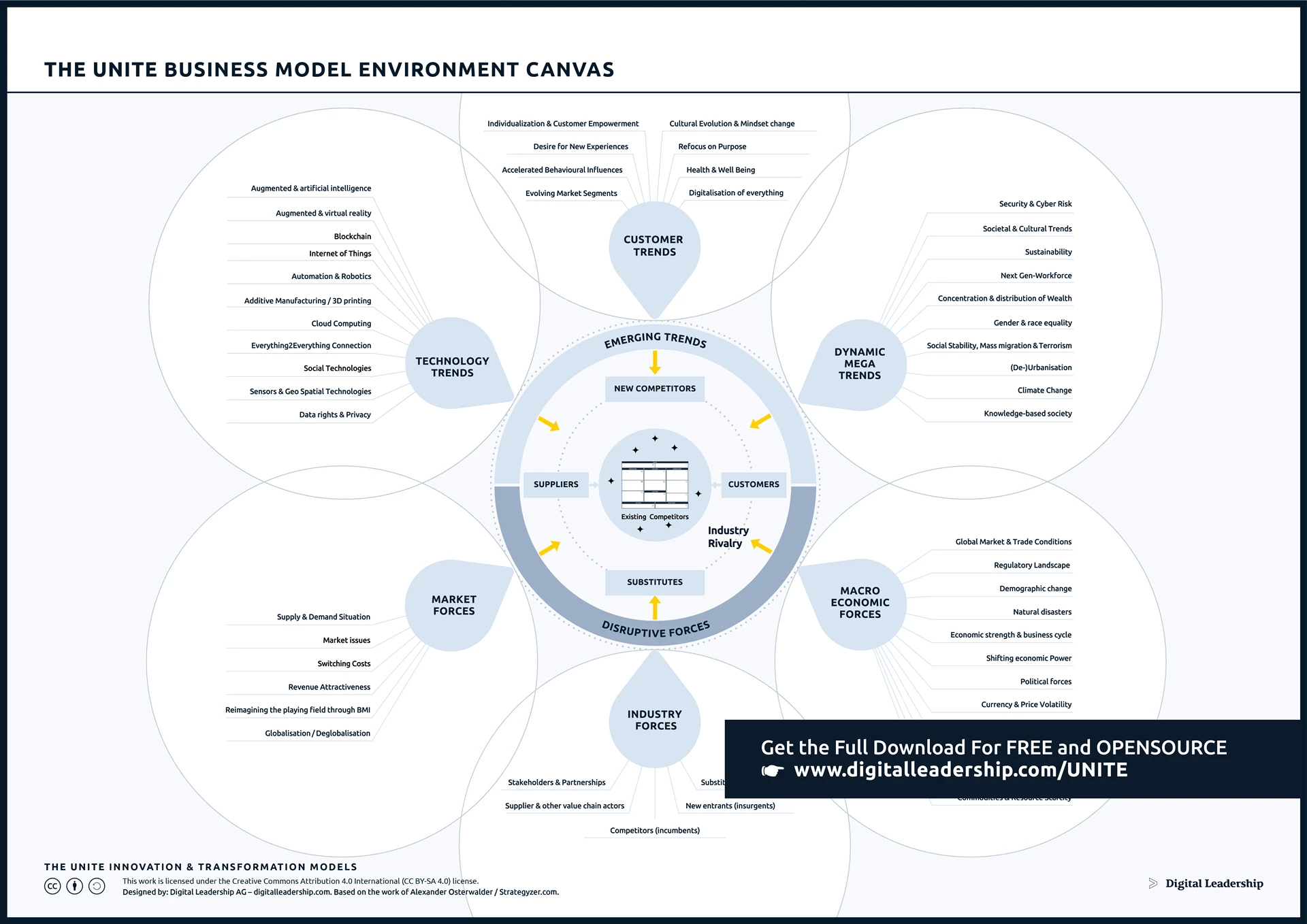
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Based on the work of Alexander Osterwalder
11) Organization Structure
The organizational structure stands as a foundational pillar in the intricate architecture of innovation strategy. It serves as more than a framework for work distribution; rather, it profoundly influences the very culture and dynamics that drive innovation within an organization. A structure that encourages open communication and collaboration, often associated with flat and decentralized models, creates an environment conducive to the free flow of innovative ideas.
The composition of cross-functional teams, facilitated by the organizational structure, brings together diverse expertise, fostering creativity and enhancing the effectiveness of innovation initiatives. Resource allocation, leadership styles, and decision-making processes, all intricately linked to organizational structure, play pivotal roles in shaping the innovation landscape. Flexible and adaptable structures enable organizations to respond nimbly to changing circumstances, a vital trait in the dynamic realm of innovation.
Some organizations even carve out dedicated innovation units within their structures, underscoring the strategic importance placed on generating and implementing novel ideas. Ultimately, the alignment of organizational culture, incentive structures, and the overall ethos of an organization with the principles of innovation is intricately woven into its structural fabric, delineating the path for successful innovation strategies and sustained competitive relevance.
9 Steps of Developing Innovation Strategy Framework
Innovation strategy framework serves as a guiding compass, this framework provides organizations with a systematic approach to navigating the complexities of innovation. By aligning innovative endeavors with an overarching business purpose, it ensures a directed and purposeful trajectory. Beyond direction, the framework optimizes resource allocation, mitigates risks associated with innovation, and fosters a culture that values creativity and embraces change. With a customer-centric focus, it positions organizations to understand and meet evolving customer needs, providing a competitive edge in the market.
Begin by establishing a clear understanding of your innovation approach. Whether it’s disruptive, incremental, or a combination, defining your approach sets the foundation for crafting targeted and effective innovation strategies. The Unite Innovation Approach, with its adaptive flexibility and efficient resource utilization, not only accelerates time-to-market but also enhances risk management and resilience in the face of unforeseen challenges. It serves as a catalyst for customer-centric outcomes by aligning the entire organization with a common understanding of customer needs positioning organizations to navigate the complexities of the dynamic business landscape with agility and collective intelligence.

Designed by: Digital Leadership AG
(1) Have a Clear Objective and Strategic Approach
Having a clear objective and strategic approach to innovation serves as the foundational pillar, ensuring that efforts are purposeful, aligned with business goals, and adaptable to the dynamic nature of markets and industries. This clarity becomes the bedrock upon which successful and impactful innovation initiatives can thrive.
- Importance:
- Direction Setting: A clear objective provides a roadmap for your innovation initiatives. It serves as a guiding light, ensuring that efforts are focused and purposeful.
- Alignment: The objective aligns teams and resources toward a common goal, fostering unity and cohesion in innovation endeavors.
- Resource Optimization: Clarity helps in the efficient allocation of resources as teams understand the specific outcomes they are working towards.
- Components:
- Specificity: Clearly define what you aim to achieve through innovation—whether it’s launching a groundbreaking product, optimizing processes, or entering new markets.
- Measurability: Establish measurable key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge the success of your innovation efforts, providing a quantifiable benchmark for progress.
- Timeline: Set realistic timelines for achieving your innovation objectives, ensuring that there’s a sense of urgency and accountability.
- Strategic Approach:
- Alignment with Business Strategy: Ensure that your innovation objectives align with broader business goals. This alignment strengthens the overall strategic impact of innovation on organizational success.
- Risk Consideration: Incorporate risk assessment into your strategic approach, acknowledging potential challenges and uncertainties that may arise during the innovation journey.
- Flexibility: While having a clear strategy is crucial, allows for flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions, emerging trends, or unexpected opportunities.
- Execution Guidance:
- Communication: Effectively communicate the innovation objective and strategy to all stakeholders, fostering a shared understanding and commitment.
- Leadership Involvement: Leadership should actively support and be involved in championing the innovation objective, emphasizing its strategic importance to the entire organization.
- Continuous Evaluation: Regularly evaluate the progress of innovation initiatives against the established objective, making adjustments as needed to stay on course.
(2) Know Your Market Target Audience and Top Competitors
Understanding your market, knowing your target audience, and staying ahead of competitors are integral components of a successful innovation strategy. By being deeply rooted in the context of your industry, you can develop innovations that not only meet but exceed the expectations of your customers while maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
- Contextual Innovation:
- Market Dynamics: Recognize that innovation doesn’t happen in isolation; it is deeply influenced by market dynamics. Understand the trends, demands, and challenges within your industry.
- Customer-Centricity: Tailor your innovations to address specific market needs. A deep understanding of your market ensures that your innovations are relevant and resonate with your audience.
- Strategies for Understanding Your Market:
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to gather insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and emerging trends. This involves both quantitative data analysis and qualitative methods such as interviews and focus groups.
- Data Analytics: Leverage data analytics tools to extract meaningful patterns and trends from large datasets. This enables you to make informed decisions based on real-time and historical data.
