Digital Transformation Strategy Framework: 10 Key Steps for Strategic Planning
Published: 25 November, 2023
Transformation
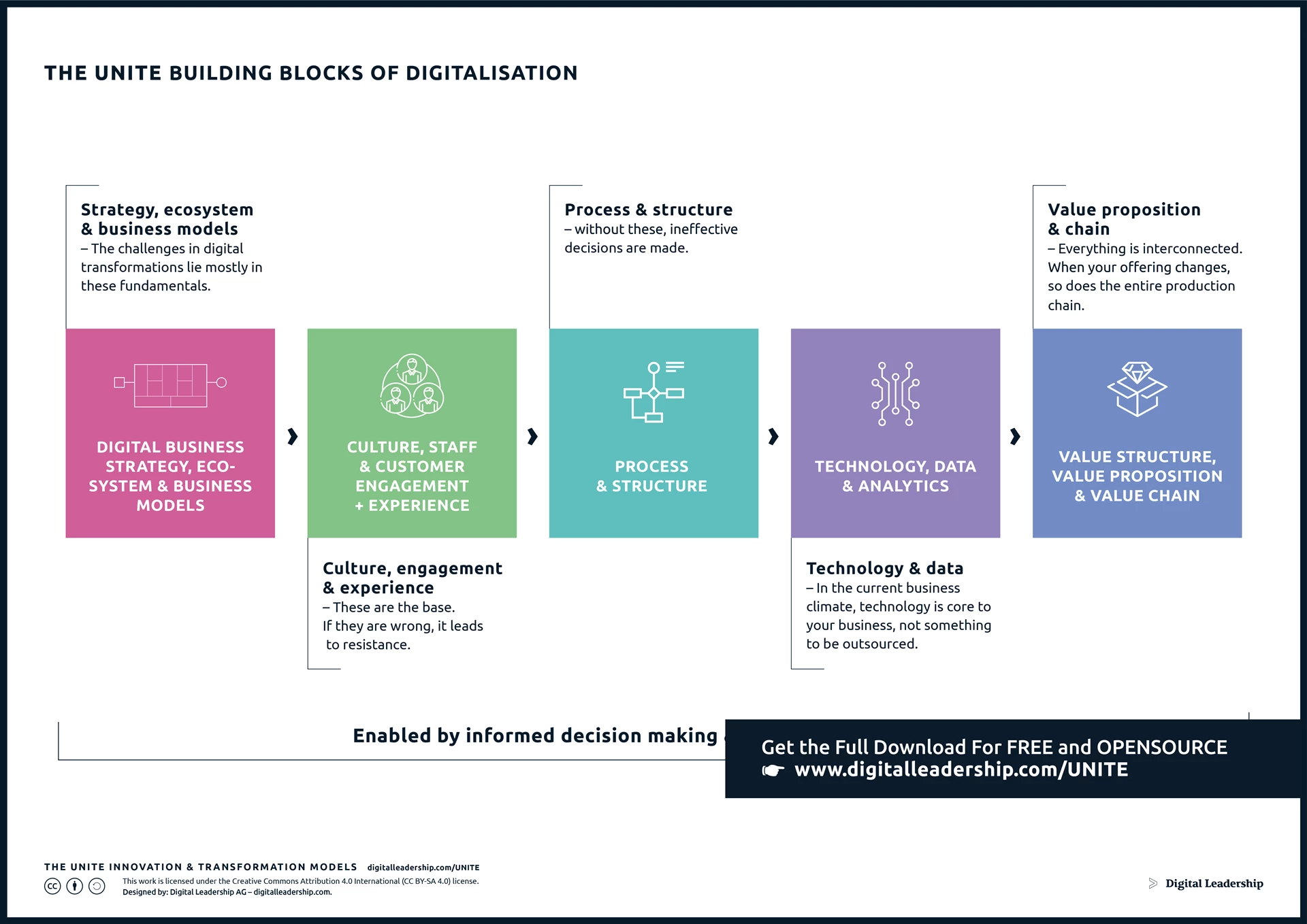
Table of Contents
At the forefront of strategic digital transformation, Digital Leadership stands as a trailblazer in guiding organizations through the intricacies of the digital landscape. As the digital revolution continues to reshape industries, businesses are compelled to not only adapt but actively shape their future in the digital realm. Digital transformation goes beyond the adoption of new technologies—it necessitates a fundamental reshaping of business processes, organizational structures, and organizational culture.
Digital transformation is a strategic approach that transcends mere technological upgrades. It is a holistic reimagining of how organizations operate, create value, and engage with their stakeholders. Through this guide, we aim to unravel the layers of developing a digital transformation strategy framework that goes beyond surface-level initiatives, delving into the core of strategic digital evolution.
The benefits of digital transformation are compelling companies worldwide to embrace a digital transformation strategy, fostering the creation of innovative business models and the development of new capabilities. As industries navigate various business transformations, the key to success lies in actional intelligence and the implementation of robust digital transformation strategies. At Digital Leadership, we specialize in providing Digital Transformation Solutions and Digital Transformation Consulting services to empower organizations by fortifying their digital capabilities. As an initial step to assist businesses in selecting tailored services that align with their specific needs and objectives for innovation, we offer an Innovation Blueprint to evaluate current innovation practices.
Defining Digital Transformation: What is Digital Transformation?
Digital transformation has become a pivotal term in the business world, It is about utilizing digital technologies to fundamentally change how organizations operate, create value, and interact with their stakeholders.
It is the process of utilizing advanced digital technologies to fundamentally alter how organizations operate, generate value, and engage with their customers, employees, and other stakeholders. Specifically, it represents a significant shift in the existing business and operating models of an organization. The integration of digital transformation is akin to updating a business plan.
While many components of these models may remain unchanged, certain aspects undergo a fundamental business transformation, creating a step-change. These transformative shifts typically trigger subsequent changes and necessary adaptations in interconnected areas of the business and operating models. Our Operating Model Canvas serves as a critical tool in the realm of digital transformation strategy, offering a structured approach to understanding and optimizing an organization’s operational dynamics. You can download it now.
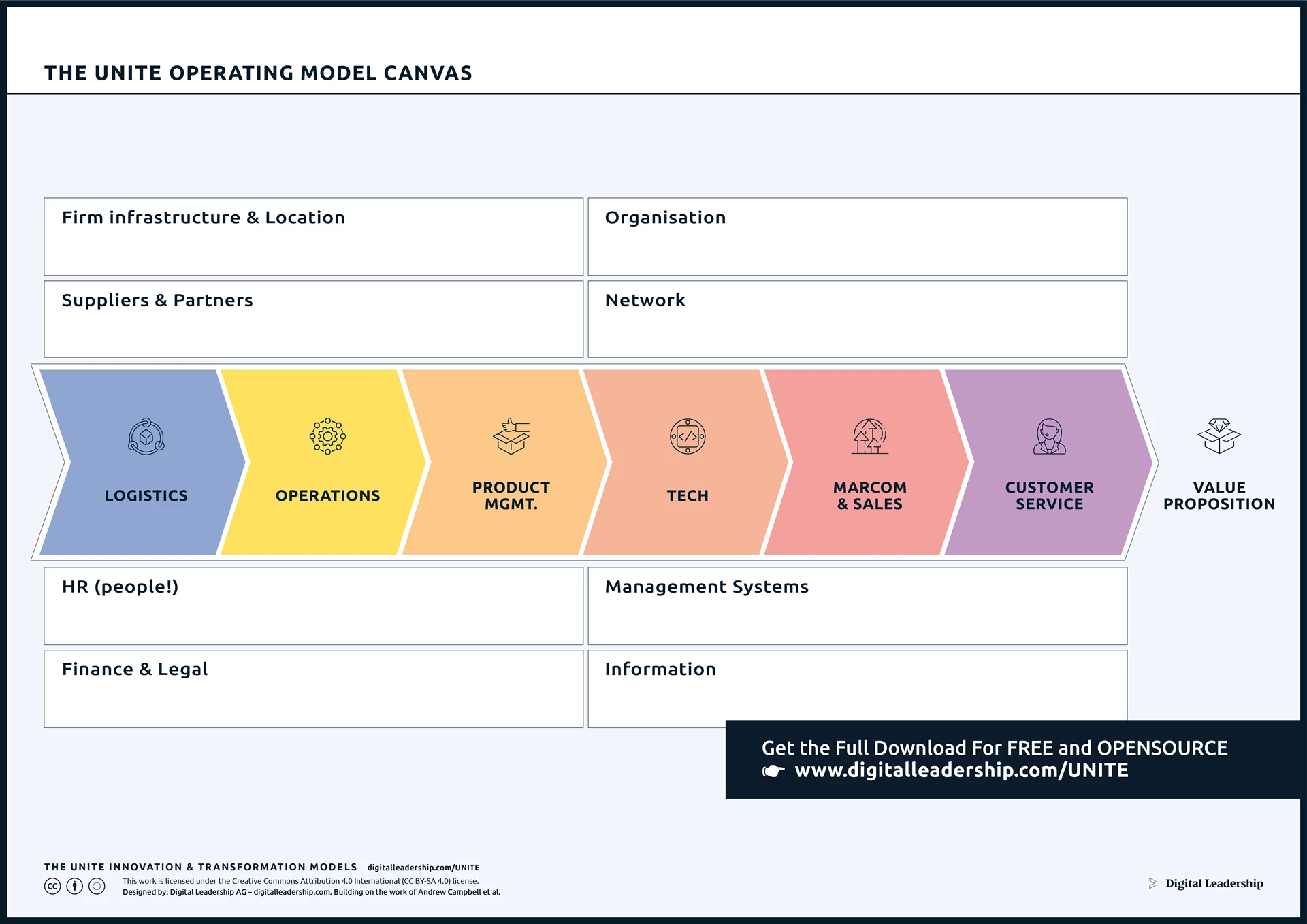
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the work of Andrew Campbell at Al.
However, digital transformation goes beyond the adoption of new technologies. It necessitates a comprehensive and holistic approach that encompasses the redesigning of business processes, organizational structures, and culture to align with the new digital reality. This transformative journey involves multiple stakeholders and functions within an organization.
The ultimate goal of digital transformation is to foster innovation, enhance efficiency, improve agility, and generate fresh value for both customers and stakeholders. In the face of a rapidly evolving digital landscape, it is imperative for organizations to not only stay competitive but also to foster innovation successfully.
The UNITE building blocks of digitalization serve as a strategic framework encompassing key elements essential for a successful Digital Transformation. It serves as a guide for organizations seeking to navigate the complexities of Digital Transformation, highlighting the importance of unified efforts across technology, people, processes, and culture. You can download it now

Designed by: Digital Leadership AG
These foundational components include not only technological aspects but also organizational and cultural considerations. The chart provides a high-level and holistic perspective, emphasizing the interconnected nature of digital initiatives.
To gain a more profound understanding of digital transformation we invite you to delve into the comprehensive insights offered in our authoritative book titled “How To Create Innovation”. You will find a detailed exploration of the intricacies involved in navigating the realms of digital transformation. Unravel the layers of complexity surrounding digitalization and digitization, gaining a clear perspective on how these processes intersect and diverge. Register for the download now!
What are Your Main Digital Transformation Business Objectives and Strategic Intention?
The primary goal of digital transformation is to gain a competitive advantage and achieve increased revenue and cost reduction through optimized business operations. This strategic intention forms the backbone of successful digital transformation endeavours.
Strategy, often misconstrued, is, at its core, a clearly expressed direction accompanied by a verified plan outlining how to reach that destination. It goes beyond lofty ambitions and growth goals, delving into the deeper “why” that resonates with team members and customers aligning themselves with organizations driven by business purpose and values.
Importantly, a robust strategy is not just about setting ambitious Business goals; it necessitates a detailed plan for achieving those Strategic goals, providing a roadmap for the organization’s broader purpose. A well-explained strategy becomes a constant north star, guiding and federating all members of the organization. It serves as a feedback mechanism, ensuring the organization stays on the right path and makes progress toward its defined goals.
To initiate the strategic planning process for a digital transformation, the first crucial step is to articulate the organization’s Business Intention, sometimes referred to as motivation. This key directional decision serves as the highest-level definition of what the organization aims to achieve. It is imperative to document this intention, as failing to do so can lead to initiatives that deviate from the original purpose and fall outside the intended scope.
What is a Digital Transformation Framework?
A digital transformation framework is a structured approach to remodelling an enterprise, incorporating digital technology across various facets. It aims to achieve greater efficiencies, collaboration, improved delivery speed, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
It serves as a comprehensive guide, outlining principles, best practices, and guidelines to navigate the complexities of a successful digital transformation. This structured approach is crucial for organizations aiming to adapt, innovate, and thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape. At its core, the framework provides a systematic pathway from initial assessment and planning to seamless implementation and continuous improvement.
