Digital Business Models: All You Need To Know
Published: 06 September, 2023
Business Models

Table of Contents
In today’s world, there is a widespread acknowledgment of the presence and validity of modern technologies and software solutions. The term “Artificial intelligence” is now a household term, with most individuals having a basic understanding of its meaning. However, a persistent area of ambiguity, even among some chief executive officers (CEOs), pertains to the concept of digital business models and the factors that make them exceptionally successful.
Recognizing the importance of digital business models transcends mere relevance; it stands as a strategic necessity for organizations across various sectors and scales. Within this context, Digital Leadership steps in to offer Digital Transformation Solutions and Business Model Strategy services, equipping organizations with the necessary tools, technologies, and strategies to adeptly navigate the complexities of this transformation. Our expertise extends to assisting businesses in rethinking their current models or crafting entirely fresh approaches that harmonize seamlessly with the digital terrain.
In an era marked by rapid technological advancement and evolving consumer behaviors, gaining a deeper comprehension of these digital business models is imperative for anyone looking to thrive in the ever-changing landscape of commerce. In this discussion, we will explore what digital business models entail and delve into the reasons behind their remarkable effectiveness in today’s business environment.
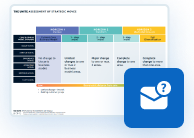
Structuring your business model cannot be overstated, as it serves as the blueprint for how your organization creates, delivers, and captures value. The UNITE Business Model Innovation Patterns are invaluable for structuring a business model as they provide a systematic framework for innovation, offering comprehensive coverage across diverse industries. It summarizes 95% of all business model innovations and gives you the necessary tools to systematically innovate your business model. These patterns streamline the innovation process and enhance adaptability in the face of rapid change, reducing risks associated with business model evolution. You can download it now.
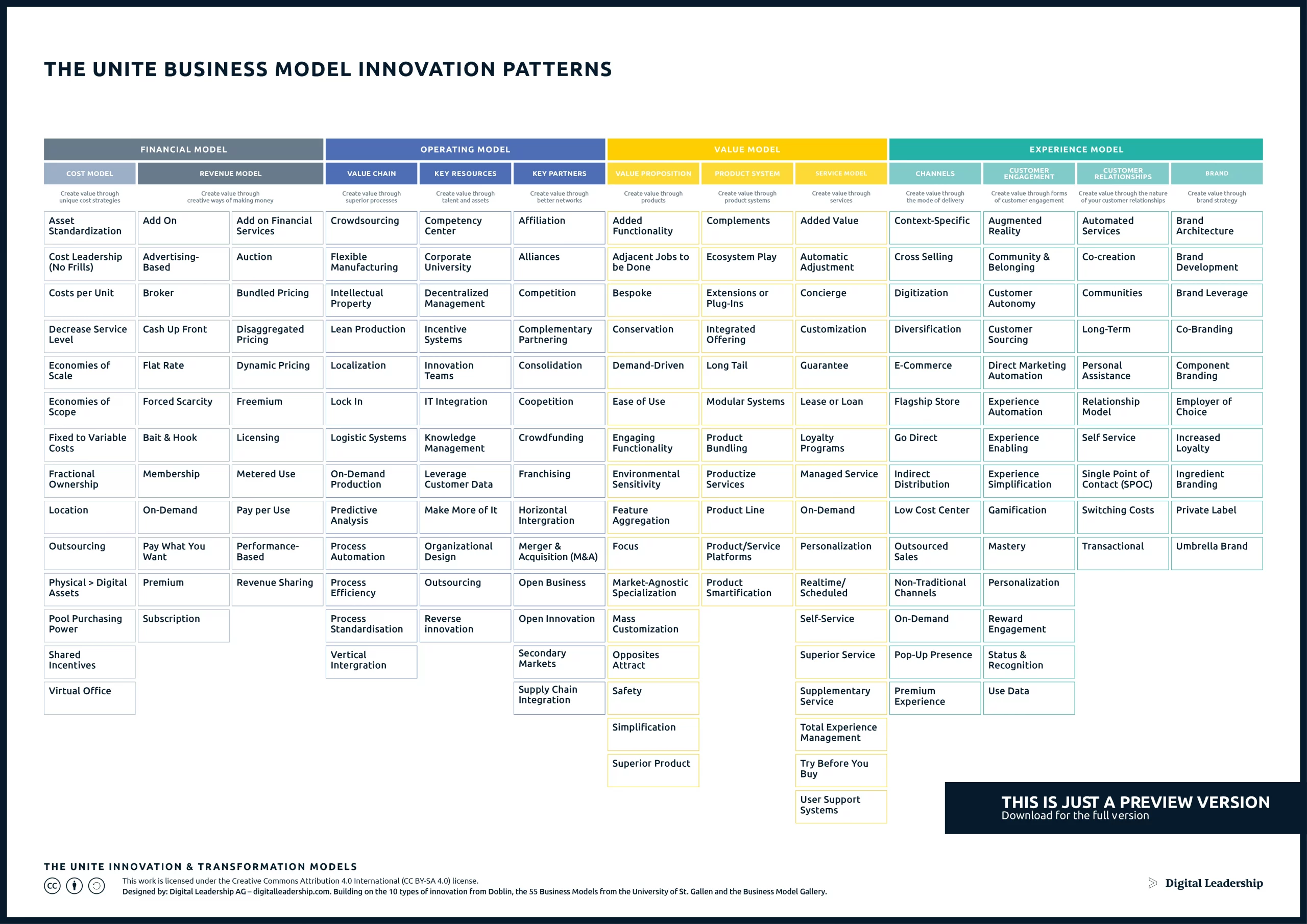
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the 10 types of Innovation from Doblin, The SS Business Models from the University of St.Gallen & The Business Model Gallery
Discover extensive insights into digital business models and innovative strategies in our released FREE book titled “HOW TO CREATE INNOVATION.” This resource encompasses comprehensive methodologies, mindsets, organizational structures, and strategies for achieving innovation more efficiently, with fewer resources, and greater success. Don’t miss out; sign up for the download today!
What are digital business models?