- Identifying Your Target Audience:
- Persona Development: Create detailed customer personas that represent your ideal target audience. This involves considering demographics, psychographics, and behavioral traits to humanize your audience and guide your innovation efforts.
- Customer Segmentation: Divide your target audience into segments based on shared characteristics. This segmentation allows for more personalized and targeted innovation strategies.
- Staying Ahead of the Competition:
- Competitor Analysis: Regularly analyze your top competitors to understand their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis). Identify gaps in the market that your innovations can fill.
- Benchmarking: Benchmark your innovation efforts against industry leaders and best practices. This helps set ambitious yet realistic goals and benchmarks for success.
- Adaptability and Proactiveness:
- Agile Innovation: Embrace agile methodologies that allow for rapid adaptation to changing market conditions. This ensures that your innovations remain responsive to evolving customer needs and competitive landscapes.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement systems for continuous monitoring of market trends and competitor activities. Being proactive in staying informed helps you anticipate shifts and position your innovations strategically.
- Customer Feedback and Iteration:
- Feedback Loops: Establish robust feedback loops with your customers to understand their experiences with your products or services. This ongoing dialogue provides invaluable insights for refining and iterating your innovations.
- Iterative Development: Innovate iteratively based on customer feedback and market changes. This approach allows you to make incremental improvements and stay ahead of evolving market expectations.
(3) Align All Innovation Strategies with Your Business Strategy
A crucial aspect of this strategy is the development and implementation of a robust business innovation model. Business Model Canvas model serves as the blueprint for translating innovative ideas into tangible outcomes. By outlining the processes, structures, and frameworks for fostering creativity and managing innovation initiatives, a well-defined business innovation model becomes a guiding framework. It not only enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of innovation efforts but also aligns them with overarching business goals, ensuring that innovation becomes an integral and purposeful component of the organization’s growth strategy.
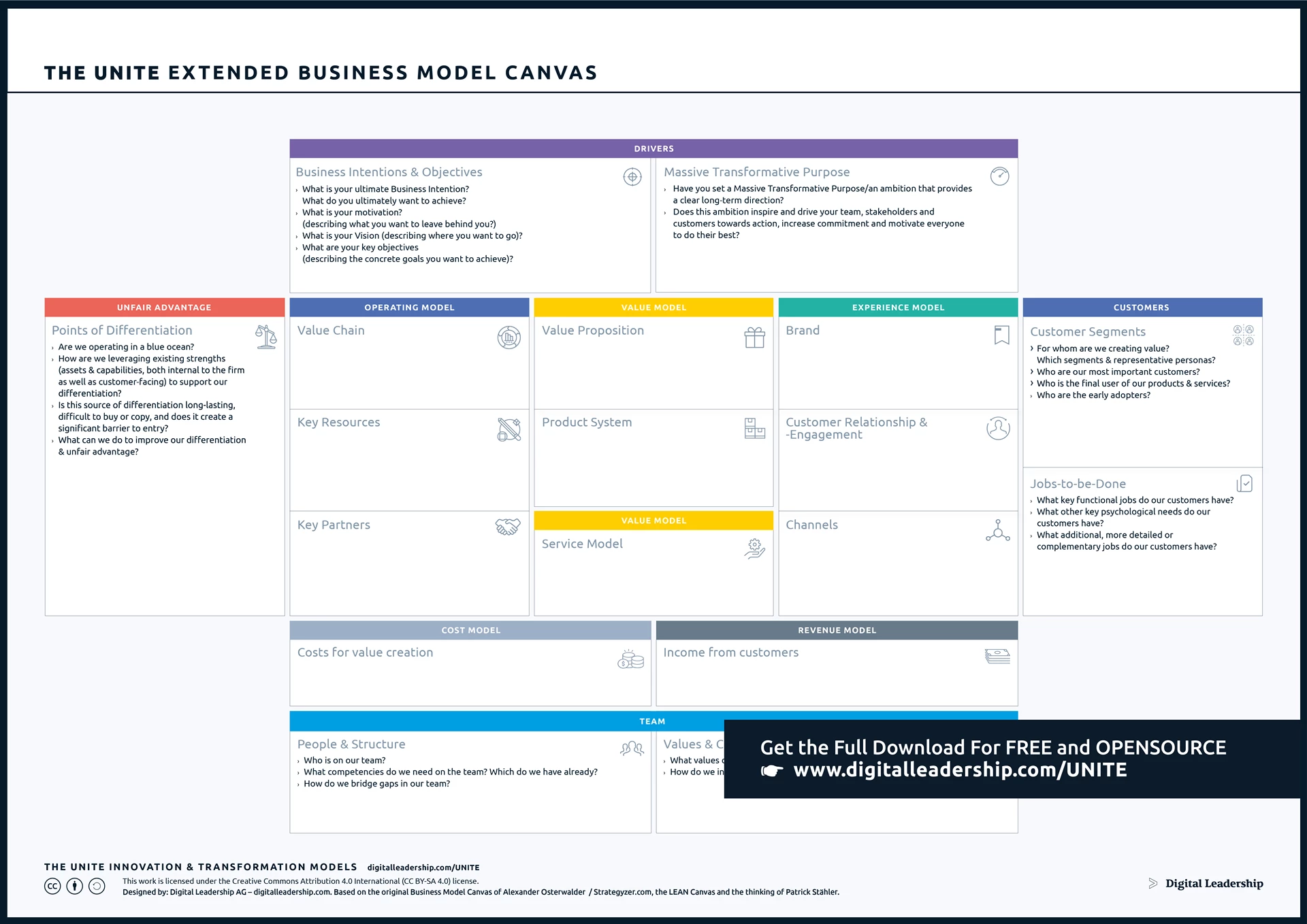
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the work of Alexander Osterwalder, the Lean Canvas and the thinking of Patrick Stahler
Ensuring harmony between innovation and business strategy is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. Regular evaluations, dynamic adaptations, and effective communication contribute to a symbiotic relationship where innovation becomes a strategic enabler for organizational success. This alignment reinforces the idea that innovation is not just a standalone activity but an integral part of the overall business strategy.
- Importance:
- Strategic Cohesion: Ensuring alignment between innovation and business strategy is critical for maintaining strategic cohesion. It prevents innovation efforts from becoming isolated or disjointed from the overall organizational vision.
- Resource Optimization: Alignment facilitates efficient resource allocation, directing innovation initiatives toward areas that directly contribute to the achievement of broader business goals.
- Market Relevance: Innovation that aligns with business strategy is more likely to address market needs and stay relevant in the competitive landscape.
- Strategic Alignment:
- Goal Consistency: The first step is to ensure that the goals of innovation strategies are consistent with the overarching business goals. This consistency reinforces the collective pursuit of organizational objectives.
- Time Horizon: Align the time horizons of innovation initiatives with the business strategy. Short-term and long-term innovation goals should complement the corresponding business strategy timelines.
- Risk Tolerance: Consider the risk tolerance outlined in the business strategy and ensure that innovation strategies are in harmony with the organization’s risk appetite.
- Integration of Innovation into Business Processes:
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between innovation teams and other functional areas. This collaboration ensures that innovation is integrated seamlessly into various aspects of the business.
- Budget Allocation: Align budgetary allocations for innovation with the financial allocations outlined in the broader business strategy. This alignment strengthens financial discipline and strategic coherence.
- Dynamic Adaptation:
- Continuous Assessment: Regularly assess the alignment of innovation strategies with business goals, considering evolving market conditions and shifts in organizational priorities.
- Adaptability: Foster a culture of adaptability, allowing for adjustments to innovation strategies when there are changes in the business environment or shifts in strategic priorities.
- Communication and Leadership:
- Communication Channels: Establish clear communication channels to convey the alignment between innovation and business strategy to all stakeholders. This communication ensures a shared understanding across the organization.
- Leadership Buy-In: Leadership plays a pivotal role in championing the alignment. Leaders should communicate the strategic importance of innovation and actively support initiatives that contribute to the broader business strategy.
(4) Research Customer Needs
Effectively researching customer needs is a dynamic and ongoing process that requires a combination of methodologies, technological tools, and a genuine commitment to understanding the customer’s perspective. It forms the bedrock upon which customer-driven innovation flourishes, leading to products and services that genuinely resonate with the intended audience.
- Customer-Centric Foundation:
- Innovation Catalyst: Recognize that customer needs are the catalyst for meaningful innovation. Understanding and addressing these needs become the cornerstone of successful product or service development.
- Market Relevance: Aligning innovation with customer needs ensures that products and services remain relevant and valuable in the eyes of the target audience.
- Methods for Effective Research:
- Surveys and Feedback Mechanisms: Implement surveys and feedback systems to gather quantitative and qualitative data directly from customers. This method provides structured insights into their preferences, pain points, and expectations.