A pivotal component within the Digital Transformation Framework is the digital transformation strategy. This strategy acts as the heartbeat of the framework, offering a clear direction and business purpose to the entire transformation initiative. It is crafted to align technological advancements with broader business objectives, answering the crucial “why” and “how” of digital transformation. Developed during the initial stages of the framework, the strategy sets the vision, defines specific strategic goals, and establishes a roadmap for execution.
By seamlessly incorporating the digital transformation strategy into this comprehensive framework, organizations can systematically navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by the digital landscape. This integrated approach ensures that every facet of the business transformation aligns with the organization’s overarching goals, fostering sustainable growth, and promoting a culture of innovation.
What is Digital Transformation Strategy: Digital Transformation Strategy Definition
A digital transformation strategy entails reshaping the enterprise by integrating digital technology across relevant aspects. Its aim is to attain various objectives, ranging from enhancing efficiencies and fostering collaboration to accelerating delivery speed and improving customer satisfaction.
It serves as the guiding blueprint for organizations seeking to reinvent themselves through the integration of digital technology into key facets of their operations. This strategic approach goes beyond the mere adoption of digital tools; it involves a comprehensive overhaul to achieve specific objectives. These objectives span a spectrum of goals, including the enhancement of operational efficiencies, the cultivation of collaborative environments, the expeditious delivery of products or services, and the elevation of customer satisfaction.
A well-defined digital transformation strategy provides a roadmap for aligning technology initiatives with overarching business objectives, ensuring a purposeful and impactful journey into the digital realm. As organizations embark on this transformative journey, the strategy becomes a pivotal tool in navigating the complexities of the digital landscape, fostering innovation, and ultimately driving sustained success in an ever-evolving business environment.
At Digital Leadership, we recognize the transformative power of a well-crafted digital transformation strategy. Our expertise lies in helping organizations define and implement strategies that not only keep them relevant in the digital age but position them as leaders in their respective industries.
What Drives the Digital Transformation Strategy?
The impetus behind a Digital Transformation Strategy is multifaceted, driven by a combination of internal and external factors that prompt organizations to embark on the transformative journey. One of the primary drivers is the rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Advances in digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things, present new opportunities for innovation and efficiency. Organizations are often motivated by the need to stay competitive in their respective industries, and leveraging these technologies becomes imperative for sustained relevance.
The drivers behind a Digital Transformation Strategy are a complex interplay of technological advancements, changing customer expectations, internal operational considerations, and external competitive dynamics. A comprehensive understanding of these drivers is crucial for organizations to formulate a strategy that not only addresses current challenges but also positions them for future success in the digital age
- Customer expectations and behaviours also play a pivotal role in steering digital transformation initiatives. As customers increasingly embrace digital distribution channels for interactions, purchases, and services, organizations recognize the need to adapt and meet these evolving expectations. Enhancing customer experiences, therefore, becomes a strategic driver, necessitating the incorporation of digital tools and strategies.
- Internal factors, such as the desire for operational excellence, cost optimization, and the pursuit of agility, also contribute to the impetus for digital transformation. Organizations seek to streamline processes, reduce operational costs, and improve agility to respond effectively to market dynamics.
- Moreover, external competitive pressures and the emergence of disruptive competitors often act as catalysts for organizations to reassess their strategies and embrace digital transformation. The fear of falling behind or becoming obsolete in the face of digital-native competitors can be a powerful motivator.
Digital Transformation in 3 Horizon of Growth Model
The Three Horizons of Growth model serves as a strategic compass for organizations navigating the dynamic landscape of innovation for digital transformation. It offers a structured approach to balance short-term objectives with long-term visions. Its significance lies in guiding organizations to allocate resources effectively across three horizons, ensuring a harmonized strategy that spans refining existing processes with digital enhancements (H1), exploring emerging digital opportunities for growth (H2), and engaging in radical digital innovation for future sustainability (H3).
This model aids in risk management, helping organizations categorize initiatives based on their innovation level, and facilitates optimal resource allocation by aligning investments with expected returns over different timeframes. You can download it now.

Designed By: Digital Leadership AG
To operate as a successful organization that effectively manages its core functions and pioneers new initiatives, resource allocation across the Three Horizons is imperative. This involves concurrently sustaining day-to-day operations, transforming the core business, and introducing novel business models. Each horizon is distinctly characterized by its role in either enhancing an existing business (H1), fundamentally reshaping an existing business through significant changes to its business model (H2), or innovating entirely new business models (H3).
- Enhance—Horizon 1 (H1): This entails making incremental improvements to the current business model to enhance the execution of existing systems and processes. This is a familiar focus, as it aligns with the daily efforts of most individuals within the organization.
- Transform—Digital Transformation Horizon 2 (H2): The emphasis here is on digitally evolving the existing business in new directions. This involves more than incremental changes, seeking a step-change by strategically incorporating digital technologies. Digital transformation in H2 aims to bring about a substantial evolution in the business model.
- Innovate—Horizon 3 (H3): This horizon is dedicated to pioneering radical innovation by exploring unknown possibilities through a complete innovation of the business model itself. It involves venturing beyond established boundaries and envisioning entirely new approaches to conducting business.
Developing a Digital Transformation Strategy Importance for Business
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity:
- Automation of routine tasks, such as data entry and processing, reduces errors and accelerates task completion, enabling employees to focus on high-value activities that require human expertise.
- Advanced analytics and AI-driven insights empower organizations to make data-informed decisions. Predictive analytics anticipates trends, optimizing resource allocation and operational workflows for increased efficiency.
2. Improved Customer Experience:
- Utilizing customer data for personalized experiences goes beyond basic interactions, creating tailored offerings that resonate with individual preferences. This fosters a sense of connection and leads to increased customer loyalty and advocacy.
- Multichannel Engagement: Consistent experiences across various customer touchpoints, such as social media, websites, and mobile apps, contribute to a unified and satisfying customer journey, enhancing overall satisfaction.
3. Fostering Innovation Culture and Agility:
- Beyond technology adoption, fostering a culture of continuous innovation encourages employees to contribute creative solutions. This proactive approach ensures sustained leadership by staying ahead of industry trends.
- Agile methodologies not only enhance project management but also instil an organizational mindset that adapts quickly to market dynamics. This agility is a key component of maintaining a competitive edge.
4. New Revenue Streams:
- Diversification: Exploring partnerships, joint ventures, or new market segments can lead to diversified revenue streams, reducing dependence on a single source. This strategic approach to revenue generation enhances financial stability.
- E-commerce and Digital Products: Investing in e-commerce platforms and developing digital products, such as apps or online services, opens avenues for direct customer engagement and revenue generation outside traditional channels.
5. Employee Empowerment:
- Skill Development: Implementing training programs and mentorship opportunities ensures that employees continuously acquire relevant digital skills. This not only contributes to personal growth but also enhances organizational capabilities.
- Remote Collaboration: Virtual collaboration tools enhance communication and collaboration among remote teams, fostering a cohesive and connected work environment. This empowerment supports flexible work arrangements and talent retention.
6. Data-Driven Insights:
- Analytics for Strategic Planning: Predictive analytics aids in forecasting market trends and consumer behaviour, facilitating strategic planning and future-proofing business operations. This strategic use of data ensures informed decision-making.
- Customer Behavior Analysis: In-depth analysis of customer interactions and feedback provides actionable insights for tailoring products and services to meet evolving preferences. Understanding customer behaviour is crucial for staying relevant in the market.
7. Enhanced Security Measures:
- Cybersecurity Protocols: Investing in advanced cybersecurity measures, including encryption and threat detection, safeguards not only customer data but also preserves the organization’s reputation. This commitment to security builds customer trust.
- Compliance: Regular audits and compliance checks ensure adherence to data protection laws, reducing legal risks and enhancing customer trust. Compliance measures also demonstrate commitment to ethical business practices.
8. Sustainable Growth:
- Scalability: Cloud-based solutions offer scalable infrastructure, allowing businesses to grow without significant capital investments. This ensures optimal performance during peak periods and supports seamless scalability.
- Market Expansion: Digital marketing strategies and online platforms provide opportunities for global reach, supporting business expansion into new markets. This strategic growth approach is facilitated by digital transformation.
9. Improved Supply Chain Management:
- Visibility and Traceability: IoT sensors and blockchain technology enhance visibility into the supply chain, allowing real-time tracking of goods and minimizing delays. This transparency ensures efficient supply chain management.
- Predictive Analytics: Anticipating demand fluctuations through predictive analytics optimizes inventory levels, reducing holding costs and improving overall supply chain efficiency. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions.
10. Customer-Centric Innovation:
- Feedback Loops: Continuous feedback loops, facilitated by digital channels, foster a customer-centric approach by addressing pain points and enhancing features based on real-time insights. This iterative improvement aligns products and services with evolving customer expectations.
- Rapid Prototyping: Agile development methodologies enable rapid prototyping and iterative improvements, ensuring that products and services align with evolving customer expectations. This iterative approach fosters customer satisfaction through continuous enhancements.
11- Competitive Advantage:
- Strategic implementation of digital transformation provides a competitive advantage by aligning business processes with evolving market trends, enhancing customer satisfaction, and fostering a culture of innovation. Organizations embracing digital transformation gain a strategic edge in a rapidly changing business landscape.
How to Develop a Digital Transformation Strategy Roadmap
Building a roadmap is a critical component of ensuring the success of your digital transformation strategy. This comprehensive guide breaks down the process into 10 actionable steps, guiding you from vision to execution. Let’s dive into the key elements that make up an effective digital transformation strategy roadmap.
10 Steps to Develop and Plan Digital Transformation Strategy Roadmap:
Step 1: Assess the Current State and Identify Gaps
Conducting a comprehensive assessment of the current digital landscape is a critical and foundational step in the digital transformation journey. At Digital Leadership, we understand the paramount importance of a comprehensive and strategic approach to digital transformation. Our Blueprint Innovation services are designed to guide organizations through a transformative journey, ensuring that every step is informed by a deep understanding of the current state, identified gaps, and a visionary roadmap for the future.
This thorough examination involves a meticulous analysis of various facets, including:
- Existing Technologies:
- Evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of current systems.
- Examine digital tools and platforms in use, assessing integration capabilities.
- Align current technologies with organizational objectives outlined in the Digital Transformation Strategy.
- Operational Processes:
- Scrutinize workflows, communication channels, and collaboration mechanisms.
- Identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas ripe for optimization.
- Understand the human element in the context of technology usage.
- Organizational Culture:
- Assess adaptability to change and openness to embracing digital innovations.
- Recognize the role of cultural aspects in determining readiness for change.
The assessment aims to provide a nuanced understanding of the organization’s:
- Strengths:
- Identify areas where current technologies and processes are effective.
- Recognize aspects of the organizational culture that support digital transformation.
- Weaknesses:
- Highlight areas where improvements are needed in technologies and processes.
- Assess cultural aspects that may pose challenges to the digital transformation journey.
- Opportunities:
- Explore possibilities for leveraging existing strengths.
- Identify areas where technology, process, or cultural enhancements can yield positive outcomes.
- Threats:
- Recognize challenges that may impede the successful execution of digital transformation.
- Assess risks associated with technology, process, or cultural factors.
The identification of gaps becomes the linchpin of strategic planning, serving as focal points for targeted interventions, including:
- Technology Upgrades:
- Address disparities in existing technologies to align with strategic goals.
- Process Optimizations:
- Streamline workflows, eliminate redundancies, and enhance operational efficiency.
- Cultural Shifts:
- Implement strategies to foster an organizational culture conducive to digital innovation.
The Organizational Culture Canvas Model is instrumental in digital transformation strategy success, offering a structured framework to shape and optimize culture. Its importance lies in aligning culture with digital goals, identified through a comprehensive assessment. This process identifies strengths and areas for improvement, fostering a positive and adaptive environment. The canvas promotes high employee engagement, crucial for effective digital adoption, and encourages innovation. You can download it now.