Let’s delve into the fundamental underpinnings of digital business models. As with all comparatively new terms, there is no clear agreement on a universally valid definition. However, one can limit oneself to certain commonalities.
Interestingly, when you examine this definition closely, you’ll find that it shares substantial similarities with traditional business models. The key distinction lies in the integration of digital technologies. This begs the question: What sets digital business models apart and accounts for their significant success in today’s business landscape? To unravel this, we must embark on a deeper exploration of the intricacies that define digital business models and elucidate the precise factors contributing to their contemporary prominence.
Digital business models revolve around delivering added value to one or more customers through the strategic use of digital technologies. The ultimate objective is to ensure that the customer benefits derived from these digital solutions reach a level at which consumers are not only satisfied but also willing to pay for this value. Let’s delve deeper into the foundational principles that make digital business models so integral to contemporary business success:
- Digital Transformation: Digital business models are the result of a transformative shift in how businesses operate. They harness the potential of digital technologies to fundamentally reshape traditional processes and create innovative ways of delivering value.
- Customer-Centricity: Central to digital business models is a relentless focus on meeting customer needs and preferences. Through data-driven insights and personalized experiences, they aim to not only satisfy but delight consumers.
- Agility and Innovation: These models thrive on agility and rapid innovation. They empower businesses to adapt swiftly to changing market dynamics, experiment with new offerings, and iterate based on real-time feedback.
- Global Reach: The internet has erased geographical boundaries, providing digital business models with access to global markets. This expansive reach allows companies to connect with diverse customer bases and unlock new revenue streams.
- Data as a Driver: Data lies at the heart of digital business models. They leverage data analytics and insights to make informed decisions, identify emerging trends, optimize operations, and enhance customer experiences.
Importance of Digital Business Model
The importance of digital business models in today’s world cannot be overstated, and the reasons behind it are quite straightforward. It’s no longer a choice; it’s a necessity. The evolution of consumer behavior, where consumers now expect seamless digital experiences, coupled with businesses prioritizing customer-centric approaches, has given rise to an entirely new paradigm. Companies have realized that the technological capabilities that are now available to them are so much more than a website.