- User Interviews: Conduct in-depth interviews with a diverse range of customers to gain nuanced, qualitative insights. This approach helps uncover unarticulated needs and emotional drivers behind customer behaviour.
- Observational Research: Observe customers in real-life situations to understand their behaviours, preferences, and challenges. This method provides contextual insights that may not be captured through direct inquiries.
- Focus Groups: Organize focus groups to facilitate group discussions and explore collective opinions and perceptions. This method is valuable for uncovering shared experiences and preferences.
- Technological Tools:
- Analytics and Big Data: Leverage analytics tools and big data analysis to derive insights from customer interactions with digital platforms. This data-driven approach can unveil patterns, trends, and areas for improvement.
- Social Media Listening: Monitor social media platforms to gauge customer sentiment, identify emerging trends, and address concerns in real-time. Social listening tools provide a continuous pulse on customer perceptions.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Create detailed customer journey maps to visualize the end-to-end experience of customers. This method helps identify touchpoints, pain points, and areas where innovation can enhance the overall journey.
- Iterative Feedback Loops:
- Continuous Feedback Channels: Establish mechanisms for ongoing customer feedback. Regularly seek input at various stages of product or service development to ensure that innovations align with evolving customer expectations.
- Prototyping and Testing: Develop prototypes or minimum viable products (MVPs) and conduct user testing. This iterative process allows for real-time adjustments based on direct customer interaction, minimizing the risk of misalignment.
- Empathy and Understanding:
- Empathetic Engagement: Foster a culture of empathy within the organization, encouraging teams to deeply understand and connect with the experiences and needs of customers.
- Persona Development: Create detailed customer personas that encapsulate various demographics, behaviors, and preferences. Personas serve as archetypes to guide innovation efforts with a human-centric focus.
- Strategic Integration:
- Alignment with Business Strategy: Ensure that insights from customer research align with broader business goals. This strategic integration guarantees that innovations not only meet customer needs but also contribute to organizational success.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Facilitate collaboration between customer-facing teams and innovation teams. This collaboration ensures a seamless flow of insights from the front lines to the innovation process.
(5) Conduct Your Business SWOT Analysis
Conducting a SWOT analysis serves as a pivotal step in shaping a robust innovation strategy. It provides a strategic roadmap that aligns internal and external factors, guiding the organization toward innovation initiatives that capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and navigate threats effectively.
The SWOT model, encapsulating Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, plays a critical role in guiding organizations toward innovation initiatives that are not only aligned with their inherent capabilities but also responsive to the dynamic business environment.
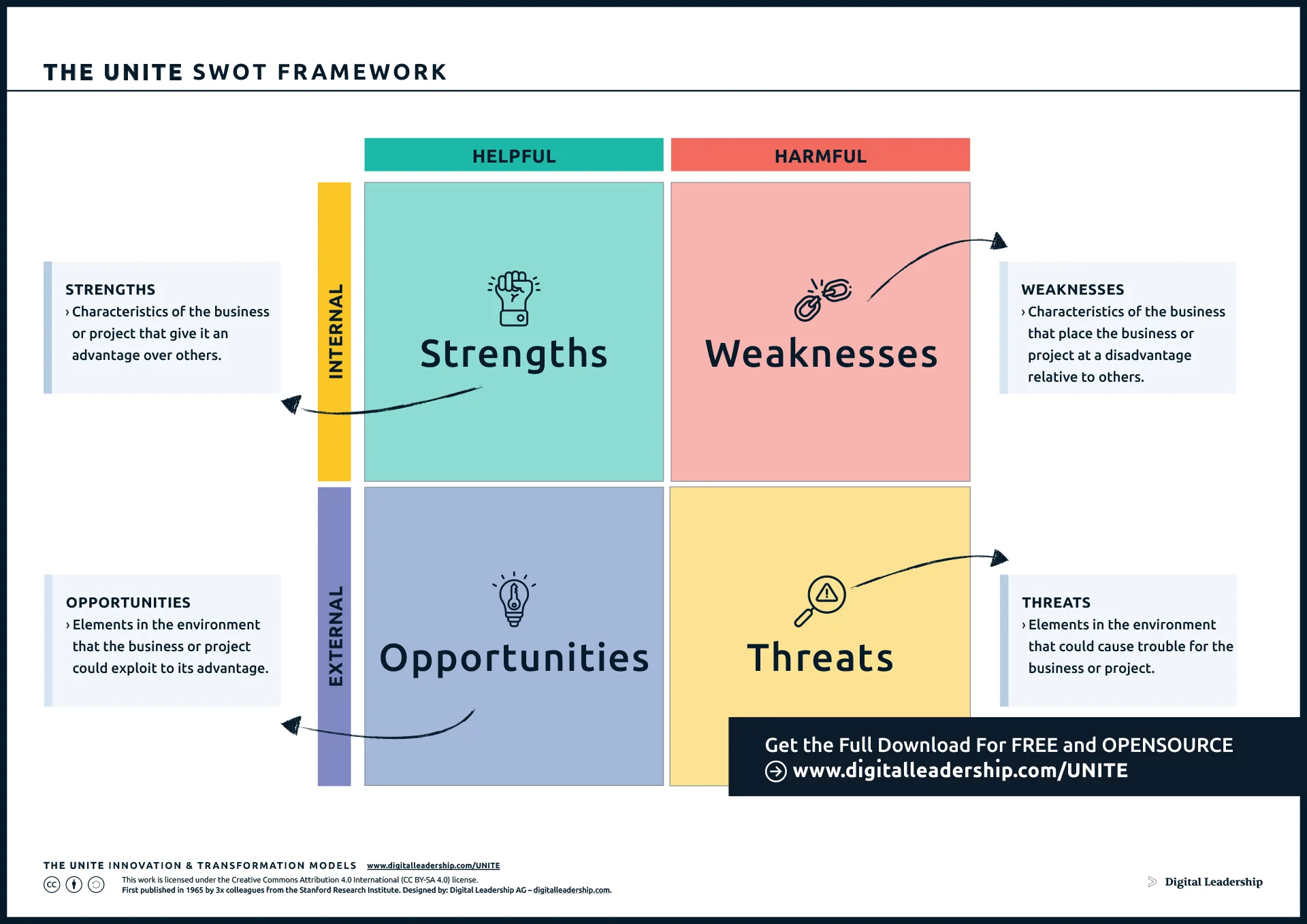
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG
- Strategic Insight:
- Holistic Assessment: A SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive and structured framework for assessing internal Strengths and Weaknesses, as well as external Opportunities and Threats. This holistic view is crucial for strategic decision-making.
- Informed Decision-Making: The insights gained from a SWOT analysis inform not only innovation strategy but also broader business strategies, ensuring that both are aligned for maximum impact.
- Components of SWOT Analysis:
- Strengths:
- Identify internal capabilities that give your business a competitive advantage.
- These could include strong brand recognition, a talented workforce, or advanced technological infrastructure.
- Weaknesses:
- Recognize internal limitations that may hinder innovation efforts.
- These might involve outdated processes, resource constraints, or gaps in skill sets.
- Opportunities:
- Identify external factors that could be leveraged for innovation.
- These may include emerging market trends, technological advancements, or shifts in consumer behaviour.
- Threats:
- Recognize external challenges that could impact innovation negatively.
- These might encompass competitive pressures, regulatory changes, or economic uncertainties.
- Strengths:
- Innovation Strategy Formulation:
- Strengths Utilization: Leverage internal strengths to identify areas where innovation can enhance or capitalize on existing capabilities. This may involve optimizing processes, expanding product lines, or entering new markets.
- Weaknesses Mitigation: Develop innovation strategies that address internal weaknesses. This could involve investing in skill development, modernizing infrastructure, or forming strategic partnerships to compensate for internal limitations.
- Opportunities Exploitation: Align innovation initiatives with identified opportunities. Innovation strategies can capitalize on emerging trends, technological breakthroughs, or unmet customer needs that align with external opportunities.
- Threats Mitigation: Develop innovation strategies that proactively address external threats. This might involve diversifying offerings, enhancing flexibility in operations, or developing contingency plans to navigate potential challenges.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Input from Various Departments: Involve representatives from various departments in the SWOT analysis process. This ensures a diverse perspective and facilitates cross-functional collaboration in formulating innovation strategies.
- Innovation Ecosystem Enhancement: Use the SWOT analysis to identify areas where collaboration and information sharing between departments can strengthen the overall innovation ecosystem.
- Continuous Evaluation:
- Dynamic SWOT Analysis: Recognize that the business environment is dynamic. Regularly revisit and update the SWOT analysis to reflect changes in the internal and external landscape.