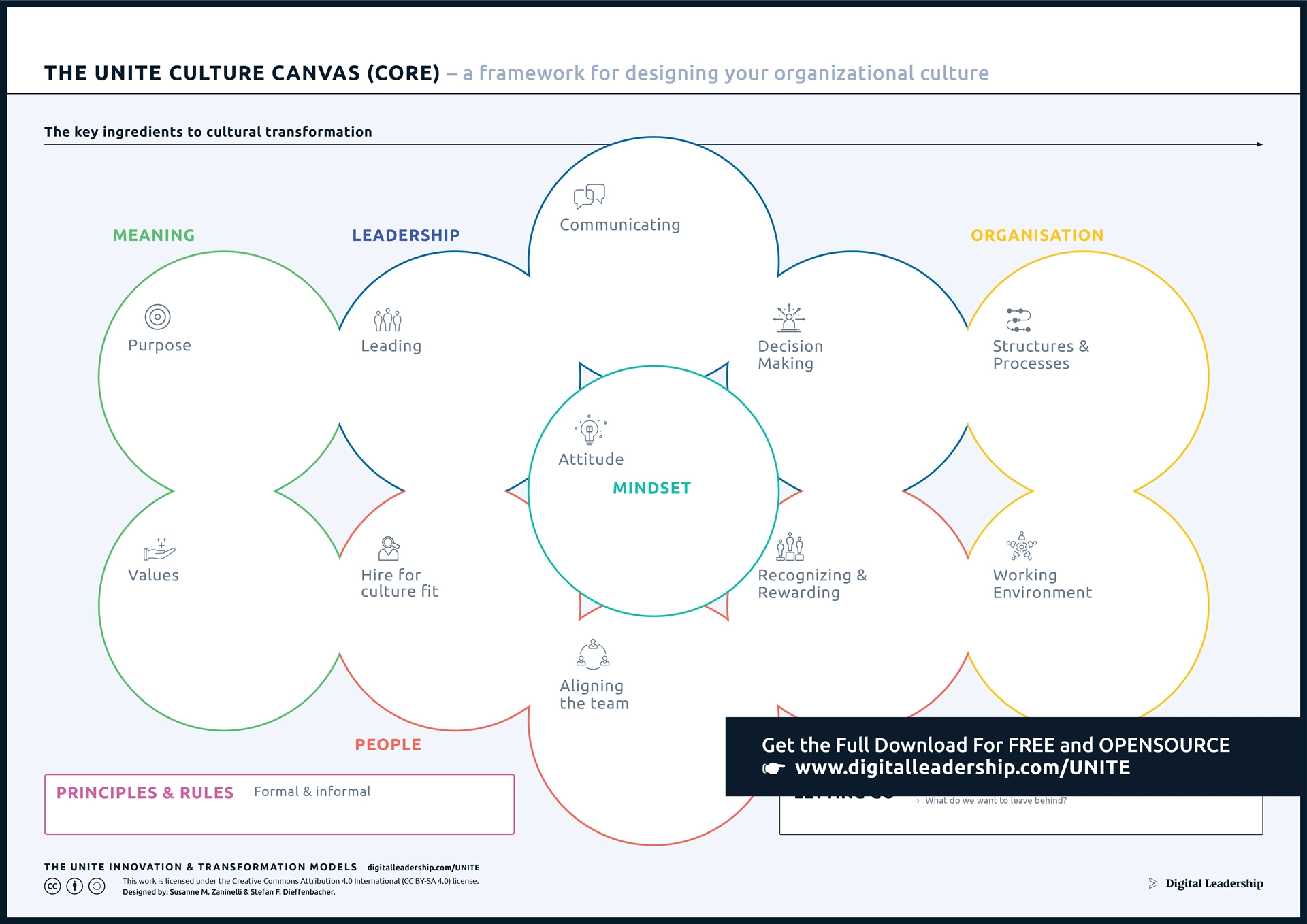
Designed by: Susanne M.Zaninelli & Stefan F.Dieffenbacher
This strategic approach ensures that the subsequent stages of the digital transformation roadmap directly address the areas where transformational efforts are most needed, maximizing impact and fostering a seamless transition toward the desired future state.
Step 2: Define Your Vision and Objectives
Defining a clear vision and objectives is not a static task; it is a dynamic process that shapes and is shaped by the evolving digital landscape. The adaptability embedded in this step allows organizations to stay attuned to emerging opportunities, fostering a transformative journey that remains purpose-driven and aligned with strategic goals. As stakeholders collectively commit to the articulated vision, the organization sets sail on a unified and purposeful digital transformation expedition.
- Strategic Collaboration with Key Stakeholders:
- Engage in collaborative efforts with key stakeholders to meticulously define a clear and compelling vision and objectives.
- This step transcends mere formality; it is a strategic imperative.
- Vision as the Guiding Light:
- Craft an articulated vision that serves as the organization’s guiding light.
- This vision provides a shared sense of purpose and direction, reaching beyond the digital realm.
- SMART Objectives for Strategic Milestones:
- Formulate SMART objectives—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- These objectives act as strategic milestones, guiding decision-making and meticulously measuring progress.
- Touchstones for Decision-Making:
- As the organization progresses, these objectives become touchstones for decision-making.
- They ensure unwavering alignment with the overarching purpose outlined in the Digital Transformation Strategy.
- Precision in Resource Allocation:
- Guide resource allocation with precision and efficacy based on the defined objectives.
- Inclusivity of stakeholder perspectives fosters a sense of ownership and commitment.
- Fostering Unity in Transformation:
- Stakeholder involvement lays the groundwork for a unified and cohesive transformation effort.
- The dynamic and iterative nature of the process allows for adjustments to maintain relevance.
- Adaptability to Emerging Opportunities:
- Embrace the adaptability highlighted in the Digital Transformation Strategy.
- This flexibility allows for adjustments to seize emerging opportunities and overcome challenges.
- Seamless Integration with Broader Strategy:
- Seamlessly integrate the articulated vision and objectives into the broader Digital Transformation Strategy.
- This integration ensures that every facet of the organization resonates with the defined business purpose and ambitious goals.
Step 3: Engage Stakeholders
Digital transformation is a collaborative endeavour that necessitates active involvement from all key stakeholders. This step involves ongoing processes to cultivate shared ownership and commitment to the transformative journey.
- Representation Across Departments:
- Involving stakeholders from diverse departments, including leadership, middle management, and front-line employees, ensures a comprehensive perspective on organizational challenges, opportunities, and aspirations.
- Open Communication Platforms:
- Platforms such as town hall meetings, workshops, and collaborative sessions create opportunities for stakeholders to express views, share concerns, and contribute ideas. This inclusive approach gathers valuable insights and instils a sense of transparency.
- Alignment of Goals:
- Effective engagement works towards aligning digital transformation objectives with broader organizational goals. This alignment is crucial for creating a unified approach where every stakeholder understands their role in achieving shared objectives.
- Collaborative Decision-Making:
- Stakeholder involvement extends beyond providing input; it includes active participation in decision-making processes. Valuing stakeholders’ input strengthens commitment and enhances organizational agility in responding to challenges and opportunities.
- Education and Awareness:
- The engagement process serves as a platform for education and awareness. As digital transformation often introduces new technologies and ways of working, ensuring stakeholders understand the ‘why’ and ‘how’ behind these changes is crucial for building confidence and buy-in.
By incorporating stakeholder engagement into the digital transformation roadmap, organizations establish a foundation for a collective and united effort. This collaborative spirit propels the organization forward and creates resilience for navigating the complexities of the digital landscape.
Step 4: Prioritize Initiatives
In the intricate landscape of digital transformation, the prioritization of initiatives is a pivotal step that demands a judicious balance between impact and feasibility. The recognition that not all initiatives can be addressed simultaneously underscores the importance of strategic prioritization, aiming to optimize resources and maximize outcomes.
The prioritization process involves a comprehensive evaluation of potential initiatives based on their potential impact on the organization’s objectives and their feasibility in the current context. Impact, in this context, refers to the extent to which an initiative aligns with the overarching goals of the digital transformation strategy and its potential to yield tangible benefits.
Feasibility, on the other hand, considers the practical aspects of implementation, taking into account factors such as technological readiness, resource availability, and organizational preparedness. Striking the right balance between impact and feasibility ensures that selected initiatives are not only aligned with the strategic vision but are also realistically attainable within the organization’s current capabilities.
An effective strategy in the prioritization process is the identification of quick wins—initiatives that can be implemented with relative ease and speed, showcasing immediate success. These quick wins serve as powerful catalysts, demonstrating the tangible benefits of the digital transformation journey to key stakeholders.
By delivering visible and early successes, quick wins play a crucial role in building momentum and confidence within the organization. They serve as compelling evidence of the positive outcomes achievable through digital transformation, motivating teams and leadership to stay committed to the broader and more complex initiatives on the roadmap.
Furthermore, prioritization is an iterative process that acknowledges the evolving nature of digital transformation. As the organization progresses, priorities may need to be reassessed based on emerging trends, technological advancements, and shifting organizational dynamics. Flexibility in prioritization ensures that the digital transformation strategy remains agile and adaptive, ready to respond to the dynamic nature of the digital landscape.
Step 5: Develop a Detailed Action Plan
Embarking on a digital transformation journey requires a meticulous and well-defined action plan to translate strategic priorities into actionable steps. This phase involves breaking down overarching objectives into granular tasks, setting realistic timelines, assigning responsibilities, and understanding interdependencies.
- Precise Task Definition: The first aspect involves defining tasks with precision, leaving no room for ambiguity. This clarity ensures that everyone involved comprehends their roles and responsibilities, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Realistic Timelines: Time is a critical factor, and the action plan sets achievable timelines for each task. Balancing ambition with practicality, these timelines guide the pace of execution and allow for regular evaluations to ensure the journey stays on course.
- Ownership and Responsibility: Assigning responsibilities is crucial for success. The action plan designates tasks to individuals or teams, fostering a sense of accountability and ensuring dedicated champions for each aspect of the transformation.
- Understanding Interdependencies: Tasks within a digital transformation often have interconnected relationships. The action plan delineates these interdependencies, providing a holistic view of how different elements influence one another. This understanding is vital for seamless execution and avoiding bottlenecks.
- Contingency Measures: Acknowledging the dynamic nature of digital transformation, the action plan incorporates contingency measures. It outlines strategies for mitigating risks and addressing unforeseen circumstances, enhancing the plan’s resilience.
- Alignment with Strategy: Every task within the action plan is aligned with the broader business strategy. This alignment ensures that each step contributes meaningfully to the overarching vision and goals of the digital transformation, fostering a cohesive and purposeful journey.
- Communication and Monitoring: Communication is pivotal throughout the execution phase. The action plan includes a communication strategy to keep stakeholders informed. Regular monitoring and evaluation mechanisms are integrated to provide real-time insights, allowing for adjustments and adaptations as needed.
Step 6: Align with Business Strategy
The success of a digital transformation hinges on its seamless integration with the broader business strategy. This step ensures that the digital transformation roadmap is not a standalone initiative but a strategic enabler of the organization’s overarching goals.
- Complementary Objectives: The digital transformation roadmap should be intricately woven into the fabric of the broader business strategy, sharing common objectives and outcomes. It’s not merely an independent venture but a synchronized effort that amplifies the impact of both.
- Strategic Contribution: Each element of the digital transformation should contribute meaningfully to the long-term success of the organization. This alignment guarantees that resources, efforts, and innovations driven by digital transformation directly support the strategic direction of the business.
- Holistic Integration: Integration goes beyond avoiding conflicts; it’s about creating synergies. The digital transformation roadmap should seamlessly integrate with existing business processes, technologies, and structures, fostering a cohesive and harmonized operational environment.
- Flexibility for Adaptation: While alignment is crucial, the digital transformation roadmap should also exhibit the flexibility to adapt to changes in the business landscape. This adaptability ensures that the organization can pivot when needed without compromising the overall strategic vision.
- Measurable Impact: The impact of digital initiatives should be measurable in the context of broader business goals. Key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with the business strategy provide a tangible way to gauge the success and contribution of the digital transformation.
- Continuous Assessment: Alignment is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Regular assessments and evaluations are integrated into the roadmap, allowing for adjustments based on the evolving needs of the business and the dynamic digital landscape.
- Stakeholder Involvement: In ensuring alignment, stakeholders from various levels of the organization are engaged. Their insights and perspectives contribute to a holistic understanding of how digital transformation aligns with and enhances the overall business strategy.
In essence, aligning the digital transformation roadmap with the business strategy is the linchpin that ensures that the journey is purposeful, and impactful, and contributes significantly to the sustained success of the organization.
Step 7: Invest in the Right Technologies
Strategic investment in technologies is a pivotal aspect of a successful digital transformation. This step involves identifying, evaluating, and adopting technologies that align seamlessly with the defined digital transformation objectives, propelling the organization into a realm of innovation and competitiveness.
- Strategic Alignment: The selection of technologies is not arbitrary but a strategic decision grounded in the alignment with the digital transformation objectives. Each chosen technology should contribute directly to the realization of specific business goals outlined in the roadmap.
- Objective-driven Adoption: The adoption of technologies is purposeful, driven by the need to enhance operational efficiency, customer experience, or other targeted outcomes. Whether it’s Artificial Intelligence (AI) for data analysis, the Internet of Things (IoT) for connectivity, or cloud computing for scalability, each technology serves a defined business purpose.
- Innovation Catalyst: The right technologies act as catalysts for innovation within the organization. They enable the exploration of digital business models, streamlined processes, and enhanced products or services. The investment is not just in tools but in the potential for transformative change.
