Strategic Goals Examples, Importance & Definition
Published: 12 February, 2023
Digital Strategy
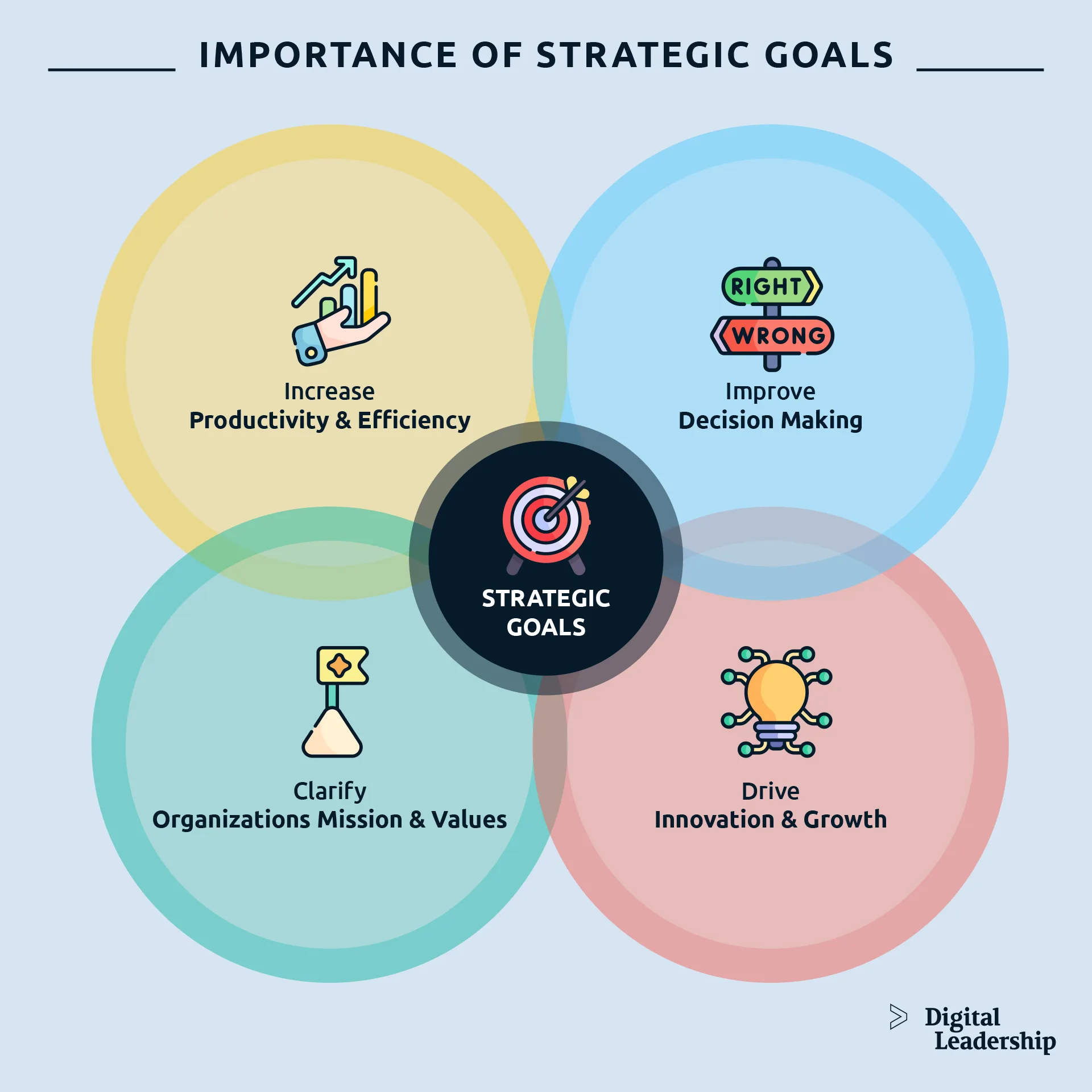
Table of Contents
Strategic goals are a critical component of an overall business strategy because they provide the focus and direction needed to align resources, efforts, and decision-making. Strategic goals provide specific, measurable, and actionable objectives that shape a company’s strategic planning process.
Additionally, strategic goals are a bridge between the company’s overall vision and its day-to-day operations. By defining clear and achievable goals, a company can ensure that all stakeholders are working toward the same end and that resources are being used effectively to achieve your business goals.