- Iterative Innovation Strategies: The iterative nature of innovation strategies allows for adjustments based on the evolving insights from a regularly updated SWOT analysis.
- Communication and Strategy Integration:
- Communication of Findings: Effectively communicate the findings of the SWOT analysis to all relevant stakeholders. This fosters a shared understanding of the business landscape and ensures that innovation strategies are collectively informed.
- Integration with Business Strategy: Align the outcomes of the SWOT analysis with broader business strategies. This integration guarantees that innovation is not only responsive to immediate concerns but is also aligned with the long-term vision of the organization.
(6) Define Your Value Proposition
In the intricate process of developing your innovation strategy, a pivotal step is defining your value proposition. A well-defined value proposition is not static; it evolves in response to market dynamics and customer feedback. By continuously refining and adapting your value proposition, you ensure that your innovations remain not only relevant but also compelling in the eyes of your target audience. This step holds strategic significance as it not only sets your offerings apart from competitors but also serves as a magnet for customer attraction and retention. It communicates the unique benefits of your innovations and creates a distinctive position for your brand in the market.
The Value Proposition Canvas, which is a key tool in this step of developing an innovation strategy, becomes invaluable. This canvas provides a structured framework for understanding customer needs, pains, and gains, aligning them with your product or service features. It facilitates a deep understanding of customer segments and aids in crafting a value proposition that directly addresses their requirements. The iterative nature of the canvas allows businesses to stay agile, refining their value proposition based on real-time insights. In essence, the Value Proposition Canvas is a dynamic tool that ensures your innovation strategy is grounded in a customer-centric approach, enhancing the resonance and effectiveness of your offerings in the market.
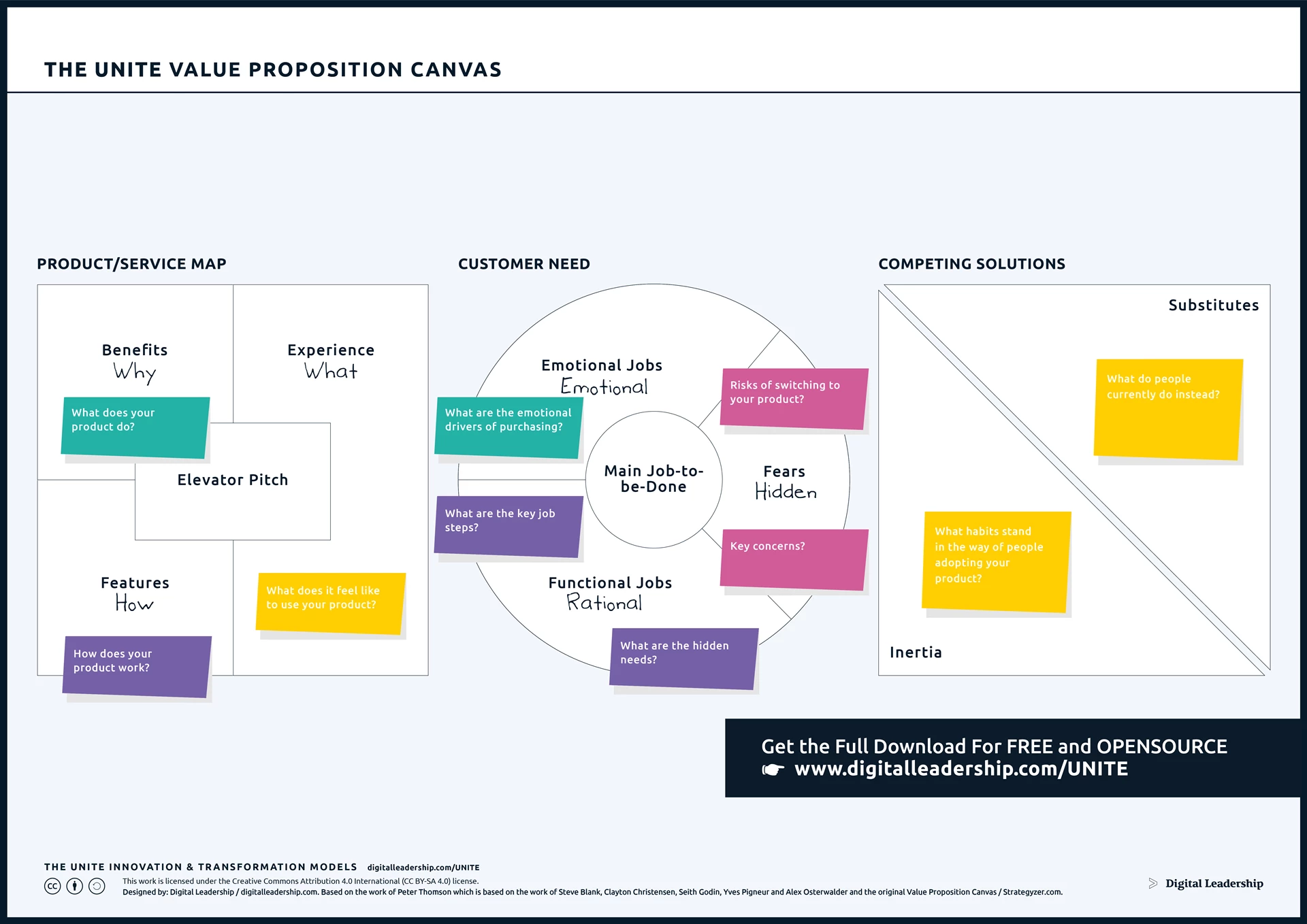
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Based on the work of Peter Thomson which is based on the work of Steve Blank, Clayton Christensen, Seith Godin, Yves Pigneur and Alex Osterwalder and the original Value Proposition Canvas
The following sub-steps elucidate the components and development process of a compelling value proposition, providing a roadmap for businesses to articulate their differentiation, address customer needs, and effectively communicate the quantifiable and emotional value of their innovations.
- Strategic Significance:
- Competitive Edge: Your value proposition is a critical element that sets your innovations apart from competitors. It serves as the unique selling point that positions your offerings in the market.
- Customer Attraction: A compelling value proposition is instrumental in attracting and retaining customers by clearly communicating the benefits of your innovations.
- Components of a Compelling Value Proposition:
- Clear Differentiation:
- Clearly articulate how your innovations differ from existing solutions in the market.
- Highlight unique features, functionalities, or qualities that make your offerings stand out.
- Customer Relevance:
- Demonstrate a deep understanding of customer needs and pain points.
- Showcase how your innovations directly address and fulfill these customer requirements.
- Quantifiable Value:
- Provide measurable outcomes or benefits that customers can expect from choosing your innovations.
- This could include cost savings, efficiency improvements, enhanced user experience, or other tangible advantages.
- Emotional Appeal:
- Appeal to the emotions of your target audience by highlighting the positive feelings or experiences associated with your innovations.
- Create a connection that goes beyond functionality and resonates with the emotional aspects of customer satisfaction.
- Clear Differentiation:
- Value Proposition Development Process:
- Market Research:
- Conduct in-depth market research to understand customer preferences, pain points, and the competitive landscape.
- Identify gaps in existing offerings and opportunities for differentiation.
- Customer Feedback:
- Incorporate direct customer feedback into the value proposition development process.
- Consider customer testimonials, reviews, and preferences to tailor your value proposition to resonate with your audience.
- Competitor Analysis:
- Analyze the value propositions of competitors to ensure yours is distinct.
- Identify areas where you can outperform competitors or offer unique advantages.
- Market Research:
- Communication Strategies:
- Clear and Concise Messaging:
- Craft a value proposition that is clear, concise, and easily understood by your target audience.
- Avoid jargon or complex language that may obscure the core message.
- Multi-Channel Consistency:
- Ensure consistency in how your value proposition is communicated across various channels.
- From your website to marketing materials, consistency builds a strong and recognizable brand identity.
- Visual Representation:
- Use visual elements to reinforce your value proposition.
- Infographics, videos, or visual storytelling can enhance the impact of your message.
- Clear and Concise Messaging:
- Iterative Refinement:
- Feedback Incorporation:
- Actively seek feedback from customers, sales teams, and other stakeholders.
- Use this feedback to refine and improve your value proposition iteratively.
- Adaptation to Market Changes:
- Recognize that market dynamics can evolve.
- Regularly assess and update your value proposition to stay aligned with changing customer needs and industry trends.
- Feedback Incorporation:
- Integration with Brand Identity:
- Alignment with Brand Values:
- Ensure that your value proposition aligns with the overall values and identity of your brand.
- Consistent alignment strengthens brand integrity and customer trust.