- Competitive Edge: The selected technologies should position the organization competitively within its industry. Whether it’s gaining a speed advantage, improving quality, or offering unique features to customers, the right technologies contribute to a sustainable competitive edge.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The chosen technologies should have the scalability to grow with the organization’s evolving needs. Additionally, they should offer flexibility to adapt to changes in the business environment, ensuring that the technology stack remains relevant over time.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with existing systems and processes is crucial. The investment in technologies should not create silos but should enhance the overall ecosystem, creating a unified and efficient digital infrastructure.
- Return on Investment (ROI): The decision to invest is measured not just in terms of immediate benefits but with a keen eye on long-term returns. Organizations should assess the potential ROI of each technology investment, considering both quantitative and qualitative factors.
- Continuous Evaluation: The landscape of digital technologies is dynamic. Continuous evaluation of emerging technologies is integrated into the digital transformation strategy, allowing for the timely adoption of innovations that can further elevate the organization’s capabilities.
Step 8: Build Agile and Adaptive Teams
Creating agile and adaptive teams is a fundamental pillar in the edifice of successful digital transformation. This step involves fostering a culture within the organization that embraces agility, adaptability, continuous learning, and improvement.
- Agile Culture Cultivation: Building agile teams starts with cultivating a culture that values flexibility and responsiveness. This involves encouraging team members to embrace change positively, view challenges as opportunities, and remain open to adapting strategies based on evolving circumstances.
- Agile Methodologies Adoption: Embracing agile methodologies is crucial for enhancing the organization’s ability to respond efficiently to changes in the digital landscape. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, facilitate iterative development, allowing teams to deliver value incrementally and adapt their approach based on feedback.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Agile and adaptive teams thrive on cross-functional collaboration. Breaking down silos and promoting collaboration among different departments or teams fosters a holistic understanding of the digital transformation goals and ensures that diverse perspectives contribute to innovative solutions.
- Continuous Learning: A culture of continuous learning is essential for staying abreast of the latest technologies, methodologies, and market trends. Providing learning opportunities, training programs, and resources empowers team members to enhance their skills and contribute more effectively to the digital transformation journey.
- Innovation Encouragement: Agile teams are more likely to innovate and experiment with new ideas generation. Creating an environment that encourages innovation, where team members feel empowered to propose and test novel solutions, is crucial for driving digital transformation success.
- Adaptability as a Core Competency: The ability to adapt is elevated to a core competency within agile teams. Team members are encouraged to be proactive in identifying changes, learning from experiences, and adjusting strategies accordingly. This adaptability ensures resilience in the face of uncertainties.
- Leadership Support: Leadership plays a pivotal role in building agile and adaptive teams. Providing support, guidance, and resources for teams to embrace agility requires leadership commitment. Leaders should exemplify the values of agility and foster an environment where teams feel safe to experiment and learn.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing feedback mechanisms is integral to agile teams. Regular retrospectives, feedback loops, and transparent communication channels ensure that teams continuously reflect on their processes, identify areas for improvement, and make adjustments to enhance performance.
- Scalability Considerations: As the organization grows, scalability becomes a consideration. Agile frameworks should be scalable to accommodate larger teams and complex projects while maintaining the principles of flexibility and adaptability.
Step 9: Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The establishment of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) stands as a pivotal step in the digital transformation journey, providing organizations with a compass to navigate the effectiveness of their initiatives. This step involves defining measurable KPIs that serve as barometers for progress and success.
- KPI Definition: The first aspect of this step is to clearly define the KPIs relevant to the digital transformation objectives. These indicators should align with the overarching business goals and the specific outcomes expected from the transformation journey. A well-defined set of KPIs ensures that organizations are measuring what truly matters in the context of their unique transformation goals.
- Measurability and Tangibility: KPIs should be inherently measurable and tangible, allowing for quantifiable assessment. Whether it’s enhancing operational efficiency, improving customer satisfaction, or achieving cost reductions, each KPI should have a clear metric associated with it. This ensures that progress can be tracked objectively, providing valuable insights into the impact of digital transformation efforts.
- Alignment with Strategy: The selected KPIs should align seamlessly with the digital transformation strategy. Each indicator should reflect a specific aspect of the strategy, whether it’s related to process optimization, customer experience enhancement, or innovation metrics. This alignment ensures that KPIs become meaningful tools for assessing progress in the context of strategic goals.
- Real-Time Monitoring: The digital landscape evolves rapidly, and real-time monitoring of KPIs is essential. Establishing mechanisms for continuous monitoring allows organizations to stay agile and make informed decisions promptly. Real-time insights enable proactive adjustments to strategies, ensuring that organizations remain on course even in dynamic environments.
- Adaptability of KPIs: Digital transformation is a dynamic process, and KPIs should be adaptable to changing circumstances. Organizations should be prepared to revisit and adjust KPIs based on evolving business priorities, technological advancements, and market shifts. This adaptability ensures that KPIs remain relevant and reflective of the organization’s evolving objectives.
- Cross-functional involvement: Involving key stakeholders from various departments in the KPI definition process enhances alignment and ownership. Cross-functional perspectives contribute to a comprehensive set of indicators that capture the holistic impact of digital transformation across the organization. This involvement fosters a shared understanding of how each department contributes to the overall success of the strategy.
- Balanced Scorecard Approach: Adopting a balanced scorecard approach ensures a well-rounded assessment. Instead of focusing solely on financial metrics, consider a mix of indicators that cover financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth perspectives. This comprehensive approach provides a nuanced view of the organization’s performance in the digital transformation landscape.
- Continuous Improvement: KPIs should not be static but subject to continuous improvement. Regularly assess the relevance and effectiveness of selected indicators. Solicit feedback from stakeholders, evaluate the correlation between KPIs and business outcomes, and be willing to refine or introduce new indicators as needed.
- Transparency and Communication: Establish transparent communication channels regarding KPIs. Regularly share updates with relevant stakeholders, fostering a culture of accountability and collaboration. Transparent communication ensures that everyone is informed about progress, challenges, and the collective impact of their efforts.
Step 10: Monitor, Evaluate, and Iterate
The final step in the digital transformation roadmap is a dynamic and iterative process that involves continuous monitoring, thorough evaluation, and a readiness to iterate based on insights gained. This ongoing cycle is crucial for ensuring the long-term success and relevance of the digital transformation strategy.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuous monitoring involves the real-time tracking of key performance indicators (KPIs), project milestones, and other relevant metrics. This proactive approach allows organizations to identify emerging trends, address potential issues promptly, and make informed decisions on the fly. Continuous monitoring serves as a radar system, providing early detection of shifts in the digital landscape and enabling organizations to respond swiftly.
- Progress Assessment: Regularly assessing the progress of digital transformation initiatives is essential. This involves comparing actual outcomes against predefined objectives and KPIs. Analyzing the data provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of the strategy, revealing areas of success and identifying aspects that may require adjustment. Progress assessments serve as checkpoints, offering a comprehensive view of the journey’s advancement.
- Gathering Stakeholder Feedback: In addition to quantitative data, gathering qualitative feedback from key stakeholders is integral to the evaluation process. This feedback provides nuanced insights into the human and organizational aspects of the transformation. Stakeholder perspectives offer a holistic understanding of how the initiatives impact different facets of the organization, contributing to a well-rounded evaluation.
- Iterative Approach: The digital landscape is dynamic, and strategies must evolve accordingly. An iterative approach involves revisiting the digital transformation roadmap based on insights gained from monitoring and evaluation. This may entail refining existing strategies, introducing new initiatives, or adjusting the prioritization of activities. An iterative mindset acknowledges that digital transformation is not a one-time event but an ongoing, adaptive process.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Organizations must embrace flexibility and adaptability during the monitoring and iteration phase. The ability to pivot in response to changing circumstances, emerging technologies, or shifts in market dynamics is a key factor in sustaining the effectiveness of the digital transformation strategy. Flexibility allows organizations to capitalize on new opportunities and navigate challenges effectively.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: The monitoring and evaluation process should be driven by data. Data analytics and insights gleaned from the performance metrics and feedback mechanisms guide decision-making. This data-driven approach ensures that adjustments to the roadmap are rooted in empirical evidence, enhancing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
- Communication and Transparency: Transparent communication regarding the results of the monitoring and evaluation process is essential. Sharing both successes and challenges with stakeholders fosters a culture of openness and collaboration. Transparent communication builds trust and reinforces the collective commitment to the digital transformation journey.
- Learning and Continuous Improvement: Each iteration should be viewed as an opportunity for learning and continuous improvement. Organizations should capture lessons learned, document successful strategies, and apply insights to enhance future initiatives. The learning process is intrinsic to the adaptive nature of digital transformation.
Digital Transformation Strategy Examples
1. IT Digital Transformation Strategy
Organizations often embark on digital transformation journeys to enhance operational efficiency, cybersecurity, and user experiences. This strategic evolution aligns with comprehensive IT strategic planning, ensuring that technological advancements are integrated seamlessly into the organization’s broader objectives and goals.
Key Components of IT Digital Transformation Strategy
- Cloud Adoption:
Organizations strategically migrate on-premise infrastructure to cloud platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure, to achieve scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency.
Hybrid Cloud Models: Implementation of hybrid cloud models allows for a balanced approach, retaining certain on-premise elements while leveraging the benefits of cloud infrastructure.
- Cybersecurity Integration:
Advanced Threat Intelligence: Incorporation of advanced threat intelligence solutions to proactively identify and mitigate potential cybersecurity threats.
Encryption Protocols: Implementation of robust encryption protocols ensures the security and integrity of sensitive data, safeguarding against cyber threats and unauthorized access.
- Agile Methodologies:
DevOps Implementation: Adoption of DevOps practices and principles to integrate organizational development and operations seamlessly, leading to faster and more reliable software delivery.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Implementation of CI/CD pipelines ensures the rapid and automated deployment of software updates, reducing time-to-market.
- Data Analytics:
Actionable Insights: Utilization of big data analytics tools to derive actionable insights from vast datasets, enabling informed decision-making.
Predictive Analytics: Implementation of predictive analytics models to forecast trends, optimize IT resources, and proactively address potential issues.
Case Study:
A multinational IT corporation underwent a digital transformation by transitioning its traditional IT infrastructure to a cloud-native architecture. This shift improved agility, reduced costs, and enabled seamless scalability to meet evolving business demands. The implementation of advanced threat intelligence and encryption protocols ensured the heightened cybersecurity posture of the organization, fostering a secure IT environment.
2. HR Digital Transformation Strategy
The Human Resources (HR) function plays a pivotal role in organizational success, and digital transformation strategies are reshaping how HR operates. This evolution focuses on optimizing talent management, improving employee experiences, and enhancing overall HR processes.
Key Components of HR Digital Transformation Strategy:
- Employee Self-Service Portals:
Description: The implementation of user-friendly portals empowers employees to manage various tasks independently, such as leave requests, performance reviews, and benefits management.
Benefits: Streamlined processes, increased transparency, and improved employee satisfaction through self-service capabilities.
- Data-Driven HR:
Description: Utilizing HR analytics for workforce planning, talent acquisition, and employee engagement. Data-driven insights enable informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Benefits: Improved decision accuracy, enhanced workforce planning, and a deeper understanding of employee needs and preferences.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
Description: Automation of routine HR tasks, such as data entry and paperwork processing, to improve efficiency, accuracy, and free up HR professionals for more strategic activities.
Benefits: Increased operational efficiency, reduced errors, and time savings for HR teams.
- Learning Management Systems:
Description: Integration of digital platforms for employee training and development, offering a centralized hub for learning resources, courses, and skill development.
Benefits: Enhanced employee skills, improved training accessibility, and a culture of continuous learning within the organization.
Case Study:
A global company transformed its HR processes by implementing a comprehensive Human Resources Information System (HRIS). This centralized system streamlined recruitment processes, improved employee engagement through data-driven insights, and facilitated strategic HR decision-making. The HRIS also enabled the organization to adapt to changing workforce dynamics efficiently.
Digital transformation in HR goes beyond technology implementation; it’s about creating an agile and employee-centric HR function that aligns with the organization’s overall goals. As businesses recognize the strategic importance of their workforce, HR digital transformation becomes a critical enabler for attracting, developing, and retaining top talent in the digital age.
3. Bank Digital Transformation Strategy
Banking institutions are leading the charge in digital transformation, leveraging technology to enhance customer experiences, strengthen security measures, and optimize financial processes. Here are key components of their digital transformation strategies:
Key Components of Bank Digital Transformation Strategy:
- Digital Banking Platforms:
- Introducing user-friendly mobile and online banking interfaces that provide customers with convenient and seamless access to banking services.
- Benefits: Improved customer convenience, enhanced accessibility, and increased engagement through digital channels.
- Blockchain Integration:
- Description: Utilization of blockchain technology to ensure secure, transparent, and tamper-proof financial transactions. Blockchain enhances trust and reduces the risk of fraud.
- Benefits: Increased security, transparency, and efficiency in financial transactions, leading to greater customer trust.