Simultaneously, consumers have developed a newfound trust in digital business models. What was once viewed skeptically as a “subscription trap” a decade ago is now exemplified by the likes of Netflix, and the traditional catalog people used to order from has transformed into the convenience of Amazon. This transformation underscores the imperative for businesses to embrace digital business models to remain competitive and meet evolving customer expectations.
Comprehending digital business models is pivotal for organizations aiming to thrive and excel. These models offer a multifaceted toolkit for businesses, providing advantages that extend far beyond their basic functions.
Characteristics of Digital Business Models
In the constantly evolving realm of contemporary commerce, digital business models have emerged as powerful catalysts, reshaping the very essence of how organizations conduct their operations and engage with their customer base. These models are marked by a distinct set of core qualities that collectively serve as the bedrock of their triumph and prominence in the fiercely competitive landscape of today, distinguishing them from classic business models. Let’s explore these fundamental characteristics more comprehensively to grasp their profound influence on the tactics and functioning of enterprises in this digital era.
- Digital Transformation:
Digital business models represent a profound shift in business operations, encompassing the adoption of cloud computing, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and automation. These technologies enable organizations to not only optimize existing processes but also create entirely new ways of delivering value to customers. - Digital Value Generation:
The added value in digital business models can only be generated digitally, setting them apart from traditional models that primarily create value in analog form. While traditional models may undergo digital transformation, the core value remains unchanged, only altering the means of obtaining it. In essence, the Internet is the cornerstone of the digital business model’s core operations, without which its core business would not be possible. - Customer-Centric:
At the core of digital business models lies an unwavering commitment to understanding and satisfying customer needs. Leveraging data-driven insights, organizations can segment their customer base, personalize offerings, and anticipate customer desires, fostering deep customer loyalty. - Data-Driven:
Data serves as the lifeblood of digital business models. These models collect, process, and analyze data on customer behavior, market trends, and operational performance. The insights derived from data empower businesses to make informed decisions, refine strategies, and continually enhance the customer experience. - Agility:
Digital business models thrive on agility, allowing organizations to pivot swiftly in response to market shifts, emerging technologies, and customer feedback. This adaptability ensures that businesses remain competitive and innovative in a rapidly changing landscape. - Innovation:
A culture of innovation permeates digital business models. Companies are encouraged to experiment with emerging technologies, develop new products and services, and explore novel revenue streams. This commitment to innovation is vital for staying ahead of the competition. - Global Reach:
Enabled by the internet, digital business models transcend geographical boundaries. They provide organizations with unprecedented access to global markets, allowing them to connect with diverse customer bases and capitalize on international growth opportunities. - Revenue Diversification:
Digital business models often incorporate a variety of revenue streams. These can include subscription models, freemium offerings, advertising revenue, and data monetization. This diversification reduces reliance on a single source of income and enhances financial stability. - Ecosystem Orientation:
Many digital business models foster ecosystems that bring together various stakeholders, such as customers, partners, and developers. These ecosystems create a network effect, generating additional value and enhancing the overall customer experience. - Efficiency:
Efficiency gains are a hallmark of digital business models. Automation, streamlined processes, and optimized resource allocation not only reduce operational costs but also enable businesses to deliver products and services more efficiently and at a lower cost. - User Experience Focus:
Delivering an exceptional user experience is paramount. Digital business models prioritize creating intuitive, user-friendly interfaces and applications that enhance customer satisfaction, foster brand loyalty, and drive customer retention. - Disruption:
Digital business models have the potential to disrupt traditional industries by introducing innovative approaches that challenge established norms. This disruption can lead to the creation of entirely new markets and business opportunities. - Scalability:
These models are inherently scalable, allowing organizations to accommodate rapid growth without a proportionate increase in costs. Scalability is a critical factor in achieving sustainable expansion and competitiveness. - Sustainability:
Ensuring long-term sustainability is a key consideration. Digital business models focus on maintaining profitability by aligning revenue streams with operational costs, ensuring financial stability and continued growth.