- Alignment with Brand Values:
(7) Establish Your Innovation Systems and Techniques
Establishing robust innovation systems and techniques is an ongoing process that requires a combination of structured frameworks, creative techniques, and a supportive organizational culture. By fostering an environment where inventive ideas are consistently generated, evaluated, and implemented, businesses can stay at the forefront of innovation in a dynamic and competitive landscape.
- Systematic Foundation:
- Holistic Framework: Establishing innovation systems provides a structured and holistic framework for generating, evaluating, and implementing inventive ideas.
- Consistency: Systems ensure consistency in how innovation is approached, preventing ad-hoc efforts and promoting a continuous and reliable flow of creative solutions.
- Components of Innovation Systems:
- Idea Generation Platforms:
- Implement dedicated platforms and channels for idea generation, such as innovation workshops, online suggestion portals, or collaboration tools.
- Foster a culture where employees feel empowered to contribute ideas freely.
- Stage-Gate Process:
- Develop a stage-gate process that guides ideas from conception through evaluation to implementation.
- Each stage should have defined criteria for progression, ensuring a systematic and thorough vetting of ideas.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Encourage collaboration between departments and teams to bring diverse perspectives to the innovation process.
- Cross-functional teams can enrich the ideation and implementation phases with varied expertise.
- Innovation Metrics:
- Define key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure the success and impact of innovation efforts.
- Metrics could include the number of implemented ideas, time-to-market, or the return on investment from innovative projects.
- Idea Generation Platforms:
- Techniques for Idea Generation:
- Brainstorming Sessions:
- Conduct regular brainstorming sessions to generate a diverse range of ideas.
- Create a conducive environment that encourages free innovative thinking and creative expression.
- Hackathons and Innovation Challenges:
- Organize hackathons or innovation challenges to stimulate focused idea generation.
- Time-limited events can spur intensive creativity and problem-solving.
- Open Innovation:
- Embrace open innovation by collaborating with external partners, startups, or industry experts.
- External perspectives can introduce fresh ideas and accelerate the innovation process.
- Brainstorming Sessions:
- Iterative Prototyping and Testing:
- Rapid Prototyping:
- Implement rapid prototyping techniques to quickly visualize and test ideas.
- Prototypes allow for early feedback, reducing the risk of investing in non-viable concepts.
- User Testing:
- Conduct user testing throughout the development process to gather real-time feedback.
- User insights help refine and enhance innovations based on actual user experiences.
- Rapid Prototyping:
- Continuous Improvement Culture:
- Learning from Failure:
- Foster a culture that views failure as an opportunity to learn and improve.
- Analyze unsuccessful innovations to extract valuable insights for future endeavors.
- Agile Methodologies:
- Embrace agile methodologies, allowing for iterative and adaptive development.
- Agile frameworks like Scrum facilitate continuous improvement and responsiveness to evolving requirements.
- Learning from Failure:
- Communication and Knowledge Sharing:
- Transparent Communication:
- Establish transparent communication channels to keep all stakeholders informed about ongoing innovation initiatives.
- Transparency fosters engagement and alignment with organizational goals.
- Knowledge Repository:
- Create a knowledge repository or database to capture and share insights from past innovation projects.
- Accessible knowledge facilitates continuous learning and avoids redundancy in ideation.
- Transparent Communication:
- Leadership Involvement:
- Executive Support:
- Secure active support and involvement from leadership in championing innovation initiatives.
- Leadership commitment reinforces the strategic importance of innovation throughout the organization.
- Executive Support:
- Adaptability and Scalability:
- Flexibility:
- Design systems that allow for flexibility and adaptability to accommodate changes in market dynamics or organizational priorities.
- The ability to pivot and adjust is crucial for sustained innovation.
- Scalability:
- Consider scalability in your innovation systems to handle a growing volume of ideas and projects.
- Scalable systems ensure that innovation efforts can expand alongside the organization’s growth.
- Flexibility:
(8) Integrate and Communicate Your Strategy to Your Team
Integrating and communicating the innovation strategy to the team is a dynamic and ongoing process. It requires a combination of clear communication, leadership involvement, training initiatives, and a culture that values and celebrates innovation. When the entire team is aligned and actively engaged, the organization can leverage the collective intelligence and creativity of its members to drive impactful and sustainable innovation.
- Collective Effort Significance:
- Team Alignment: Innovation thrives when every team member is aligned with the overall strategy. Integration ensures that everyone understands their role in the innovation process.
- Shared Vision: Communicating the innovation strategy fosters a shared vision, creating a sense of purpose and unity among team members.
- Integration into Organizational Culture:
- Cultural Alignment: Integrate the innovation strategy seamlessly into the existing organizational culture. This alignment ensures that innovation becomes a natural and integral part of how the organization operates.
- Values Reinforcement: Ensure that the values driving the innovation strategy align with the core values of the organization. This reinforcement strengthens the cultural resonance of innovation efforts.
- Importance of Communication:
- Clarity of Message:
- Communicate the innovation strategy with utmost clarity. Clearly articulate the goals, processes, and expected outcomes to avoid ambiguity.
- Use language that is accessible to all team members, regardless of their role or department.
- Regular Updates:
- Provide regular updates on the progress of innovation initiatives. This transparency keeps the team informed and engaged in the journey.
- Updates can be shared through newsletters, team meetings, or dedicated communication channels.
- Two-Way Communication:
- Encourage a two-way communication flow. Create platforms for team members to share their thoughts, ideas, and feedback regarding the innovation strategy.
- Actively listen to team input, demonstrating that their perspectives are valued.
- Visual Communication:
- Utilize visual aids, such as infographics, charts, or presentations, to convey complex concepts related to the innovation strategy.
- Visual communication enhances understanding and retention of key information.
- Storytelling:
- Craft narratives that highlight the impact of innovation on the organization’s journey. Storytelling creates a compelling narrative that resonates with team members on an emotional level.
- Clarity of Message:
- Leadership Involvement:
- Lead by Example:
- Leadership involvement is pivotal. Leaders should exemplify the values and behaviors expected in the pursuit of innovation.
- Actively participate in innovation initiatives, demonstrating commitment and enthusiasm.
- Visibility and Accessibility:
- Leaders should be visible and accessible during the communication of the innovation strategy. This accessibility fosters a sense of connection and trust among team members.
- Lead by Example:
- Training and Development:
- Training Programs:
- Implement training programs that equip team members with the skills and knowledge necessary for effective participation in innovation activities.
- Training ensures that the entire team is well-prepared to contribute meaningfully to the innovation process.
- Skill Development Initiatives:
- Identify specific skill areas relevant to the innovation strategy and initiate skill development programs.
- This ensures that the team possesses the capabilities needed to execute innovation initiatives successfully.
- Training Programs:
- Recognition and Rewards:
- Acknowledgement of Contributions:
- Recognize and celebrate the contributions of team members to innovation efforts. Acknowledgement reinforces the importance of individual and collective contributions.
- Implement reward systems that recognize innovative ideas, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Acknowledgement of Contributions:
- Embedding Innovation in Performance Evaluation:
- Alignment with Performance Metrics:
- Align performance evaluation metrics with innovation goals. This alignment ensures that innovation is a recognized and valued component of individual and team achievements.
- Inclusion in performance evaluations reinforces the strategic importance of innovation.
- Alignment with Performance Metrics:
- Long-Term Vision Communication:
- Link to Organizational Vision:
- Clearly articulate how the innovation strategy aligns with the long-term vision and goals of the organization.
- This connection reinforces that innovation is not a standalone effort but a means to achieve broader organizational objectives.
- Link to Organizational Vision:
(9) Measure Your Growth Systematically
Systematic measurement and continuous optimization form a dynamic and interconnected cycle that propels innovation efforts toward sustained growth and impact. By adopting a data-driven approach and leveraging insights gained from measurement, organizations can adapt, innovate, and stay resilient in an ever-evolving business landscape.
- Strategic Importance of Measurement:
- Performance Evaluation: Measurement serves as a critical tool for evaluating the performance and impact of your innovation strategy.
- Continuous Improvement: Systematic measurement provides valuable insights that enable continuous optimization and refinement of innovation initiatives.
- Systematic Measurement Approaches:
- Innovation Metrics:
- Define key innovation metrics aligned with your strategic objectives. These could include the number of new products/services, time-to-market, or the success rate of innovations.
- Regularly track and analyze these metrics to gauge the effectiveness of your innovation strategy.
- Customer Feedback:
- Gather and analyze customer feedback related to innovative products or services. This feedback provides a direct indication of how well innovations are meeting customer needs and expectations.
- Use surveys, reviews, and direct interactions to capture qualitative and quantitative insights.
- Financial Impact:
- Evaluate the financial impact of innovation initiatives. Assess metrics such as revenue growth attributed to new products, return on investment (ROI), and cost savings.
- Financial metrics provide a tangible measure of the bottom-line impact of innovation efforts.