- AI-Powered Customer Service:
- Implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) through chatbots and virtual assistants to provide personalized and efficient customer interactions. AI-driven solutions enhance customer support and streamline query resolution.
- Benefits: Improved customer service, 24/7 availability, and personalized interactions, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
- Risk Management Solutions:
- Adoption of advanced analytics tools to assess and mitigate financial risks. Predictive analytics and machine learning contribute to more accurate risk assessments.
- Benefits: Enhanced risk management, proactive identification of potential issues, and improved decision-making.
Case Study:
A leading bank embraced digital transformation by introducing a mobile banking app equipped with features such as biometric authentication, real-time transaction alerts, and AI-driven financial insights. This strategy resulted in a significant increase in customer satisfaction and engagement. The mobile app not only provided customers with convenient access to their accounts but also personalized financial guidance based on their transaction history and preferences.
The banking sector’s digital transformation journey is a response to the evolving expectations of customers and the need for greater efficiency. By embracing cutting-edge technologies, banks aim to stay competitive, build customer trust, and create innovative financial solutions for the digital age.
Strategy for Digital Transformation Types
(1) Cultural Transformation
Cultural digital transformation is a specialized aspect of a broader digital transformation strategy, focusing specifically on reshaping the cultural fabric of an organization to thrive in the digital age. This strategy recognizes that cultural change is not just a byproduct but a critical driver of successful digital transformations. Here’s a comprehensive guide to crafting a digital transformation strategy for cultural change:
1. Leadership Commitment:
- Ensure top-level executives are committed to driving cultural change.
- Actions:
- Communicate the importance of cultural transformation.
- Lead by example in embracing digital practices.
- Allocate resources for cultural initiatives.
2. Vision and Values:
- Define a clear vision and values that align with digital transformation goals.
- Actions:
- Articulate a compelling vision for the digital future.
- Establish values that promote innovation and adaptability.
3. Communication Strategy:
- Foster a culture of open communication and transparency.
- Actions:
- Regularly communicate the rationale behind digital initiatives.
- Encourage feedback and two-way communication channels.
- Use various platforms for consistent messaging.
4. Employee Involvement:
- Engage employees at all levels in the transformation process.
- Actions:
- Create cross-functional teams for collaborative projects.
- Solicit input and ideas from employees.
- Implement employee-driven innovation programs.
5. Training and Development:
- Equip employees with the necessary skills for the digital era.
- Actions:
- Provide ongoing training on digital tools and technologies.
- Offer upskilling programs tailored to individual roles.
- Foster a culture of continuous learning.
6. Recognition and Rewards:
- Reinforce desired behaviours through recognition and rewards.
- Actions:
- Establish a system for acknowledging digital contributions.
- Link recognition to adherence to digital values.
- Celebrate milestones and successes.
7. Agile Mindset:
- Instil an agile mindset to embrace change and experimentation.
- Actions:
- Implement agile methodologies in project management.
- Encourage risk-taking and learning from failures.
- Foster a flexible and adaptive work environment.
8. Metrics and Measurement:
- Define metrics to measure cultural transformation progress.
- Actions:
- Develop key performance indicators (KPIs) related to cultural change.
- Regularly assess employee sentiment and engagement.
- Use data to refine and adjust cultural initiatives.
9. Collaboration and Cross-Functional Teams:
- Break down silos and promote collaboration across departments.
- Actions:
- Establish cross-functional teams for digital projects.
- Encourage inter-departmental collaboration.
- Create a culture of knowledge-sharing.
- Effectively manage the transitions associated with cultural change.
- Actions:
- Communicate the benefits of cultural change.
- Provide resources and support for employees adapting to change.
- Address resistance through a structured change management process.
(2) Process Transformation
Process digital transformation involves reimagining and optimizing existing business processes through the strategic integration of digital technologies. Here’s a detailed exploration of the digital transformation strategy for process digital transformation:
1. Assessment and Identification:
- Evaluate the current state of existing processes, identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
- Actions:
- Conduct a comprehensive audit of existing processes.
- Identify pain points and areas with the potential for automation.
- Gather feedback from stakeholders involved in each process.
2. Define Clear Objectives:
- Clearly outline the objectives of the process of digital transformation, aligning them with overall business goals.
- Actions:
- Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives.
- Ensure alignment with the organization’s broader digital transformation strategy.
3. Technology Integration:
- Identify and integrate relevant digital technologies to streamline and enhance existing processes.
- Actions:
- Assess emerging technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), and workflow automation.
- Select technologies that align with the organization’s goals and the specific requirements of each process.
4. Process Redesign and Optimization:
- Rethink and redesign business processes to leverage the capabilities of digital technologies.
- Actions:
- Collaborate with process owners and stakeholders to redesign workflows.
- Eliminate redundant steps and automate repetitive tasks where applicable.
- Ensure that the redesigned processes align with industry best practices.
5. Employee Training and Change Management:
- Equip employees with the skills needed to navigate and contribute to the transformed processes.
- Actions:
- Provide training on new technologies and tools.
- Communicate the benefits of the changes to employees.
- Establish a change management plan to address potential resistance.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement:
- Implement mechanisms for ongoing monitoring and refinement of the transformed processes.
- Actions:
- Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the transformed processes.
- Regularly assess performance against KPIs and gather feedback.
- Iteratively improve processes based on insights and changing business requirements.
7. Integration with Organizational Culture:
- Ensure that the transformed processes align with the organization’s culture and values.
- Actions:
- Communicate how the changes contribute to the overall digital transformation journey.
- Foster a culture that embraces continuous improvement and innovation in processes.
8. Stakeholder Collaboration:
- Involve key stakeholders in the process digital transformation journey.
- Actions:
- Collaborate with process owners, IT teams, and end-users throughout the transformation.
- Solicit feedback and insights from stakeholders to inform the transformation process.
9. Data Security and Privacy:
- Integrate robust security measures to protect sensitive data throughout the transformed processes.
- Actions:
- Implement encryption and access controls where necessary.
- Ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
10. Scalability and Flexibility:
- Design processes with scalability and flexibility in mind to accommodate future changes and growth.
- Actions:
- Choose technologies and solutions that can scale with the organization.
- Build processes that can adapt to evolving business requirements.
Process digital transformation, when strategically planned and executed, not only optimizes efficiency but also positions the organization for sustained growth and competitiveness in the digital age. This comprehensive strategy ensures that each step contributes to the overarching goals of the organization’s digital transformation journey.
(3) Business Model Transformation
Business model digital transformation involves a strategic overhaul of the fundamental structures and processes that define how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value. Here are key components of the strategy for business model digital transformation:
- Assessment of Current Business Model:
Before embarking on transformation, conduct a thorough analysis of the existing business model. Identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Understand current revenue streams, customer segments, and value propositions.
Before embarking on transformation, conduct a thorough analysis of the existing business model. Identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Understand current revenue streams, customer segments, and value propositions. The Business Model Canvas, a widely acclaimed strategic management tool, serves as an invaluable asset in this assessment. By visually representing key elements such as customer relationships, revenue streams, and cost structures, the canvas provides a holistic view of the current state of the business. It not only facilitates a comprehensive understanding but also fosters collaborative discussions within the organization, ensuring that every aspect is thoroughly examined and considered. You can download it now.
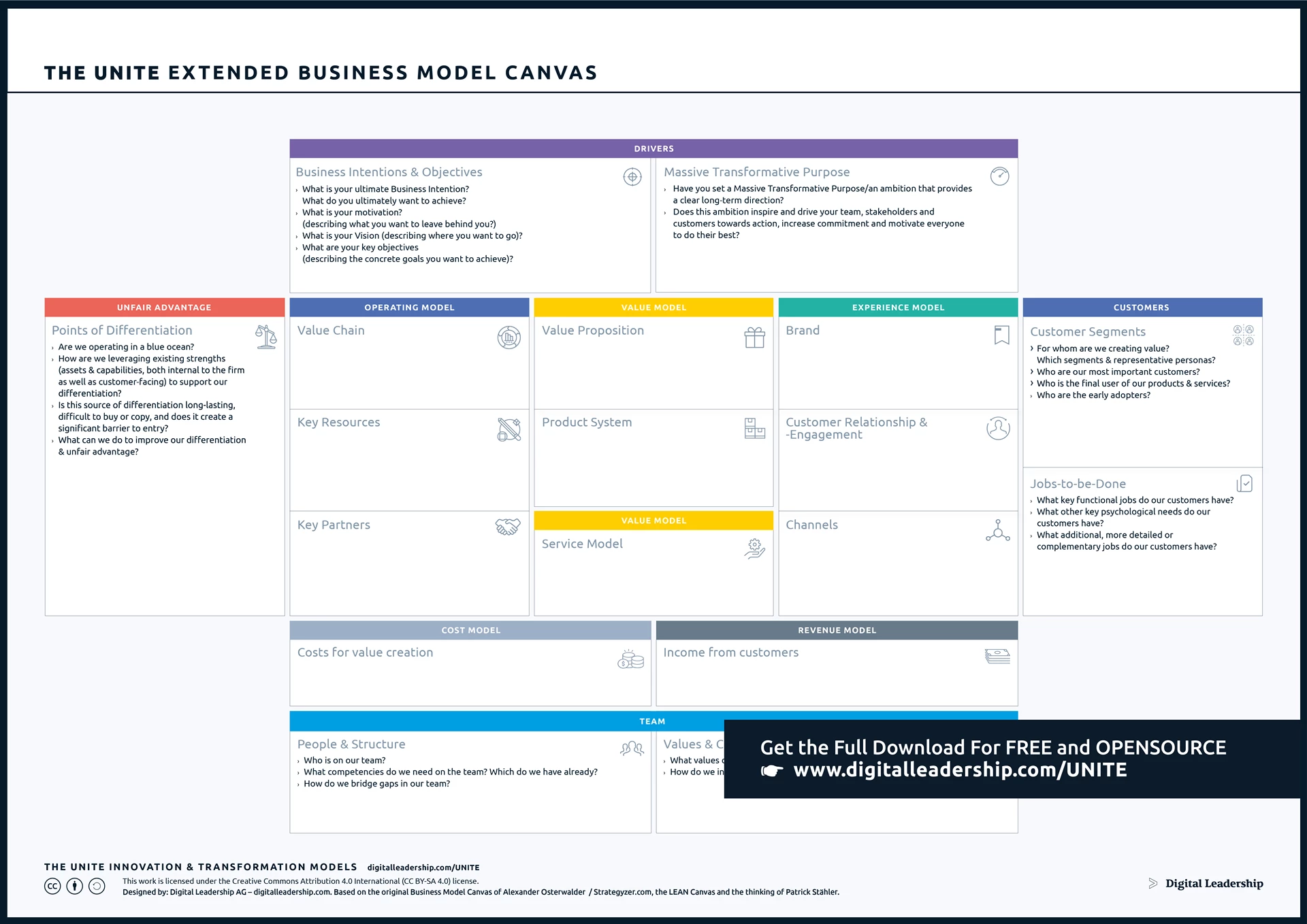
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the work of Alexander Osterwalder, the Lean Canvas and the thinking of Patrick Stahler
Utilizing the Business Model Canvas in this phase is crucial for capturing a detailed snapshot of the business landscape. Its visual nature allows stakeholders to identify interdependencies, uncover potential gaps, and recognize areas ripe for innovation. As an interactive tool, it encourages cross-functional engagement, enabling diverse perspectives to contribute to the assessment. In essence, the Business Model Canvas transforms the assessment process into a dynamic and collaborative exercise, laying a strong foundation for informed decision-making in the subsequent stages of the digital transformation journey.
- Define Clear Objectives:
Clearly articulate the objectives of the business model digital transformation. This may include expanding market reach, optimizing revenue streams, improving customer satisfaction, or fostering innovation. Objectives should align with broader organizational goals.
- Explore Innovative Revenue Streams:
Identify and explore new avenues for generating revenue. This could involve introducing new products or services, adopting subscription models, or leveraging digital platforms for additional income streams.
- Customer-Centric Approach:
Place the customer at the center of the business model transformation. Understand evolving customer needs, preferences, and behaviors. Tailor the business model to enhance the overall customer experience and satisfaction.
- Technology Integration:
Leverage digital technologies to facilitate and enhance the transformed business model. This may include incorporating AI for personalized experiences, utilizing data analytics for informed decision-making, or implementing e-commerce solutions.
- Agile and Adaptive Culture:
Cultivate an organizational culture that embraces agility and adaptability. A flexible culture enables the business to respond swiftly to changes in the market and technological landscape.
- Collaboration and Ecosystem Building:
Consider partnerships and collaborations that complement the transformed business model. Building a strong ecosystem can enhance innovation, provide access to new markets, and streamline operations.
- Risk Management:
Acknowledge and mitigate potential risks associated with the transformation. This includes addressing internal resistance, ensuring data security and compliance, and anticipating market dynamics.