Related: https://digitalleadership.com/unite-articles/extended-business-model-canvas/
Types of Digital Business Models with a Real-Life Examples
Let’s take a closer look at the individual models to understand how they work and how they are structured to align with digital business strategy. Because even if the differences sound simple, they are not always. And especially with digital business models, it is interesting to see how the revenue streams emerge again. While in the beginning there was a lack of definition, there are now more and more possible distinctions. The largest and most established models are the following:
- Free:
- In this model, the approach is still relatively intuitive. The entire offer in the form of the product or service is provided free of charge.
- The “Free” model offers core products or services at no cost to users.
- Revenue is generated purely through advertising on the respective URL. through alternative means, such as advertising, freemium upgrades, or data monetization.
- Example: Facebook is a social media platform that offers its core services (connecting people, and sharing content) for free to users. It generates revenue primarily through digital advertising. Advertisers pay to display targeted ads to users based on their interests and behaviors.
- On-Demand:
- On-demand models provide immediate access to products or services when users need them.
- Examples include ride-sharing services like Uber and food delivery apps like DoorDash.
- Convenience and real-time fulfillment are key features.
- Example: Uber is a ride-sharing service that allows users to request rides on-demand using a mobile app. Users can request rides in real-time, and drivers respond to these requests, providing convenient transportation.
- E-commerce:
- E-commerce businesses sell products or services online, often through their websites or platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce.
- They can range from small online boutiques to large-scale retailers like Amazon.
- E-commerce often involves various business models, including B2C (business-to-consumer) and B2B (business-to-business).
- Example: Amazon is one of the world’s largest e-commerce platforms, offering a wide range of products for sale online. It operates both as a B2C (selling products directly to consumers) and a B2B (offering marketplace services to third-party sellers) e-commerce platform.
- Marketplace (also peer-to-peer):
- Online marketplaces act as intermediaries connecting buyers and sellers.
- They often charge fees or commissions for transactions.
- Marketplaces can focus on various niches, such as products, services, or accommodation.
- Example: Airbnb is an online marketplace that connects travelers with hosts offering accommodations, which can be apartments, houses, or even unique stays. It charges hosts and guests fees for bookings made through the platform, acting as an intermediary.
- Access-Over-Ownership:
- This model emphasizes access to goods or services rather than ownership.
- Businesses rent or lease products to users, offering cost-effective and sustainable alternatives.
- Car-sharing services like Zipcar and equipment rental platforms follow this model.
- Example: Zipcar is a car-sharing service that allows users to rent cars by the hour or day. Users access Zipcar’s fleet of vehicles when needed, avoiding the need to own a car themselves.
- Ecosystem:
- Ecosystem models create an interconnected network of products, services, or platforms.
- They encourage users to stay within the ecosystem for various needs.
- Example: Apple Ecosystem includes hardware devices (iPhone, Mac), software (iOS, macOS), the App Store, iCloud, and other services. Users are encouraged to stay within the Apple ecosystem, as products and services work seamlessly together (e.g., iCloud for data storage). The Apple ecosystem is known for its seamless integration, such as AirDrop, which can create a sense of vendor lock-in, where users are incentivized to use Apple products exclusively.
- Experience:
- Experience-based models focus on providing unique and immersive experiences.
- Businesses charge for access to experiences, such as virtual reality (VR) experiences, live events, or themed entertainment.
- Example: Disneyland is a theme park known for providing unique and immersive experiences to visitors. Visitors purchase tickets for entry and pay for additional experiences and attractions within the park.
- Subscription:
- Subscription models offer recurring revenue streams and build customer loyalty.
- Businesses often offer tiered pricing with varying features or content access.
- They require a focus on retaining subscribers and continuously providing value.
- Example: Netflix is a subscription-based streaming service that offers a vast library of movies and TV shows. It offers multiple subscription tiers with varying features and content access, including options for streaming quality.
- Open Source:
- Open-source models involve sharing software, code, or intellectual property freely with the community.
- Revenue is often generated through support, customization, or premium versions.
- Example: Linux Operating System is an open-source operating system widely used for servers and embedded systems. Companies and individuals can use Linux for free, but revenue is generated through support services, certifications, and customized solutions.
- Hidden Revenue:
- Hidden revenue models offer a free or low-cost product but generate income through less visible channels.
- For instance, some mobile apps collect user data and sell it to advertisers without explicit user knowledge.