- Employee Engagement:
- Measure the engagement levels of employees in the innovation process. High levels of engagement indicate a culture that encourages and values innovation.
- Employee surveys, participation rates, and idea submission metrics can be useful indicators.
- Time-to-Market:
- Assess the time-to-market for new innovations. Efficient time-to-market is often a crucial factor in staying competitive.
- Monitor and optimize the various stages of the innovation process to reduce time delays.
- Success Rate of Prototypes:
- Track the success rate of prototypes and minimum viable products (MVPs) developed during the innovation process.
- A high success rate indicates effective testing and validation processes.
- Market Share Growth:
- Measure changes in market share as a result of innovative products or services.
- Market share growth reflects the competitiveness and acceptance of innovations in the market.
- Cost of Innovation:
- Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of your innovation strategy. Compare the costs associated with innovation initiatives against the returns generated.
- Identify areas where cost optimization can be achieved without compromising innovation quality.
- Innovation Metrics:
- Continuous Optimization Strategies:
- Benchmarking:
- Compare your innovation metrics against industry benchmarks and best practices. Benchmarking provides context for assessing the competitiveness of your innovation strategy.
- Identify areas where you can surpass industry standards and set new benchmarks.
- Iterative Improvement:
- Embrace an iterative approach to improvement based on measurement outcomes. Regularly analyze measurement data and use the insights to refine and enhance your innovation strategy.
- Encourage a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
- Agile Methodologies:
- Apply agile methodologies not only to the development of innovations but also to the measurement and optimization processes.
- Adapt and adjust strategies based on real-time feedback and changing market conditions.
- Feedback Loops:
- Establish feedback loops with key stakeholders, including customers, employees, and leadership. Regularly communicate measurement results and gather input for improvement.
- Act on feedback to demonstrate a commitment to addressing identified areas for enhancement.
- Scenario Analysis:
- Conduct scenario analysis to anticipate potential challenges and opportunities in the future. Use this analysis to proactively adjust your innovation strategy.
- Scenario planning enables strategic flexibility and resilience in the face of uncertainties.
- Benchmarking:
- Communication of Results:
- Transparent Reporting:
- Transparently report measurement results to all relevant stakeholders. Clearly communicate successes, challenges, and the strategic adjustments made based on measurement outcomes.
- Transparency builds trust and reinforces the commitment to continuous improvement.
- Transparent Reporting:
- Integration with Organizational Strategy:
- Strategic Alignment:
- Ensure that measurement metrics align with broader organizational strategies. This alignment reinforces the contribution of innovation to the achievement of organizational goals.
- Periodically assess and adjust measurement metrics to stay aligned with evolving organizational priorities.
- Strategic Alignment:
Successful Innovation Strategy Examples
These companies showcase diverse approaches to innovation, emphasizing the importance of understanding customer needs, leveraging disruptive technologies, and continually adapting to stay ahead in rapidly evolving industries.
(1) Apple Innovation Strategy:
Apple’s innovation strategy is the cornerstone of its competitive advantage and overall business approach. The company’s strategic focus revolves around pioneering disruptive innovations to carve out new markets, rendering competition inconsequential in its wake.
- At its core is an unwavering commitment to user-centric design and excellence, with a deep understanding of user needs and preferences driving the creation of intuitive and aesthetically pleasing products. The strategy extends beyond individual products to encompass a seamless ecosystem where hardware, software, and services work harmoniously. This integration not only enhances user convenience but also fosters brand loyalty.
- A key driver of Apple’s innovation is its relentless pursuit of disruptive technologies, evident in consistent investments in groundbreaking advancements. Notable innovation examples include the introduction of touchscreens with the iPhone and innovations in wearable tech exemplified by the Apple Watch. This commitment keeps Apple at the forefront of technological evolution.
- Furthermore, Apple’s innovation strategy is characterized by a focus on sustainability, strategic partnerships, services expansion, and a strong emphasis on privacy and security. These elements collectively contribute to a holistic approach that goes beyond individual product features, reinforcing the brand’s global reputation for innovation and excellence.
- In summary, Apple’s multifaceted innovation strategy, marked by user-centric design, ecosystem integration, and a commitment to disruptive technologies, reflects a dedication to providing a seamless and cutting-edge experience for users while addressing broader concerns such as sustainability and privacy.
(2) Tesla Innovation Strategy:
Tesla’s innovation strategy is characterized by a relentless pursuit of advancements that redefine the automotive industry and extend into broader energy solutions. At the forefront of this strategy is the development and popularization of electric vehicles (EVs). Tesla disrupted the automotive landscape by not only producing high-performance electric cars but also continually pushing the boundaries of range, charging infrastructure, and overall EV capabilities.
It goes beyond the products themselves, encompassing the entire ecosystem of electric vehicles, autonomous technology, renewable energy, and customer experience. By consistently pushing the boundaries of what is possible, Tesla has positioned itself as a transformative force in multiple industries.
Key elements of Tesla’s innovation strategy include:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs):
Central to Tesla’s strategy is the production of electric vehicles that not only address environmental concerns but also deliver high performance. The Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y have collectively reshaped the perception of electric cars. - Autonomous Driving Technology:
Tesla is a pioneer in autonomous driving technology. The Autopilot feature and the ongoing development of Full Self-Driving (FSD) capabilities showcase Tesla’s commitment to revolutionizing transportation through automation. - Renewable Energy Solutions:
Beyond cars, Tesla expands its innovation into renewable energy. The acquisition of SolarCity and the development of solar panels and energy storage solutions contribute to Tesla’s vision of a sustainable energy ecosystem. - Innovative Manufacturing Processes:
Tesla has implemented innovative manufacturing processes, such as the Gigafactory concept, to scale production and drive down costs. This approach is crucial for making EVs more accessible to a broader market. - Over-the-Air Software Updates:
Tesla’s vehicles can receive over-the-air software updates, allowing for continuous improvements and the addition of new features. This approach not only enhances customer experience but also reflects Tesla’s commitment to iterative innovation. - Direct-to-Consumer Sales Model:
Tesla’s direct-to-consumer sales model challenges traditional dealership approaches, enabling the company to maintain control over the customer experience and better communicate its brand values. - Brand Innovation and Marketing:
Tesla’s brand is synonymous with innovation and sustainability. Elon Musk’s visionary leadership and the company’s bold marketing approach contribute to the overall narrative of Tesla as a trailblazer in the automotive and energy sectors.
(3) Amazon Innovation Strategy:
Amazon’s innovation strategy is a driving force behind the company’s evolution from an online bookseller to a global e-commerce giant and technology powerhouse. Central to Amazon’s approach is a commitment to customer obsession, technological innovation, and diversification.
It allows the company to adapt to changing market conditions and continuously explore new opportunities. By combining a customer-centric philosophy with technological prowess and diversification, Amazon has positioned itself as a global leader not only in e-commerce but also in cloud computing, digital content, and innovative retail experiences.
Key elements of Amazon’s innovation strategy include:
- Customer Obsession:
Amazon places an unwavering focus on customer satisfaction. This customer-centric approach involves understanding and anticipating customer needs, providing a seamless online shopping experience, and offering a wide range of products at competitive prices. - Technological Innovation:
Amazon leverages cutting-edge technologies to optimize its operations and enhance customer services. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is evident in product recommendations, personalized content, and the optimization of logistics and supply chain management. - Diversification Beyond E-commerce:
Amazon has diversified its business beyond e-commerce into various sectors. Amazon Web Services (AWS), the company’s cloud computing division, has become a major player in the industry, providing services to a wide range of businesses globally. - Logistics and Supply Chain Innovation:
Amazon has revolutionized logistics and supply chain management. The introduction of Prime and initiatives like Amazon Fulfillment Centers showcase the company’s commitment to fast and efficient order fulfilment, setting new standards in the e-commerce industry. - Digital Content and Streaming Services:
Amazon has ventured into digital content and streaming services with Amazon Prime Video and Amazon Music. This diversification enhances the value of Amazon Prime memberships, contributing to customer retention and loyalty. - Smart Devices and Innovation in AI:
Amazon’s foray into smart devices, such as the Echo line of smart speakers powered by the virtual assistant Alexa, demonstrates the company’s innovation in the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence. These devices not only enhance user convenience but also provide a platform for Amazon’s services. - Acquisitions and Strategic Partnerships:
Amazon strategically acquires companies to expand its capabilities and enter new markets. Notable acquisitions include Whole Foods Market, PillPack, and Zappos. Strategic partnerships, such as collaborations with third-party sellers, further extend Amazon’s reach and influence. - Amazon Go and Cashierless Stores:
Amazon Go, a cashierless shopping experience, exemplifies Amazon’s commitment to innovation in retail. Using technologies like computer vision and sensor fusion, these stores offer a frictionless shopping experience.