At Digital Leadership, we believe that strategic goals and planning are vital elements of a business’s success. We want to see every endeavor create a lasting future for itself and its clients. If you have questions about your strategic vision, or how to bridge the gap between hope and execution, we invite you to contact our Agile Consultants.
In this article, we explore the role strategic goals play in your business plan. What comes first: the goals or the plan? As you’ll see, it’s not really a matter of what goes on paper before the other that determines success, but rather, how both goals and plans are integrated into your overall business plan and business model.
What are Strategic Goals?
Strategic goals are specific, long-term objectives that a company sets for itself to achieve its desired future state, These strategic goals are both financial and non-financial objectives, so they can take a lot of different forms depending on the organization’s particular business model. It encompasses the precise financial and non-financial targets that a company endeavors to attain within a designated timeframe, typically spanning the upcoming three to five years.
These goals serve as a roadmap for a company. They provide direction and focus for decision-making, business strategy, resource allocation, and operational execution.
Strategic goals are different from tactical goals, which are short-term, specific, and focused on achieving specific tasks or milestones. Strategic goals are broader and longer-term, usually spanning somewhere between three and five years, and serve as the foundation for a company’s overall business strategy.
The Importance of Strategic Goals

Strategic goals are important because they help a business know where it wants to go and how it wants to get there. They provide direction, focus, and purpose for a business, making it easier to achieve success.
Let’s take a look at some of the ways the development of strategic goals benefits a business.
- Clarify the Organization’s Mission & Values
- Improve Decision Making
- Drive Innovation & Growth
- Increase Productivity & Efficiency
Clarify the Organization’s Mission & Values
Articulating strategic goals has a clarifying effect on an organization’s mission and values. Merely undertaking the process of setting goals on the page pushes leadership to reconsider all of its decisions within a different—and productive—context.
Business goals also play a significant role in shaping its organizational strategy. Mission and values help determine the shape of an organization as higher priorities attract a representative value of resources.
Improve Decision Making
Once leaders are given a clearly articulated mission or set of values, they can solidify the direction they should be taking when making their decisions.
Strategic goals serve as a guiding light that motivates and guides decision-making.
Drive Innovation & Growth
When strategic goals include growth and change, they can be tremendous motivators for innovation.
Because everyone within the organization agrees that growth is an important goal, proper resources are easily allocated for these efforts.
Increase Productivity & Efficiency
Similarly, because strategic goals offer such a clear purpose, they allow for improved productivity and increased efficiency.
Everyone’s in agreement. Resources can be clearly directed and decisions are made much more quickly.
Characteristics of Strategic Goals
Strategic goals form the cornerstone of an organization’s long-term vision and planning, serving as the guiding stars that illuminate the path to success. These goals encapsulate the company’s aspirations, providing a framework for decision-making and resource allocation. To be effective, strategic goals possess a unique set of characteristics that distinguish them from other objectives within an organization. In this discussion, we’ll delve into the key traits that define strategic goals, shedding light on their crucial role in shaping a company’s future and driving its growth:
- Long-term Focus: Strategic goals are oriented toward the future and typically cover an extended period, often spanning several years, to allow for significant planning and execution.
- Broad and High-Level: They are overarching objectives that guide the entire organization, providing a sense of direction without getting into detailed specifics.
- Alignment with Vision and Mission: Strategic goals should align with the company’s vision and mission, ensuring that they contribute to the overarching purpose and values of the organization.
- Measurable and Specific: While they are high-level, strategic goals should still be measurable and specific enough to gauge progress and success effectively.
- Challenging Yet Achievable: They should be ambitious enough to inspire effort and innovation but also realistic enough that they can be accomplished with concerted effort and resources.
- Time-Bound: Strategic goals are set within a defined timeframe, which helps create a sense of urgency and ensures accountability.
- Guiding Decision-Making: These goals serve as a reference point for decision-making at all levels of the organization, helping to prioritize actions and allocate resources effectively.
- Adaptive: Strategic goals should be flexible enough to adapt to changing circumstances and market dynamics while remaining true to the organization’s core objectives.
- Communicated and Shared: They should be well-communicated across the organization to ensure that all employees understand and align their efforts with these overarching goals.
- Impactful: Strategic goals should have a significant impact on the organization’s growth, profitability, market position, or other key performance areas.
- Continuous Improvement: Achieving strategic goals often involves a continuous improvement process, where progress is monitored, and adjustments are made as needed.
- Comprehensive: They may encompass various aspects of the business, including financial, operational, customer-related, and innovation-driven objectives.