- Pilot Programs and Iterative Testing:
Rather than implementing wholesale changes, consider piloting aspects of the transformed business model. Use iterative testing to gather feedback, measure outcomes, and make adjustments based on real-world results.
- Continuous Monitoring and Optimization:
Implement robust monitoring mechanisms to track the performance of the new business model. Regularly assess key performance indicators (KPIs) and be prepared to optimize strategies based on evolving market trends and organizational needs.
(4) Domain Transformation
Domain transformation within the realm of digital transformation involves reshaping and optimizing specific areas or domains within an organization to leverage digital technologies effectively. Below, we explore the strategic approach to domain digital transformation:
- Assessment and Opportunity Identification:
- Before initiating domain transformation, conduct a thorough assessment of existing processes, technologies, and challenges within the specific domain.
- Strategic Approach: Identify pain points, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement. Utilize data analytics and feedback mechanisms to gather insights.
- Strategic Vision and Alignment:
- Objective: Clearly define the vision for the transformed domain and align it with the overall organizational strategy.
- Strategic Approach: Ensure that the objectives of domain transformation contribute to the broader goals of the organization. Establish a roadmap that aligns with business priorities.
- Technology Integration:
- Objective: Identify and integrate relevant digital technologies to enhance domain operations.
- Strategic Approach: Leverage technologies such as IoT, AI, or blockchain based on the specific needs of the domain. Ensure seamless integration with existing systems to avoid disruptions.
- Cross-functional Collaboration:
- Objective: Promote collaboration among different functions and departments involved in the domain.
- Strategic Approach: Break down silos and encourage open communication. Establish cross-functional teams to ensure a holistic and integrated approach to domain transformation.
- Agile Methodologies:
- Objective: Foster agility within the domain to adapt to changing requirements and market dynamics.
- Strategic Approach: Implement agile methodologies to streamline processes, promote flexibility, and enable quick responses to evolving challenges. Encourage a culture of continuous improvement.
- Change Management:
- Objective: Address cultural shifts and ensure a smooth transition to the transformed domain.
- Strategic Approach: Develop and implement change management strategies that focus on communication, training, and stakeholder engagement. Manage resistance to change through a proactive and inclusive approach.
- Performance Metrics and Evaluation:
- Objective: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of domain transformation.
- Strategic Approach: Define measurable metrics aligned with the objectives of the transformation. Regularly assess and adjust the strategy based on performance insights.
- Scalability and Future-readiness:
- Objective: Ensure that the transformed domain is scalable and prepared for future advancements.
- Strategic Approach: Design the transformation strategy with scalability in mind. Stay informed about emerging technologies to proactively adapt the domain to future trends.
- User-Centric Design:
- Objective: Prioritize the needs and experiences of end-users within the transformed domain.
- Strategic Approach: Incorporate user-centric design principles to enhance usability and satisfaction. Gather feedback from end-users throughout the transformation process.
- Continuous Monitoring and Optimization:
- Objective: Implement continuous monitoring processes to optimize and refine the transformed domain.
- Strategic Approach: Utilize data analytics and feedback loops to monitor the performance of the domain. Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of implemented strategies and make data-driven adjustments.
6 Key Components of Digital Transformation Strategy
1. Customer Experience and Centricity
In the realm of digital transformation, putting the customer at the center of strategic initiatives is paramount. Customer experience and centricity go beyond merely offering products or services; it involves creating meaningful and seamless interactions that resonate with the customers. Here are the key components to consider:
- Understanding Customer Needs:
- Start by comprehensively understanding the needs, preferences, and pain points of your customers. Utilize data analytics, feedback mechanisms, and market research to gain insights into customer behavior.
- Personalization Strategies:
- Implement personalized experiences based on customer data. Leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to tailor products, services, and communication to individual preferences, creating a more engaging and relevant customer journey.
- Omnichannel Presence:
- Provide a consistent and integrated experience across various channels – online and offline. This includes your website, social media, physical stores, and any other touchpoints. An omnichannel approach ensures a seamless transition between different platforms.
- User-Friendly Interfaces:
- Simplify the user interface and enhance usability. Intuitive and user-friendly designs contribute to a positive customer experience. This involves optimizing website navigation, mobile app interfaces, and any other digital platforms.
- Feedback Mechanisms:
- Establish robust feedback loops to capture customer opinions and insights. Act on this feedback to continuously improve products, services, and overall customer satisfaction.
- Customer Journey Mapping:
- Map out the entire customer journey, identifying key touchpoints and moments of interaction. This visual representation helps in understanding the customer experience from awareness to post-purchase engagement.
- Real-time Responsiveness:
- Implement real-time responsiveness to customer inquiries, issues, or feedback. Rapid response times enhance customer satisfaction and contribute to a positive perception of the brand.
2. Agile Methodologies and Adaptive Culture
Agile Methodologies and Adaptive Culture are pivotal components of a robust Digital Transformation Strategy. Let’s delve into each of these components:
- Agile Methodologies:
- Agile methodologies involve an iterative and flexible approach to project management and product development. It emphasizes collaboration, adaptability, and customer feedback throughout the development process.
- Importance in Digital Transformation:
- Flexibility and Responsiveness: Agile allows organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions, customer feedback, and emerging technologies. This flexibility is crucial in the dynamic digital landscape.
- Continuous Improvement: Agile encourages a mindset of continuous improvement, with regular iterations and feedback loops. This iterative approach aligns with the evolving nature of digital technologies.
- Customer-Centric Approach: By involving customers throughout the development process, Agile ensures that the end product or service meets customer expectations and delivers value.
- Adaptive Culture:
- An adaptive culture is an organizational mindset that embraces change, values innovation, and encourages employees to be proactive and responsive in a dynamic environment.
- Importance in Digital Transformation:
- Embracing Change: Digital transformation often involves significant changes in processes, technologies, and organizational structures. An adaptive culture helps employees embrace and drive these changes rather than resist them.
- Innovation and Creativity: An adaptive culture fosters innovation by encouraging employees to explore new ideas generation, experiment with emerging technologies, and contribute to the organization’s overall growth.
- Resilience: In the face of uncertainties and challenges posed by digital disruptions, an adaptive culture instils resilience in employees. They become more adept at navigating change and finding solutions in complex situations.
3. Digital Innovation and Technology Adoption
Digital Innovation and Technology Adoption are two crucial elements that play a pivotal role in shaping the success and sustainability of any strategic initiative in digital transformation. Let’s delve into the significance of these key components and how they contribute to the overall Digital Transformation Strategy.
1- Digital Innovation:
Digital innovation is the driving force behind transformative change in organizations. It involves the exploration and application of new technologies, ideas, and processes to bring about significant improvements or entirely new ways of operating. Here’s a closer look at the key aspects of digital innovation within a Digital Transformation Strategy:
- Creativity and Ideation:
- Digital innovation starts with fostering a culture of creativity and ideation within the organization. Encouraging employees to think outside traditional boundaries and propose novel solutions is essential.
- Experimentation and Prototyping:
- Embracing a mindset of experimentation allows organizations to test new ideas and technologies in a controlled environment. Prototyping enables quick iterations and validations of concepts before full-scale implementation.
- Collaboration and Ecosystem Engagement:
- Successful digital innovation often involves collaboration with external partners, startups, or industry ecosystems. Engaging with a broader network brings diverse perspectives and accelerates the pace of innovation.
- Agile Methodologies:
- Agile methodologies play a crucial role in digital innovation, allowing organizations to adapt to changing requirements and feedback rapidly. Agile practices promote flexibility and responsiveness in the face of uncertainty.
2- Technology Adoption:
While innovation sparks new ideas, the effective adoption of technology ensures that these ideas become operational realities. Technology adoption involves integrating and leveraging the latest digital tools and solutions to enhance organizational capabilities. Here are key considerations for successful technology adoption:
- Strategic Alignment:
- Technology adoption should align with the overall strategic objectives of the organization. It’s crucial to select technologies that complement the broader vision and goals of the Digital Transformation Strategy.
- Scalability and Integration:
- Chosen technologies must be scalable to accommodate future growth and seamlessly integrate with existing systems. Compatibility with the current IT infrastructure is vital for a smooth adoption process.
- User-Centric Design:
- Prioritize technologies with a user-centric design to ensure a positive and intuitive user experience. User-friendly interfaces enhance adoption rates and contribute to the overall success of the digital transformation journey.
- Change Management and Training:
- Implementing new technologies requires effective change management strategies. Providing adequate training and support to employees ensures a smooth transition and minimizes resistance to technological changes.
4. Digital Landscape
The Digital Landscape, as a key component of a robust Digital Transformation Strategy, plays a pivotal role in shaping an organization’s approach to the rapidly evolving digital realm. This component encompasses a broad spectrum of considerations, ranging from technological advancements to market trends and competitive landscapes. Let’s delve into the intricacies of the Digital Landscape and its significance in the context of a Digital Transformation Strategy.
- Technological Innovations and Trends:
- Stay Ahead with Emerging Technologies: A comprehensive understanding of emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Internet of Things (IoT), Blockchain, and others is crucial. Organizations need to assess how these technologies can be strategically integrated to enhance operations, innovate processes, and create new value.
- Competitive Intelligence:
- Analyzing Market Dynamics: A thorough examination of the competitive landscape is imperative. This involves identifying competitors, their digital initiatives, and understanding how your organization can differentiate itself. Strategic insights into market dynamics enable informed decision-making and the formulation of competitive digital strategies.
- Regulatory Environment:
- Navigating Compliance Challenges: The digital landscape is subject to various regulations and compliance standards. Organizations must be vigilant in understanding and adhering to these regulations to mitigate risks. Building a strategy that aligns with regulatory requirements ensures a smooth and legally compliant digital transformation journey.
- Cybersecurity Considerations:
- Safeguarding Digital Assets: With the increasing reliance on digital platforms, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Integrating robust cybersecurity measures into the Digital Transformation Strategy is essential to protect sensitive data, maintain customer trust, and safeguard the organization’s digital assets.
- Data Privacy and Ethics:
- Prioritizing Ethical Practices: As organizations leverage data for insights and decision-making, ensuring data privacy and ethical considerations is non-negotiable. A sound Digital Transformation Strategy should incorporate measures to uphold data privacy, adhere to ethical practices, and build trust among stakeholders.
- Adaptability to Change:
- Embracing Agility: The digital landscape is dynamic, and characterized by rapid changes and advancements. A successful strategy acknowledges the need for organizational agility, fostering a culture that embraces change and can swiftly adapt to evolving digital trends and disruptions.
- Globalization and Market Expansion:
- Exploring Global Opportunities: Organizations aiming for digital transformation should assess global market opportunities. Understanding the nuances of operating in diverse global markets and adapting digital strategies accordingly is vital for sustained growth and competitiveness.
5. Data Curation and Privacy Protection
In digital transformation, ensuring the proper handling of data is paramount to success. Two critical components that serve as the bedrock for a robust digital transformation strategy are Data Curation and Privacy Protection.
1. Data Curation: Building a Foundation of Quality and Relevance
At the heart of any digital transformation strategy lies data—its collection, analysis, and utilization. Data curation involves the careful management, organization, and enhancement of data to ensure its quality and relevance. This process is instrumental in deriving meaningful insights, fostering innovation, and making informed decisions.
Key Steps in Data Curation:
- Data Quality Assessment: Evaluate the accuracy, consistency, and completeness of data to ensure its reliability.
- Data Organization: Establish effective data categorization and classification systems for streamlined access and analysis.
- Data Enrichment: Augment existing data with additional information to enhance its value and utility.
- Data Governance: Implement policies and procedures to regulate data usage, ensuring compliance and accountability.
A well-crafted data curation strategy not only optimizes internal processes but also lays the groundwork for advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and other transformative technologies.
2. Privacy Protection: Safeguarding Trust and Compliance
In an era where data breaches make headlines, prioritizing privacy protection is non-negotiable. Customers, employees, and stakeholders entrust organizations with their sensitive information, demanding a commitment to robust privacy measures.
Key Components of Privacy Protection:
- Compliance Frameworks: Adhere to global and regional data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) to avoid legal repercussions.
- Data Encryption: Implement encryption techniques to secure data during transmission and storage, preventing unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Restrict data access to authorized personnel, minimizing the risk of internal and external breaches.
- Transparency and Consent: Clearly communicate data practices to users, seeking explicit consent for data collection and processing.
6. Business Process Optimization
In the realm of digital transformation, Business Process Optimization stands out as a pivotal component, acting as the cornerstone for successful and impactful organizational change. This facet involves strategically refining and enhancing the various processes within an organization to harness the full potential of digital technologies. Let’s delve into the significance and strategic steps associated with Business Process Optimization in the context of a Digital Transformation Strategy:
- Strategic Assessment:
- Begin with a comprehensive assessment of the existing business processes. Identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement. This involves evaluating the current state of processes, understanding inefficiencies, and recognizing potential areas for optimization.