(4) Netflix Innovation Strategy:
Netflix’s innovation strategy has been a transformative force in the entertainment industry, reshaping how content is produced, distributed, and consumed. At the core of Netflix’s approach is a commitment to streaming technology, original content creation, and data-driven personalization.
It reflects a dynamic and forward-thinking approach to entertainment, leveraging technology, data, and creative collaborations to redefine the streaming experience. By focusing on original content, global reach, and a commitment to technological excellence, Netflix has become a leading player in the evolving landscape of digital entertainment.
Key elements of Netflix’s innovation strategy include:
- Streaming Technology:
Netflix disrupted traditional entertainment models by pioneering streaming technology. The shift from physical media to online streaming allowed users to access a vast library of content on-demand, fundamentally altering the way people consume movies and TV shows. - Original Content Creation:
A pivotal aspect of Netflix’s strategy is the investment in creating original content. By producing and distributing exclusive series, films, documentaries, and stand-up specials, Netflix has become a content creator in addition to a streaming platform, attracting subscribers with diverse and high-quality offerings. - Data-Driven Personalization:
Netflix leverages data analytics to personalize user experiences. Algorithms analyze viewing habits, preferences, and ratings to provide tailored content recommendations, enhancing user satisfaction and retention. - Global Expansion:
Netflix has pursued an aggressive global expansion strategy, making its streaming service available in numerous countries. This global footprint allows Netflix to tap into diverse markets and cultures, tailoring content to a wide range of audiences. - Partnerships and Collaborations:
Netflix collaborates with various content creators, production houses, and talent. Partnerships with renowned directors, producers, and actors contribute to the creation of exclusive and high-profile content, reinforcing Netflix’s position as a content innovator. - Interactive Content:
Netflix has experimented with interactive content, allowing viewers to make choices that influence the narrative. Interactive storytelling, as seen in productions like “Black Mirror: Bandersnatch,” adds a new dimension to user engagement and immersion. - Adaptive Pricing Models:
Netflix introduced multiple pricing tiers, offering flexibility for users to choose plans based on their preferences and budget. This adaptive pricing model caters to a broad spectrum of subscribers and contributes to sustained revenue growth. - Continuous Experimentation:
Netflix fosters a culture of continuous experimentation. The company tests new features, interfaces, and content formats to gauge user response and refine its platform continuously. This iterative approach ensures that Netflix remains at the forefront of industry trends. - Investment in Technology:
Netflix continually invests in technological advancements to enhance streaming quality, support a variety of devices, and stay ahead in the competitive streaming landscape. This includes investments in codecs, bandwidth optimization, and user interface innovations. - Data-Informed Content Production:
Netflix uses data analytics not only for personalized recommendations but also to inform content production decisions. Insights derived from viewer behavior and preferences influence the types of content commissioned and produced by Netflix.
(5) Microsoft Innovation Strategy
Microsoft’s innovation strategy is characterized by a continual evolution that spans software, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, ensuring the company’s relevance in a rapidly changing technology landscape.
Key elements of Microsoft’s innovation strategy include:
- Software Dominance:
Microsoft has historically been a software powerhouse, with products like the Windows operating system and Microsoft Office suite shaping the computing landscape. The company continues to innovate in software development, introducing new features and enhancing user experiences across a range of applications. - Cloud Computing Leadership:
Microsoft’s Azure platform is a cornerstone of its innovation strategy. Embracing cloud computing, Microsoft has positioned itself as a major player in providing cloud services to businesses. Azure offers a comprehensive suite of solutions, including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). - Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Microsoft integrates artificial intelligence across its products and services. This includes AI-driven features in applications, chatbots, virtual assistants (Cortana), and advancements in natural language processing. The company’s commitment to AI innovation is evident in initiatives like Microsoft AI for Earth and AI for Accessibility. - Open Source Contributions:
Microsoft has embraced open-source development, contributing to and collaborating with various open source projects. This shift toward openness fosters a more collaborative and inclusive innovation ecosystem. - Digital Transformation Solutions:
Microsoft plays a pivotal role in helping businesses undergo digital transformation. From enterprise solutions like Microsoft 365 to Dynamics 365 for business applications, the company provides a suite of tools that enable organizations to modernize their operations and embrace digital technologies. - Innovations in Gaming:
Microsoft’s Xbox gaming platform and innovations like Xbox Game Pass reflect the company’s commitment to gaming. The acquisition of game development studios and the introduction of cloud gaming services, such as Xbox Cloud Gaming (formerly Project xCloud), underscore Microsoft’s dedication to the gaming industry. - Cybersecurity Advancements:
Given the increasing importance of cybersecurity, Microsoft has been proactive in developing and integrating cybersecurity solutions. Products like Microsoft Defender and Azure Sentinel showcase the company’s commitment to enhancing digital security for businesses and individuals. - Inclusive Design:
Microsoft has prioritized inclusive design, creating products and services that are accessible to users with diverse abilities. This commitment is reflected in features like built-in accessibility tools in Windows and inclusive design principles applied across various applications. - Quantum Computing Research:
Microsoft is actively engaged in quantum computing research. Initiatives like Microsoft Quantum aim to push the boundaries of computing capabilities, exploring the potential of quantum technologies in solving complex problems. - Sustainable Practices:
Microsoft has made substantial commitments to sustainability. The company aims to be carbon-negative by 2030 and has initiatives to promote renewable energy, reduce carbon footprint, and contribute to environmental sustainability.
(6) Google Innovation Strategy:
Google’s innovation strategy is expansive and diversified, extending beyond its foundational search engine to encompass a wide array of technological ventures. The company’s commitment to innovation is evident in its exploration of diverse areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), self-driving cars, and quantum computing.
It is marked by a relentless pursuit of technological advancements, a commitment to open source collaboration, and a willingness to explore emerging technologies with the potential to reshape industries. By maintaining a diverse portfolio of products and services, Google remains a frontrunner in the ever-evolving landscape of technology and digital innovation.
Key elements of Google’s innovation strategy include:
- Search Dominance:
Google’s core innovation lies in its search engine technology. Continuous improvements and algorithmic advancements ensure that Google remains the leading platform for information retrieval, shaping the way users access and interact with online content. - Diverse Technological Ventures:
Google explores a broad spectrum of technological frontiers. This includes investments and initiatives in artificial intelligence, machine learning, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and natural language processing. - Android Operating System:
Google’s Android operating system is a dominant player in the mobile device market. The open-source nature of Android fosters innovation among device manufacturers and app developers, contributing to the widespread adoption of mobile technology. - Online Advertising Innovations:
Google revolutionized online advertising through platforms like Google Ads and AdSense. The company’s targeted advertising model, based on user data and preferences, has become a standard in the digital advertising industry. - Cloud Computing Services:
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides a range of cloud computing services, competing with industry leaders like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. Google’s innovation in cloud services includes infrastructure, data analytics, and machine learning tools. - Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
Google integrates AI and ML across its products and services. From search algorithms to voice assistants (Google Assistant), the company leverages these technologies to enhance user experiences and provide intelligent solutions. - Self-Driving Cars (Waymo):
Google’s autonomous vehicle project, Waymo, is a pioneer in self-driving technology. Waymo’s innovations in sensors, machine learning, and navigation systems position it at the forefront of the autonomous driving industry. - Quantum Computing (Quantum AI Lab):
Google is actively engaged in quantum computing research through the Quantum AI Lab. Exploring the potential of quantum technologies, Google aims to address complex computational challenges beyond the reach of classical computers. - Open Source Contribution:
Similar to other tech giants, Google actively contributes to open source projects. This collaborative approach fosters innovation in the broader technological community. - Innovation in Internet Services:
Google continues to innovate in internet services with products like Google Maps, Google Photos, and Gmail. These services incorporate AI, machine learning, and data-driven functionalities to provide users with advanced features and personalized experiences. - Corporate Acquisitions:
Google strategically acquires companies to augment its capabilities and enter new markets. Acquisitions like YouTube, Android, and DeepMind have played pivotal roles in expanding Google’s influence and diversifying its offerings.
How to Measure The Impact of Your Innovation Strategy
- Set Clear Objectives:
- Clearly outline the specific outcomes you aim to achieve with your innovation strategy.
- Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Define measurable metrics that directly align with your innovation goals.
- Baseline Measurement:
- Establish a starting point for your KPIs to provide a reference for future assessment.
- Regular Monitoring:
- Consistently track and analyze progress to stay informed about the ongoing impact of your initiatives.
- Customer Feedback:
- Directly gather insights from customers to understand their satisfaction with new products or services.
- Employee Engagement:
- Assess the level of employee involvement and satisfaction with innovation initiatives.
- Financial Metrics:
- Use financial metrics to assess the economic impact of your innovation strategy, including revenue growth and cost savings.