- Reflective of Market and Industry Trends: Strategic goals should take into account the evolving market and industry trends to position the company competitively.
- Sustainable: Consideration of sustainability and responsible business practices may be incorporated into strategic goals to align with societal and environmental expectations.
- Inspiring and Motivating: Well-crafted strategic goals have the power to inspire and motivate employees, stakeholders, and partners, driving collective efforts toward success.
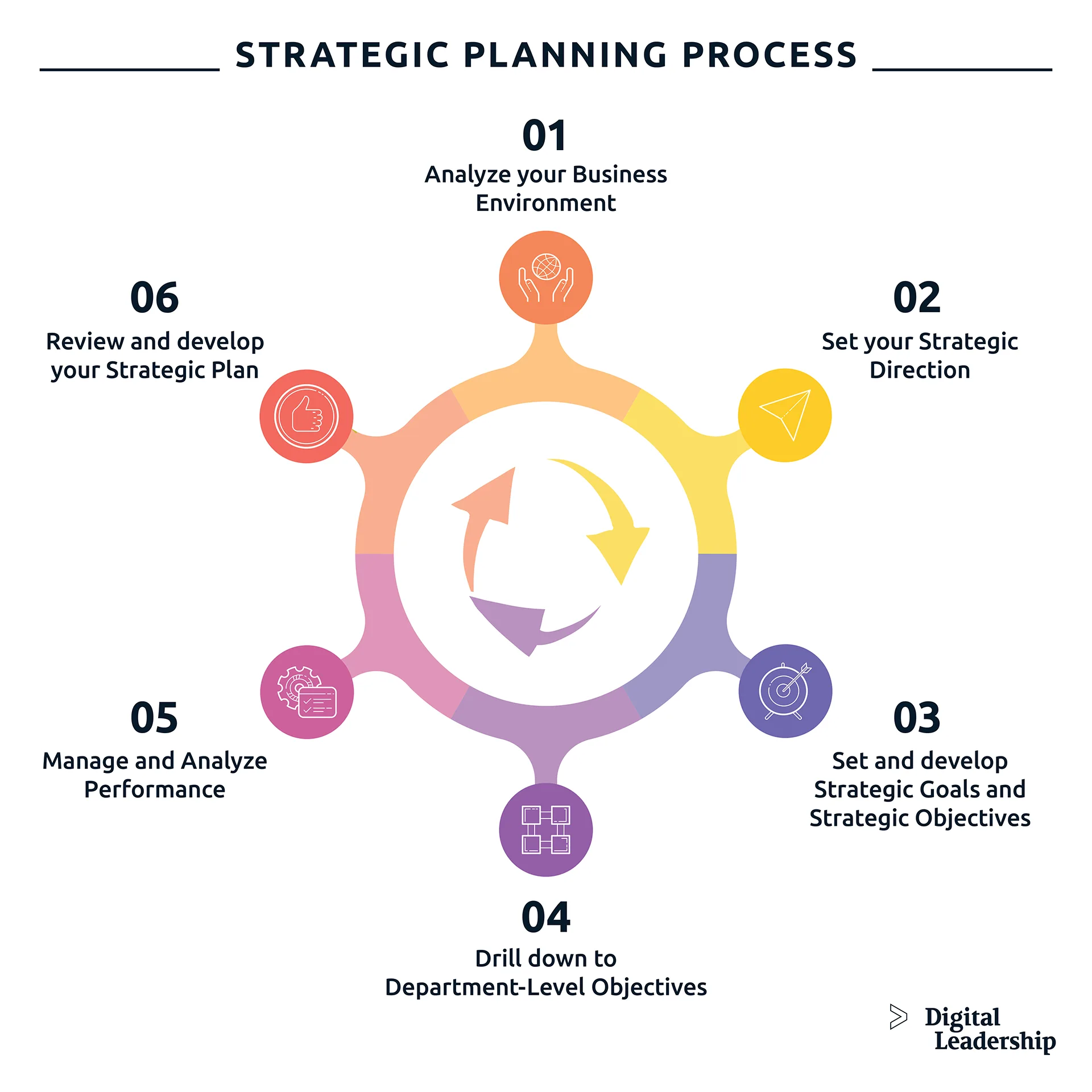
Strategic Goals vs Strategic Planning
Strategic goals and strategic planning are two closely related concepts in business, but they are not the same thing.
Strategic goals are specific, measurable, and actionable objectives.