- Aligning with Business Objectives:
- Ensure that the optimization efforts align with the broader business objectives and goals. This alignment is crucial for directing the optimization process toward achieving tangible outcomes that contribute to the overall success of the digital transformation strategy.
- Leveraging Digital Technologies:
- Integrate cutting-edge digital technologies such as automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics into the existing processes. Identify opportunities to streamline workflows, reduce manual interventions, and enhance the overall efficiency of operations through digital innovation.
- Process Redesign and Innovation:
- Rethink traditional processes and embrace innovative approaches. Redesign workflows to capitalize on digital capabilities, fostering agility and adaptability. This step involves breaking away from legacy models and embracing a mindset of continuous improvement.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Encourage collaboration among different departments and functions. Siloed approaches can hinder optimization efforts. A holistic optimization strategy involves breaking down departmental barriers, fostering communication, and ensuring that each part of the organization contributes to the overarching goals.
- Employee Training and Empowerment:
- Equip employees with the necessary skills to navigate the optimized processes. Training programs should focus on digital literacy, promoting a culture of adaptability, and empowering employees to contribute actively to the optimization journey.
- Performance Monitoring and Adjustment:
- Implement robust performance monitoring mechanisms. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the optimized processes. Regularly assess and analyze these metrics to ensure that the optimization efforts are yielding the desired results. Be prepared to make adjustments based on real-time insights.
- Compliance and Risk Management:
- Ensure that the optimized processes comply with industry regulations and standards. Simultaneously, implement risk management strategies to address potential challenges that may arise during the optimization journey.
7. Digital Transformation KPIs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) play a pivotal role as essential components within the broader framework of a Digital Transformation Strategy. These measurable metrics serve as a compass, guiding organizations on their journey to digital maturity and success. Let’s delve into the significance of Digital Transformation KPIs and their role in shaping strategic outcomes:
1. Measuring Progress and Success:
- Importance: KPIs act as the barometers of progress, offering tangible metrics to measure the success of digital initiatives. They provide a clear understanding of how well the organization is advancing toward its transformation goals.
- Example KPIs: Metrics like the adoption rate of new digital tools, completion rates of digital training programs, and the percentage increase in digital process efficiency.
2. Aligning with Business Objectives:
- Importance: KPIs should be closely tied to the overarching business objectives outlined in the digital transformation strategy. This alignment ensures that every measurable outcome contributes directly to the organizational goals.
- Example KPIs: Revenue growth attributed to digital channels, cost reductions achieved through process optimization, and improvements in customer satisfaction scores.
3. Enhancing Decision-Making:
- Importance: Digital Transformation KPIs offer actionable insights that empower decision-makers. Real-time data allows leaders to make informed choices, adjust strategies dynamically, and allocate resources effectively.
- Example KPIs: Time taken to implement new digital solutions, the impact of digital initiatives on employee productivity, and responsiveness to customer feedback.
4. Identifying Areas for Improvement:
- Importance: KPIs reveal areas of strength and weakness within the digital transformation journey. By identifying underperforming metrics, organizations can focus on refining specific aspects of their strategy.
- Example KPIs: Bottlenecks in digital processes, user engagement rates with new technologies, and the effectiveness of change management programs.
5. Ensuring Employee Engagement:
- Importance: Employee buy-in is crucial for successful digital transformation. KPIs related to employee training, satisfaction, and utilization of digital tools provide insights into the effectiveness of internal initiatives.
- Example KPIs: Employee participation in digital skills training, feedback on the user-friendliness of digital tools, and the integration of digital processes into daily workflows.
6. Adapting to Market Dynamics:
- Importance: The digital landscape evolves rapidly. KPIs help organizations stay agile by monitoring market trends and adjusting their strategies to remain competitive.
- Example KPIs: Benchmarking against industry standards, monitoring competitor digital initiatives, and tracking customer preferences in the digital space.
7. Enhancing Customer Experience:
- Importance: KPIs focused on customer interactions provide insights into the success of digital transformation in improving overall customer experience.
- Example KPIs: Net Promoter Score (NPS) for digital touchpoints, response times to customer queries through digital channels, and customer satisfaction with digital services.
Digital Strategy vs. Digital Transformation: What is the Difference Between Them?
Digital Transformation and Digital Strategy, although distinct, play complementary roles in driving organizational success.
1. Digital Transformation:
It is a holistic and comprehensive approach that goes beyond solving specific issues. It involves reimagining the entire organization, encompassing processes, culture, and technology. The goal is to achieve a profound and lasting impact on the business. It is a long-term journey characterized by continuous evolution. It requires patience, as the process involves experimentation, prototyping, and fundamental changes that may take considerable time to unfold.
2. Digital Strategy:
Digital Strategy is more focused and addresses specific challenges or goals within the organization. It is often designed for the short to medium term, with a clear understanding of the problems it aims to solve. It involves creating applications or solutions to address particular issues. It’s about leveraging technology strategically to achieve predefined objectives.
| Aspect | Digital Transformation | Digital Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Organizational Scope | Extends across the entire organization, reshaping mindset and structure. | Focuses on specific operations or processes within the organization. |
| Cultural Shift | Involves a significant cultural shift, fostering innovation and collaboration. | Aligns digital initiatives with broader organizational goals without necessarily requiring a profound cultural change. |
| Technology as Enabler | Leverages technology as an enabler for substantial shifts in organizational operations. | Utilizes technology strategically to achieve specific, immediate objectives. |
| Customer-Centric Approach | Focuses on understanding and meeting customer needs in a digital landscape. | May involve optimizing customer experiences but with a narrower, more immediate focus. |
| Data-Driven Decision-Making | Emphasizes the role of data analytics in decision-making processes. | Utilizes data for strategic decision-making but with a more specific and immediate application. |
| Agility and Flexibility | Requires an agile and flexible organizational structure for adapting to changing market conditions. | May involve enhancing operational efficiency without necessitating a comprehensive organizational shift. |
| Strategic Alignment | Focuses on aligning digital initiatives with broader organizational goals. | Identifies specific areas where digital solutions contribute to achieving strategic objectives. |
| Operational Efficiency | Aims for holistic efficiency gains throughout the organization. | Concentrates on enhancing specific operations or processes for immediate efficiency gains. |
| Measurable Outcomes | Aims for profound and lasting impact, with outcomes measured over the long term. | Designed with clear, measurable outcomes, providing tangible results within a defined timeframe. |
| Resource Allocation | Involves strategic allocation of resources, both human and technological. | Allocates resources to achieve specific, immediate digital goals. |
| Competitive Advantage | Seeks to provide a competitive edge in the market through differentiation. | Aims to create a competitive advantage through targeted digital initiatives. |
| Risk Management | Involves risk management at a broader scale, addressing uncertainties in the entire transformation journey. | Focuses on risk management specific to achieving defined digital goals within a shorter timeframe. |
Integrated Approach:
- Phased Implementation: Organizations may adopt a phased approach, starting with specific digital strategies and transitioning into a more comprehensive Digital Transformation initiative.
- Continuous Iteration: Both benefit from a culture of continuous improvement, adjusting strategies based on feedback and evolving business landscapes.
- Leadership and Change Management: Successful integration requires strong leadership guiding the organization through immediate changes and the more extended transformation journey.
The most effective organizational approach involves integrating both Digital Transformation and Digital Strategy. This strategic symbiosis allows an organization to address immediate challenges through digital solutions while simultaneously laying the foundation for long-term, transformative change. By combining the holistic and future-oriented aspects of Digital Transformation with the targeted and immediate benefits of Digital Strategy, organizations can maximize their impact in the digital landscape. This integrated approach ensures resilience, innovation, and sustained success in a rapidly changing business environment.
Related UNITE Models For Navigating Digital Transformation Strategy for Success
1- The Unite Business Model Environment Canvas
The Business Environment Canvas plays a pivotal role in shaping successful digital transformation strategies, providing a structured approach to analyzing external factors that impact an organization. By serving as a compass for informed decision-making and strategic planning, it becomes an indispensable tool that holds significant importance for businesses navigating the complexities of the digital landscape. You can download it now.
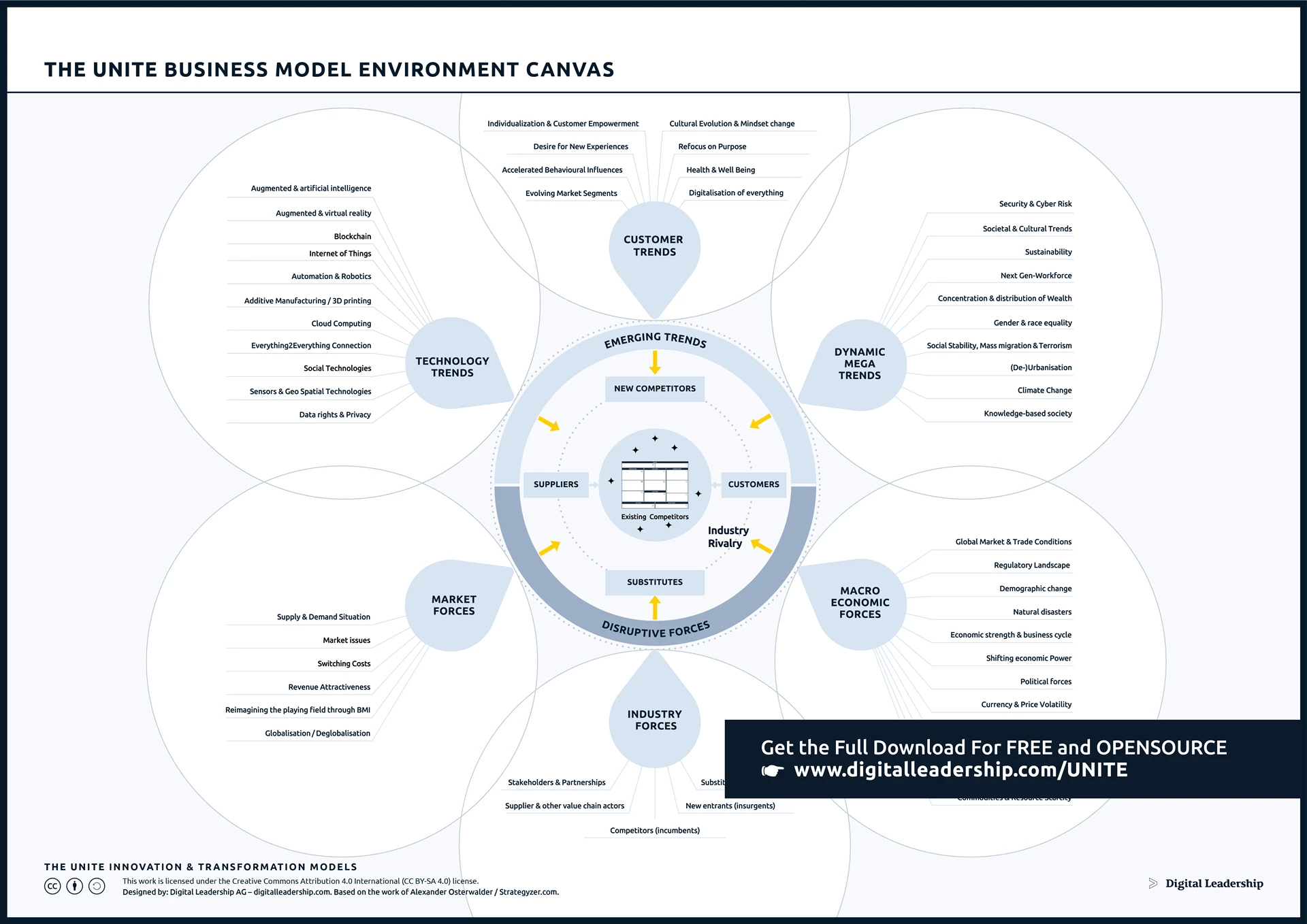
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Based on the work of Alexander Osterwalder
Here’s a concise overview of its significance:
- Holistic Analysis: The canvas enables a thorough examination of external factors such as technology, regulations, and market trends, fostering a holistic understanding crucial for business success.
- Opportunity and Threat Identification: It serves as a tool to pinpoint opportunities for growth and innovation while addressing potential threats proactively, allowing businesses to stay ahead of the curve.
- Strategic Alignment: Facilitating clear alignment of digital transformation strategies with the broader business environment, ensuring that organizational objectives are strategically positioned for success.
- Adaptation to Technology Shifts: Assists in assessing the technological landscape, ensuring the strategic integration of relevant innovations to keep businesses technologically competitive.