- Risk and Failure Metrics:
- Measure the organization’s tolerance for risk and learn valuable lessons from innovation failures.
- Competitor Benchmarking:
- Compare your innovation performance with industry peers to gauge competitiveness.
- Time-to-Value:
- Evaluate how quickly innovations contribute measurable value to the organization.
- Adoption Rates:
- Measure the acceptance and adoption of new products or processes in the target market.
- Long-Term Impact:
- Assess how innovations contribute to the organization’s long-term strategic goals and vision.
- Stakeholder Feedback:
- Gather insights from various stakeholders, including customers, employees, and partners, to gain a comprehensive perspective.
- Iterative Evaluation:
- Continuously refine your innovation strategy based on insights gained from ongoing assessments.
Frequently Asked Questions
(1) What role do senior leaders play in achieving an innovation strategy?
Senior leaders play a pivotal role in driving and achieving an innovation strategy within an organization. Their influence extends across various aspects of the innovation process, fostering a culture and environment conducive to creative thinking and groundbreaking initiatives.
Here are the key roles that senior leaders play in the pursuit of innovation:
- Setting the Vision and Direction:
- Senior leaders articulate a clear vision for innovation aligned with the overall organizational strategy. They define the direction and goals, providing a roadmap for the innovation journey.
- Creating a Culture of Innovation:
- Leaders shape the organizational culture, emphasizing the importance of innovation. By fostering an environment that values experimentation, risk-taking, and learning from failure, they encourage employees to think creatively and contribute novel ideas.
- Resource Allocation and Investment:
- Senior leaders allocate resources, both financial and human, to support innovation initiatives. They make strategic investment decisions, ensuring that innovative projects receive the necessary funding, talent, and infrastructure.
- Encouraging Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Leaders promote collaboration across departments and teams. Breaking down silos encourages the exchange of ideas, diverse perspectives, and interdisciplinary collaboration essential for innovative solutions.
- Leading by Example:
- Leadership behavior sets the tone for the organization. When senior leaders actively engage in and support innovative practices, it signals the importance of innovation to the entire workforce.
- Establishing Risk Tolerance:
- Leaders define the organization’s risk tolerance and attitude toward failure. A culture that views failure as a learning opportunity and encourages calculated risks fosters an atmosphere where employees feel empowered to explore unconventional ideas.
- Recognizing and Rewarding Innovation:
- Senior leaders establish recognition and reward systems that celebrate and acknowledge innovative contributions. This includes formal acknowledgment, incentives, and career advancement opportunities for individuals and teams driving innovation.
- Providing Continuous Learning Opportunities:
- Leaders invest in continuous learning and development programs. This ensures that employees have the skills and knowledge required for innovative endeavors, keeping the workforce adaptable in a rapidly changing landscape.
- Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Strategies:
- Leaders track the progress of innovation initiatives, using key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success. They are flexible in adjusting strategies based on feedback and insights gained from ongoing innovation efforts.
- Communicating the Importance of Innovation:
- Senior leaders communicate a compelling narrative around the importance of innovation to the organization’s long-term success. This narrative helps employees understand the strategic significance of their innovative contributions.
(2) What is a product innovation strategy in business?
A product innovation strategy in business involves a systematic approach to creating and introducing new or improved products to meet the changing needs and preferences of customers. This strategy aims to enhance a company’s competitiveness, capture market share, and drive sustainable growth.
It involves the systematic development, launch, and management of new or enhanced products. It requires a combination of market understanding, creative ideation, effective execution, and adaptability to ensure sustained success in a competitive market.
Here are the key components of a product innovation strategy:
- Market Research and Customer Insights:
- Understanding customer needs, preferences, and market trends is fundamental. Market research and customer insights guide the identification of opportunities for new or improved products.
- Idea Generation and Brainstorming:
- Encouraging creativity within the organization is crucial. This involves generating ideas through brainstorming sessions, innovation workshops, and cross-functional collaboration to uncover potential product concepts.
- Product Development and Prototyping:
- Once ideas are generated, the next step is product development. This phase involves creating prototypes, conducting feasibility studies, and refining concepts to ensure they align with market demands and technological feasibility.
- Testing and Validation:
- Rigorous testing and validation are essential to ensure that the product meets quality standards and addresses the identified market needs. This may involve pilot launches, beta testing, or focus groups to gather feedback.
- Iterative Design and Improvement:
- The product development process is often iterative. Companies continuously refine and improve products based on feedback, technological advancements, and changing market dynamics.
- Strategic Positioning:
- The innovation strategy includes defining the strategic positioning of the new product in the market. This involves considering factors such as pricing, branding, and differentiation to establish a competitive advantage.
- Market Launch and Commercialization:
- Effectively launching the product into the market is a critical step. This includes developing marketing and communication strategies, distribution plans, and sales campaigns to generate awareness and drive adoption.
- Lifecycle Management:
- Managing the product throughout its lifecycle is part of the innovation strategy. This involves monitoring market performance, identifying opportunities for product updates or extensions, and making decisions on product retirement or discontinuation.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Successful product innovation often requires collaboration across various departments, including research and organizational development, marketing, sales, and customer support. Cross-functional teams bring diverse perspectives to the innovation process.
- Intellectual Property Protection:
- Companies may incorporate intellectual property protection strategies, such as patents or trademarks, to safeguard their innovative products from imitation and secure a competitive advantage.
- Responsive to Market Feedback:
- A product innovation strategy should be responsive to market feedback. Companies need to adapt and refine their strategies based on changing customer preferences, competitive dynamics, and emerging trends.
- Continuous Improvement:
- The product innovation strategy should be a continuous and dynamic process. Companies must foster a culture of continuous improvement, learning from both successes and failures, to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving business landscape.











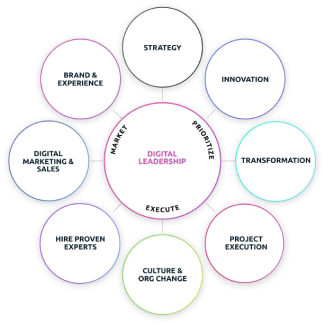

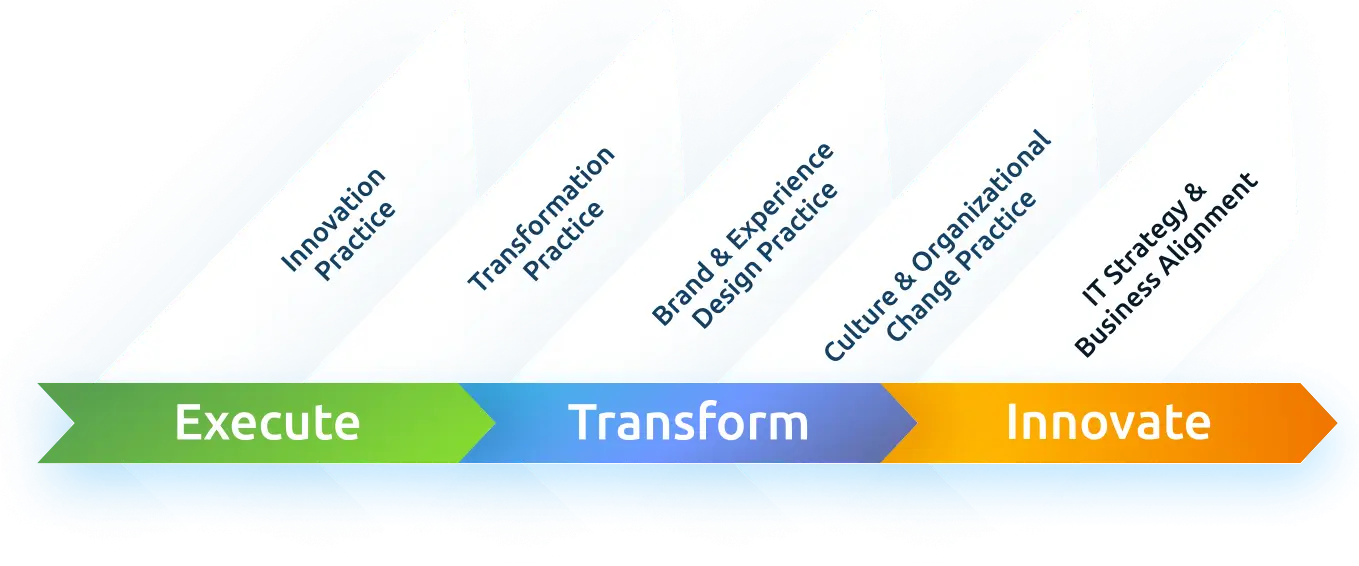















 Book How to Create Innovation
Book How to Create Innovation