- This model can raise ethical and privacy concerns.
- Example: Free Weather Apps, Some free weather apps collect user location data and weather preferences, which are used for targeted advertising and data monetization. Users may not be aware that their data is being used for these purposes, raising privacy concerns.
- Freemium:
- Freemium model attracts users with free basic features while offering premium upgrades.
- They can be effective for software, mobile apps, and online services.
- Conversion rates from free to paid users are crucial for success.
- Example: Dropbox is a cloud storage service that offers free storage with limitations and premium plans with enhanced features. Users can store and share files for free, but premium users get additional storage and advanced sharing options.
- Online Marketplace:
- Online marketplaces act as intermediaries connecting buyers and sellers.
- They often charge fees or commissions for transactions.
- Marketplaces can focus on various niches, such as products, services, or accommodation.
- Example: eBay is an online marketplace where individuals and businesses can buy and sell a wide range of products. It charges sellers fees for listing items and final value fees for completed transactions.
- Digital Advertising:
- Digital advertising models generate revenue by displaying ads to users.
- Targeted advertising, programmatic ads, and native advertising are common approaches.
- Platforms must balance user experience with ad revenue.
- Example: Google Ads is an advertising platform that displays ads on Google search results and websites within the Google Display Network. Advertisers bid on keywords and use targeting options to reach specific audiences.
- Data Monetization:
- Data-driven businesses gather and analyze user data to offer insights, targeted advertising, or market research.
- Strict data privacy regulations must be followed.
- Data is often sold to third parties or used to enhance products and services.
- Example: Facebook Data Usage, Facebook gathers user data to offer targeted advertising to businesses. User data includes interests, behaviors, and demographic information. Facebook must comply with data privacy regulations and guidelines.
- IoT Services:
- IoT businesses offer solutions for connected devices, such as smart home systems or industrial sensors.
- Data generated by IoT devices can be leveraged for analytics and insights.
- Security and privacy are paramount concerns.
- Example: Nest (by Google) offers smart home products, including thermostats and security cameras, that are part of the Internet of Things (IoT). Data generated by Nest devices, such as temperature and motion data, can be used to optimize energy use and enhance security.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrency:
- Blockchain-based businesses use decentralized ledgers for various applications.
- Cryptocurrency exchanges facilitate the buying and selling of digital assets.
- NFT (Non-Fungible Token) platforms enable unique digital asset ownership.
- Example: Bitcoin is a decentralized cryptocurrency that enables peer-to-peer digital transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. It is used for secure and transparent digital transactions, and it’s also seen as a store of value.
How to Create a Digital Business Strategy
Crafting a robust digital business strategy has become nothing short of imperative. With technology continuously shaping the way we live, work, and interact, businesses of all sizes and niches must adapt to the digital age. Whether you’re an established corporation or a budding startup, a well-crafted digital strategy is a compass that can steer you toward growth, enhanced customer engagement, and operational efficiency.
We’ll walk you through the essential steps for developing a digital business strategy that harmonizes with your goals, capitalizes on the potential of digital technologies, and positions your enterprise for triumph in the digital era.