- Regulatory Compliance: Maps out regulatory frameworks, ensuring adherence to compliance requirements, especially crucial in the digital realm where regulatory changes can significantly impact business operations.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Visualizes potential risks, contributing to a robust risk management strategy essential in the uncertain and rapidly changing digital landscape, safeguarding businesses from unforeseen challenges.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Acts as a collaborative tool for leadership teams to analyze the environment, discuss scenarios, and make informed decisions about digital transformation directions, ensuring strategic decisions are aligned with business goals.
- Resource Optimization: Informs efficient resource allocation by focusing on areas with the highest potential impact and growth during digital transformation, optimizing resource usage for overall business success.
2) The Unite Operating Model Canvas
The Operating Model Canvas serves as a critical tool in the realm of digital transformation strategy, offering a structured approach to understanding and optimizing an organization’s operational dynamics.

Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the work of Andrew Campbell at Al.
Its significance extends to businesses in several crucial ways:
- Holistic Operations View: Gain a comprehensive understanding of the operating model, ensuring businesses can streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and adapt to digital advancements.
- Strategic Alignment: Ensure the operating model is strategically aligned with digital transformation objectives, fostering a cohesive approach that drives business success in the digital era.
- Gap Identification: Identify and address inefficiencies within current operations, guiding targeted improvements that directly impact the bottom line.
- Agility and Responsiveness: Design agile operating models capable of swift adaptation to changes in technology and market dynamics, enabling businesses to stay competitive and responsive.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Foster collaboration among departments and stakeholders, promoting a unified approach that accelerates digital initiatives and overall business growth.
- Resource Optimization: Optimize resource allocation by visualizing operational components, allowing businesses to allocate resources efficiently for maximum impact and profitability.
- Innovation Integration: Identify opportunities for innovation within operational processes, ensuring businesses stay at the forefront of technological advancements, fostering innovation and maintaining a competitive edge.
- Customer-Centric Design: Prioritize customer-centric processes and interactions in the design of operating models, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty, crucial for sustained business success.
- Risk Management: Structured assessment of risks within the operating model ensures businesses can proactively manage risks related to cybersecurity, compliance, and operational disruptions.
- Continuous Improvement: Promote a culture of continuous improvement, allowing businesses to iteratively refine their operating model in response to evolving digital trends, ensuring sustained relevance and growth in the digital landscape.
3) The Unite Business Model Innovation Canvas
The Business Model Innovation Canvas stands as a vital instrument in the digital transformation playbook, offering a structured approach to reshape and optimize business models. Its importance to businesses is paramount.
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the 10 types of innovation from Doblin, the SS Business Models from the University of St.Gallen, and the Business Model Gallery
Impacting key dimensions in the following ways:
- Strategic Redefinition: Aligning the business model with digital transformation goals ensures businesses remain strategically positioned for sustained growth and relevance.
- Holistic Assessment: Comprehensive evaluations empower businesses to make informed decisions, enhancing overall operational efficiency and effectiveness.
- Opportunity Identification: Uncovering innovation opportunities within the business model directly contributes to revenue growth and competitive advantage.
- Agile Adaptation: Designing agile business models enables businesses to respond swiftly to market changes, fostering resilience and competitiveness.
- Enhanced Customer-Centricity: Reorienting business models around customer needs enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty, driving long-term business success.
- Integration of Technology: Seamless integration of digital technologies ensures businesses stay technologically competitive, a crucial factor in the digital landscape.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Identifying areas for resource reallocation enhances operational efficiency, leading to cost savings and improved profitability.
- Innovation Framework: A structured approach to innovation within the business model fosters a culture of creativity and keeps businesses at the forefront of industry advancements.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying and addressing potential risks associated with innovation safeguards businesses from unforeseen challenges, protecting brand reputation and financial stability.
- Continuous Evolution: Fostering a culture of continuous evolution ensures that businesses can adapt and thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape, securing long-term sustainability and growth.
4) The Unite Four Waves of Economic Development
The significance of understanding the Four Waves of Economic Development in the context of digital transformation cannot be overstated for businesses. This historical framework provides businesses with a roadmap that traces the evolution of economies through various technological eras. Recognizing the historical patterns of economic development equips businesses with insights into the current wave of digital transformation, guiding them in shaping strategies that align seamlessly with the ongoing technological revolution.

Designed by: Susanne M.Zaninelli & Stefan F.Dieffenbacher
- The Initial Industrial Revolution: This period, focusing on textiles, coal, and iron, brought significant socio-cultural changes. Initially challenging for workers, it relied on expensive production means, jeopardizing job security, and often leading to job losses due to technological advancements.
- The Second Industrial Revolution: characterized by electrification and mass production assembly lines, marked a transformative era. This phase centered around industrial and economic models driven by large factories, influenced by organizational visions from figures like Henry Ford and Frederick Winslow Taylor.
- The Third Industrial Revolution: Often termed the digital revolution, featured the discovery of nuclear energy and the invention of the internet. It introduced automation, digitization, and computer use, facilitating global interconnectedness. Computers and electronics gained prominence, fostering technological innovations for industrial and automation processes. Digital telecommunications spurred globalization, enabling industries to offshore production and revolutionize business models worldwide.
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution: The ongoing revolution is characterized by digital transformation, industrial IoT, automation, AI technologies, data analytics, personal connected devices, and the digital economy. This era challenges the boundaries between digital, physical, and biological realms, causing upheavals across global industries. Factories now leverage the gig economy and technologies like Big Data Analytics, Cloud, and IoT for advanced communication among key players in the production line. Additionally, this era encourages the shift from non-renewable to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal energy.
Conclusion
The Digital Transformation Strategy Framework comprises a meticulous process aimed at reshaping enterprises for the digital age. By following the 10 key steps outlined in this guide, organizations can navigate the complexities of digital transformation with confidence. At Digital Leadership, we stand as your strategic partner, providing the expertise and support needed for a successful digital transformation journey. Contact one of our partners to explore how we can guide your organization towards a digitally empowered future.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Who Should Be Involved in Creating a Digital Transformation Strategy?
Creating a robust Digital Transformation Strategy is a multifaceted endeavor that necessitates the active involvement of a diverse array of stakeholders. At the helm, executive leadership, including the CEO and board members, sets the overarching vision and secures essential resources. The IT leaders and Chief Information Officer (CIO) contribute technological insights, aligning initiatives with broader business goals. Spearheading the digital transformation process is the Digital Transformation Officer (DTO) or Chief Digital Officer (CDO), overseeing strategy alignment.
- Business unit heads provide invaluable insights into specific operational needs while customer-facing teams contribute perspectives on customer preferences and expectations.
- Data and analytics experts, including the Chief Data Officer (CDO) and data scientists, play a pivotal role in leveraging data for strategic decision-making.
- The Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO) manages cultural change, ensuring the workforce is prepared for the digital shift.
- Finance leaders, notably the Chief Financial Officer (CFO), allocate budgets and monitor financial performance, ensuring the economic viability of digital initiatives.
- Change management specialists guide the organization through cultural shifts, while external consultants bring industry insights and best practices. Frontline employees, including end-users, contribute practical perspectives, and legal and compliance experts ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
In essence, a holistic approach involves engaging stakeholders from leadership to frontline employees, combining diverse expertise to craft a comprehensive Digital Transformation Strategy. This collaborative effort ensures that the strategy is well-informed, aligned with organizational goals, and capable of navigating the complexities of digital transformation successfully.
2. How Does the Digital Transformation Strategy Impact Business?
Creating a successful Digital Transformation Strategy requires the active involvement of key stakeholders across various levels of the organization. The collaborative effort should include executives, department heads, IT professionals, and, importantly, employees who are directly impacted by the transformation.
Executive leadership provides the strategic vision and aligns the digital strategy with overall business goals. Department heads contribute domain-specific insights, ensuring that the transformation aligns with functional objectives. IT professionals play a crucial role in implementing technological solutions and ensuring seamless integration. Moreover, involving employees at all levels fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the transformation journey.
Their firsthand knowledge of daily operations and customer interactions can provide valuable perspectives that contribute to a more comprehensive and effective strategy. Inclusivity in the strategy creation process not only improves the quality of the plan but also ensures a smoother implementation phase, as the diverse expertise and perspectives help identify and address potential challenges proactively. Overall, a collaborative and inclusive approach to crafting a Digital Transformation Strategy is key to its success and the organization’s ability to navigate the complexities of the digital landscape.
3. Consequences for Businesses Lacking a Digital Transformation Strategy
Businesses that neglect to adopt a Digital Transformation Strategy expose themselves to a range of consequences that can impede their competitiveness, hinder growth, and jeopardize long-term sustainability. One of the primary consequences is the risk of becoming obsolete in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. As industries undergo digital disruption, organizations that fail to embrace digital technologies and adapt their strategies may find it challenging to stay relevant and competitive.
Lack of operational efficiency is another significant consequence. Digital transformation often involves optimizing business processes through automation, data-driven decision-making, and streamlined workflows. Organizations without a digital strategy may struggle with inefficiencies, manual processes, and outdated systems, leading to higher operational costs and reduced agility.
Customer dissatisfaction is a critical consequence for businesses that do not prioritize digital transformation. As consumer expectations evolve in the digital era, organizations must deliver seamless, personalized, and digitally-enabled experiences. Without a strategic approach to digital transformation, businesses may fail to meet these expectations, resulting in customer churn, negative reviews, and a damaged reputation.
4. How to Create a Digital Transformation Roadmap?
Crafting a comprehensive roadmap is indispensable for organizations aiming to thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape. A successful roadmap is not just a tactical guide; it’s a strategic blueprint that intricately integrates the organization’s overarching digital transformation strategy. This roadmap, a product of careful planning, serves as a navigational tool, steering the organization through the complexities of transformation. It encapsulates a detailed journey from the initial assessment of the current state to the full realization of digital initiatives in alignment with the strategic objectives.
The roadmap underscores the importance of assessing the organization’s digital maturity, ensuring that this evaluation harmonizes seamlessly with the strategic goals outlined in the digital transformation strategy. Stakeholder involvement is a crucial facet, emphasizing collaboration, buy-in, and a shared understanding of the strategic transformation goals. The integration of relevant digital technologies takes center stage, echoing the strategic role of technology outlined in the overarching strategy. Business processes are not just redesigned; they are realigned to echo the strategic intent of the digital transformation strategy, fostering a culture of innovation and efficiency.













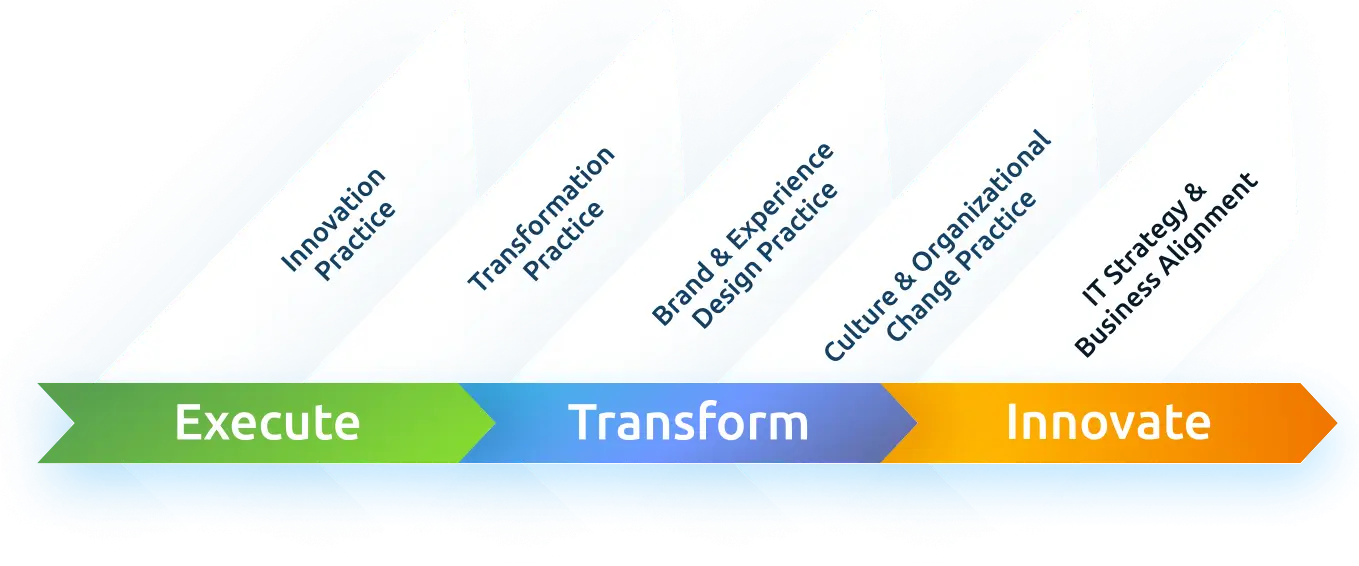















 Book How to Create Innovation
Book How to Create Innovation