Strategic planning, on the other hand, is the process of creating and implementing a strategy that supports the achievement of a business’s goals. The strategic planning process involves analyzing the business’s current situation, identifying its strengths and weaknesses, setting goals, and developing a plan to achieve those goals.
Strategic goals provide direction and focus for a business, while strategic planning is the process of creating and implementing a strategy to achieve those goals.
Strategic Goals vs. Business Goals vs. Business Objectives
In the realm of strategic planning, precision is paramount. While strategic goals, business goals, and business objectives provide the framework for a company’s vision, it’s the Business Model Canvas that transforms these abstract notions into actionable roadmaps. The Business Model Canvas is your compass, simplifying complex strategies into a visual guide that aligns aspirations with attainable steps. You can download it now.
Strategic goals, business goals, and business objectives are all terms used to describe different aspects of a company’s desired future state and the steps it takes to achieve that state. However, they each have slightly different connotations and purposes:
- Strategic goals are the long-term aspirations that a company sets for itself. They provide a broad direction for the company and set the overall tone for decision-making and resource allocation. Examples of strategic goals might include becoming a market leader in a certain industry or expanding into new geographic markets.
- Business goals are more specific and measurable than strategic goals. They provide a concrete target for the company to aim for and help it track its progress toward its desired future state. Examples of business goals might include increasing market share by a certain percentage, reducing costs by a certain amount, or launching a new product line.
- Business objectives are the specific, actionable steps that a company takes to achieve its business goals. They provide a clear roadmap for the company and help it focus its efforts and resources on the most important tasks. Examples of business objectives might include launching a new marketing campaign, increasing product quality, or reducing waste.
In short, strategic goals set the overall direction for a company, business goals provide specific targets to aim for, and business objectives provide the concrete steps needed to achieve those targets.
Examples of Strategic Goals
Various strategic goals can differ greatly from one business to another, depending on the company’s industry, size, and target market. However, many strategic goals share common characteristics such as a long-term focus, measurable targets, alignment with values, relevance to stakeholders, and adaptability. These commonalities help ensure that strategic goals are meaningful, relevant, and achievable and that they serve as a foundation for a successful business strategy.
Let’s look at some specific strategic goals businesses often adopt.
(1) Increasing market share
A larger market share usually translates into increased sales and revenue, which can increase a business’s overall profitability. A larger market share can help a business build brand recognition and increase its overall visibility and credibility, making it easier for the business to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
(2) Improving customer satisfaction
Happy customers are more likely to continue doing business with a company and to recommend it to others. Satisfied customers are less likely to switch to a competitor, reducing the costs associated with acquiring new customers, and they are more likely to share their positive experiences with others, helping a business build its reputation.
(3) Expanding into new geographic markets
Expanding into new geographic markets can help a business diversify its customer base and reduce its dependence on a single market or region. This can reduce the risk of economic downturns or market changes affecting the business. Additionally, new geographic markets can offer businesses access to new resources—such as talent, suppliers, and distribution channels—that can help them grow and innovate.
(4) Diversifying product offerings
By diversifying their product offerings, businesses can reduce their dependence on a single product or market. A business that offers a wide range of products can differentiate itself from its competitors, establishing a competitive advantage that can feature in its overall business model. A wider range of products can attract and retain more customers than you’re able to with a limited range of offerings.
(5) Reducing operating costs
Increased profitability comes from reducing costs, and it frees up additional resources for expansion and innovation. The increased flexibility that comes from having more available resources can be valuable in facilitating other goals.
(6) Improving employee satisfaction and retention
Happy and satisfied employees are more productive and engaged in their work, leading to better outcomes and results for the business. Improving employee satisfaction and retention can help a business create and maintain a positive organizational culture. This makes it easier to attract top talent, which in turn improves the business’s performance elsewhere.
(7) Developing and implementing new technologies
Developing and implementing new technologies is important for businesses because it can increase efficiency, competitiveness, customer satisfaction, innovation, and cost savings. These benefits can help a business grow and succeed in the long term.
(8) Improving supply chain management
A well-managed supply chain can help a business reduce lead times, minimize waste and errors, and increase productivity. A company that effectively manages its supply chain can establish better relationships with its suppliers and can ensure that its customers receive the products and services they need in a timely and cost-effective manner.
(9) Enhancing brand recognition and reputation
When customers associate a positive image with a brand, they are more likely to remain loyal, even in the face of competition. A well-established brand can increase the value of a company. That’s especially important if you’re trying to attract investors or potential buyers.