| Step Number | Step Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Define Your Objectives | Clearly define your business objectives for the digital strategy, such as revenue growth, customer base expansion, or market share increase. Specify measurable key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress effectively. |
| 2 | Understand Your Target Audience | Gain insights into your target audience’s needs, preferences, and behaviors through data and analytics. Develop buyer personas to create personalized digital experiences. |
| 3 | Assess Your Current State | Evaluate your existing digital capabilities and technologies to determine their effectiveness in achieving your objectives. Identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis). |
| 4 | Competitor Analysis | Conduct in-depth research on your competitors’ digital strategies to identify opportunities for differentiation. Analyze their strengths and weaknesses in the digital landscape. |
| 5 | Digital Channels and Platforms | Select the most relevant digital channels and platforms (e.g., website, social media, mobile apps) for your audience based on your objectives and audience preferences. Explore different types of business models to fit your strategy. |
| 6 | Content Strategy | Develop a comprehensive content strategy that aligns with your objectives, encompassing various digital media forms such as blogs, videos, infographics, and webinars. Explore business model examples relevant to your content. |
| 7 | Technology Stack | Choose the appropriate technology stack, including content management systems, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and analytics tools. Consider investments in software, tools, or infrastructure that align with your business modeling. |
| 8 | Data and Analytics | Implement robust data collection and analytics tools to track KPIs and make data-driven decisions. Develop a data governance framework to ensure data accuracy, privacy, and compliance in your business modeling. |
| 9 | User Experience (UX) Design | Prioritize UX design to ensure a seamless and user-friendly digital experience for your audience. Conduct usability testing and optimize user journeys as part of your digital strategies. |
| 10 | Security and Compliance | Address security and compliance requirements, particularly when handling sensitive customer data. Implement encryption, secure authentication, and compliance controls as part of your business modeling. |
| 11 | Mobile Optimization | Optimize digital assets for mobile devices, recognizing the importance of mobile responsiveness. Ensure that your website and apps provide an exceptional mobile user experience in alignment with your types of business models. |
| 12 | Content Marketing and SEO | Create a content marketing strategy with SEO techniques to enhance your online visibility. Identify relevant keywords and optimize content for search engines in your business modeling. |
| 13 | Social Media Strategy | Develop a social media strategy tailored to each platform’s unique requirements and audience expectations. Plan content calendars, engage with followers, and measure social media ROI in your digital strategies. |
| 14 | Testing and Optimization | Continuously test and optimize digital initiatives using A/B testing and user feedback for improvements. Conduct regular website and app performance audits to enhance your business models. |
| 15 | Budgeting and Resource Allocation | Allocate budget and resources to support the execution of your digital strategy, both short-term and long-term. Prioritize investments in areas that align with your objectives and types of business models. |
| 16 | Training and Skill Development | Ensure your team possesses the necessary skills and training for implementing and managing digital initiatives. Provide training on new tools and technologies as needed in your digital strategies. |
| 17 | Measurement and Reporting | Set up a robust reporting system to track KPIs and regularly review progress, adjusting the strategy as needed. Create data-driven dashboards and reports for stakeholders to support your business modeling. |
| 18 | Scalability and Future Planning | Plan for scalability as your business grows and stay informed about emerging technologies and trends for future planning. Consider the potential impact of future disruptions on your digital strategies and types of business models. |
| 19 | Execution and Monitoring | Execute your digital strategy while closely monitoring its performance, and adapting to evolving market conditions. Regularly review analytics, and address issues promptly to support your business models. |
| 20 | Feedback and Iteration | Gather feedback from customers and stakeholders to iteratively improve your digital strategy over time. Use feedback to make data-backed adjustments and optimize user experiences in your business modeling. |
So, Choosing the right digital business model strategy is a pivotal decision. It requires a deep understanding of your target audience, a clear definition of your unique value proposition, and a comprehensive evaluation of your resources and capabilities. Here are some key takeaways to guide you in this process:
- Know Your Audience: Understand your customers’ needs, preferences, and pain points. Use data and analytics to gain insights into their behavior and expectations.
- Define Your Value Proposition: Clearly articulate what sets your business apart. How will your digital strategy address customer challenges or provide unique solutions?
- Leverage Technology: Embrace digital tools and platforms that align with your strategy. Whether it’s e-commerce, mobile apps, or data analytics, technology should support your goals.
- Stay Agile: Be prepared to adapt and iterate. Digital landscapes evolve rapidly, and your strategy should have built-in flexibility to respond to market changes.
- Invest in Talent: Build a team with the right skills to execute your digital strategy effectively. Training and upskilling may be necessary to keep pace with technological advancements.
- Measure and Analyze: Implement metrics and KPIs to monitor the performance of your digital initiatives. Regularly review the data to make informed decisions.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Put the customer at the center of your strategy. Tailor your digital offerings to meet their needs and provide exceptional user experiences.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of industry trends, emerging technologies, and competitors’ strategies. Continuous learning is essential in the digital business landscape.
Remember that there is no one-size-fits-all digital business model. Your choice should align with your industry, target market, and organizational strengths. By following these guidelines and staying committed to innovation and customer satisfaction, you can create a digital business strategy that not only survives but thrives in the digital age.
Business Model Vs Digital Business Model
A business model serves as a comprehensive framework that delineates the fundamental operations and sustainability strategies of a business. It encompasses diverse facets, including how the business delivers value to its customers, the channels employed to reach these customers, the relationships cultivated with them, the requisite resources and activities for value delivery, the revenue streams generated, and the associated cost structure.
In contrast, a digital business model represents a specialized subset within the broader business model framework, meticulously tailored to harness the capabilities of digital technologies and resources. It notably accentuates the strategic utilization of digital tools, platforms, data, and communication channels to elevate and revolutionize various aspects of the business. Digital business models frequently encompass:
- Digital Customer Engagement: Utilizing digital channels such as websites, mobile applications, and social media to foster customer interactions, offering personalized experiences and real-time connectivity.
- Innovative Revenue Streams: Pioneering revenue streams facilitated by digital technologies, which may encompass subscription-based services, data monetization, or digital product sales.
- Efficient Cost Structures: Optimization of operational costs through automation, cloud computing, and data analytics to enhance overall efficiency.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Heavy reliance on data analytics to inform strategic decisions, enrich customer experiences, and drive continuous business enhancements.
- Agility and Adaptability: Structured for agility, digital business models enable organizations to promptly respond to market fluctuations and technological advancements.
Connecting The Dots With Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a powerful tool in the realm of digital business models due to its adaptability and versatility. It offers businesses a structured framework to define, conceptualize, and iterate on their digital strategies. One of its key advantages is its ability to encourage customer-centric thinking, driving businesses to identify and address the evolving needs of their digital audience. You can download it now.
Furthermore, the BMC promotes innovation by allowing organizations to experiment with different components of their model, aligning well with the ever-evolving nature of digital technologies. Its agility enables rapid adjustments to respond to market dynamics and emerging opportunities. Ultimately, the BMC is a valuable asset for organizations navigating the intricacies of the digital age, aiding in the development of comprehensive and strategic approaches to digital business models. You can easily access and utilize it to refine your own digital strategies and models.
Conclusion
In conclusion, crafting a digital business strategy is essential in today’s tech-driven world. To remain competitive, leverage tools like the Business Model Canvas to align your operations with evolving customer expectations and digital opportunities. Your Business strategy should adapt to the dynamic digital landscape, incorporating data analytics, online platforms, and customer-centric approaches. Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution; tailor your strategy to your industry and strengths. By blending digital strategy principles with the Business Model Canvas, you can navigate the digital age and ensure your business thrives amid constant change.
Frequently Asked Questions
1- What are the key elements of digital business?
Key elements of a digital business include:
- Digital Technologies: Utilizing tools like AI, IoT, cloud computing, and data analytics.
- Customer-Centricity: Focusing on meeting customer needs through personalization and user-friendly experiences.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Leveraging data for insights and informed choices.
- Innovation Culture: Encouraging creativity and experimentation to stay competitive.
- Agility: Adapting quickly to market changes and technological advancements.
- Ecosystem Engagement: Collaborating with partners, suppliers, and platforms.
- Efficiency: Optimizing processes for cost-effectiveness and productivity.
2- What is a digital business structure?
A digital business structure refers to the organizational framework designed to effectively operate within the digital landscape. It involves roles, responsibilities, processes, and technologies that support digital strategies. Common elements include digital teams, data analytics divisions, agile workflows, and technology infrastructure to facilitate digital transformation.
3- What are the 7 principles of a digital transformation strategy?
The seven principles of a digital transformation strategy are:
- Customer-Centricity: Prioritize understanding and meeting customer needs.
- Leadership Commitment: Engage leadership in championing digital initiatives.
- Innovation Culture: Foster a culture of experimentation and adaptability.
- Agile Methodologies: Implement agile practices for quicker responses to changes.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Base choices on data and analytics insights.
- Ecosystem Collaboration: Partner with external stakeholders and platforms.
- Continuous Learning: Invest in upskilling and learning to keep pace with digital advancements.



























 Book How to Create Innovation
Book How to Create Innovation