(10) Increasing revenue and profitability
Clearly, improving sales and the impact of those sales is a valuable goal. Increased profitability ensures a company’s future and the security of its team members.
(11) Implementing sustainability practices
In addition to proving the business is a responsible global citizen, studies have shown that many customers respond favorably to a company’s sustainability efforts.
(12) Improving efficiency and productivity
Improving efficiency and productivity is crucial for a business to remain competitive, reduce costs, and increase profitability. By streamlining processes and making better use of resources, a business can create a more sustainable and successful operation.
(13) Developing and maintaining strong partnerships
Strong partner relationships have positive impacts in big ways and small ways: better terms, improved service, extended credit, and quality advice. Cultivating good relationships is often a surprisingly powerful goal.
(14) Enhancing product quality and reliability
When a company offers high-quality, reliable products, customers are more likely to be satisfied with their purchases and become repeat customers. By focusing on product quality and reliability, a business can drive innovation and create new products and services that meet the needs of its customers.
(15) Increasing innovation and creativity
New and innovative products and services can help a business expand into new markets and gain market share. Innovation is valuable because customers are often willing to pay a premium for unique and cutting-edge solutions.
(16) Strengthening the organizational culture
Strengthening organizational culture is an important aspect of business success. Open and honest communication between employees and management, and create opportunities for feedback and suggestions. This builds trust and reinforces the culture of collaboration and teamwork that is vital when the business is engaged in innovative practices.
(17) Building a talent pipeline and developing a strong workforce
Building a talent pipeline and developing a strong workforce can help a business achieve greater competitiveness, improved efficiency and productivity, and better customer satisfaction. A business can create a more sustainable and successful operation with a strong foundation for future growth.
(18) Improving the customer experience
Improving the customer experience can help a business by making customers happier and more satisfied with the products and services the business provides. When customers are satisfied with their experience, they may be more likely to spend more money with the business and make larger purchases.
(19) Expanding into new product categories or services
Diversifying into new product categories or services helps reduce the risk of relying on a single product or service for the majority of a business’s revenue. This added resiliency helps a business weather changes in the market, customer expectations or needs, and political events that can otherwise destroy more fragile organizations.
(20) Investing in research and development (R&D)
It’s impossible to predict with accuracy where the next important innovation will begin. Only by properly devoting resources to research and development can a business be sure it’s ready to pivot to the next big thing. Doing it quickly, before the competition, is one of the surest ways of securing success.
Final Thoughts
In summary, strategic goals are the guiding beacons that illuminate an organization’s path to success, providing clarity, direction, and purpose for resource allocation and decision-making. Bridging the gap between overarching vision and daily operations, they underpin strategic planning and influence every facet of an organization’s strategy. These goals, characterized by specificity, measurability, and actionability, not only articulate the company’s mission and values but also enhance decision-making, spur innovation and growth, and optimize operational efficiency. By embracing diverse objectives, from market expansion to employee satisfaction and sustainability, businesses empower themselves to adapt, lead, and thrive in an ever-changing business landscape, with each strategic goal serving as a pivotal step toward a brighter future.
Our comprehensive guide, ‘How To Create Innovation‘ delves deeply into crafting a strategic business plan tailored for innovation, strategically aligned with your goals. It offers invaluable insights into utilizing the Business Model Canvas to fine-tune your business model, strengthen your value proposition, and propel your progress toward achieving strategic goals and exponential growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
How are strategic goals different from operational goals?
Strategic goals are focused on long-term success and growth, while operational goals are focused on the day-to-day operations and the efficient running of the business.
How can an organization measure its progress toward achieving its strategic goals?
By using specific, achievable Key Progress Indicators, a business can measure its progress toward its goals.
Measuring innovation is more challenging as its goals are often less concrete. While there are certainly some tangible measures you can consider—such as the number of product launches or patent applications over a given year—most experts advocate for a broader view that takes into account potential advancement as a result of innovation and its overall impact on a business’s goals.
How you measure innovation is likely dependent upon your overall strategic goals and the priorities you have built into your business model.
How can organizations adapt to changes in the business environment and maintain their focus on strategic goals?
It’s important for organizations to be proactive and agile in their approach to change. Regularly reviewing and refining the organization’s strategy can help ensure that it stays aligned with its goals and the changing business environment.
Empowered decision-makers should have the responsibility of monitoring competitors, market trends, and changes in regulations in order to understand shifts in the business model environment.



























 Book How to Create Innovation
Book How to Create Innovation