Business Level Strategy Examples, Types, Definition and Implementing Steps For Successful Strategy
Published: 19 December, 2023
Digital Strategy
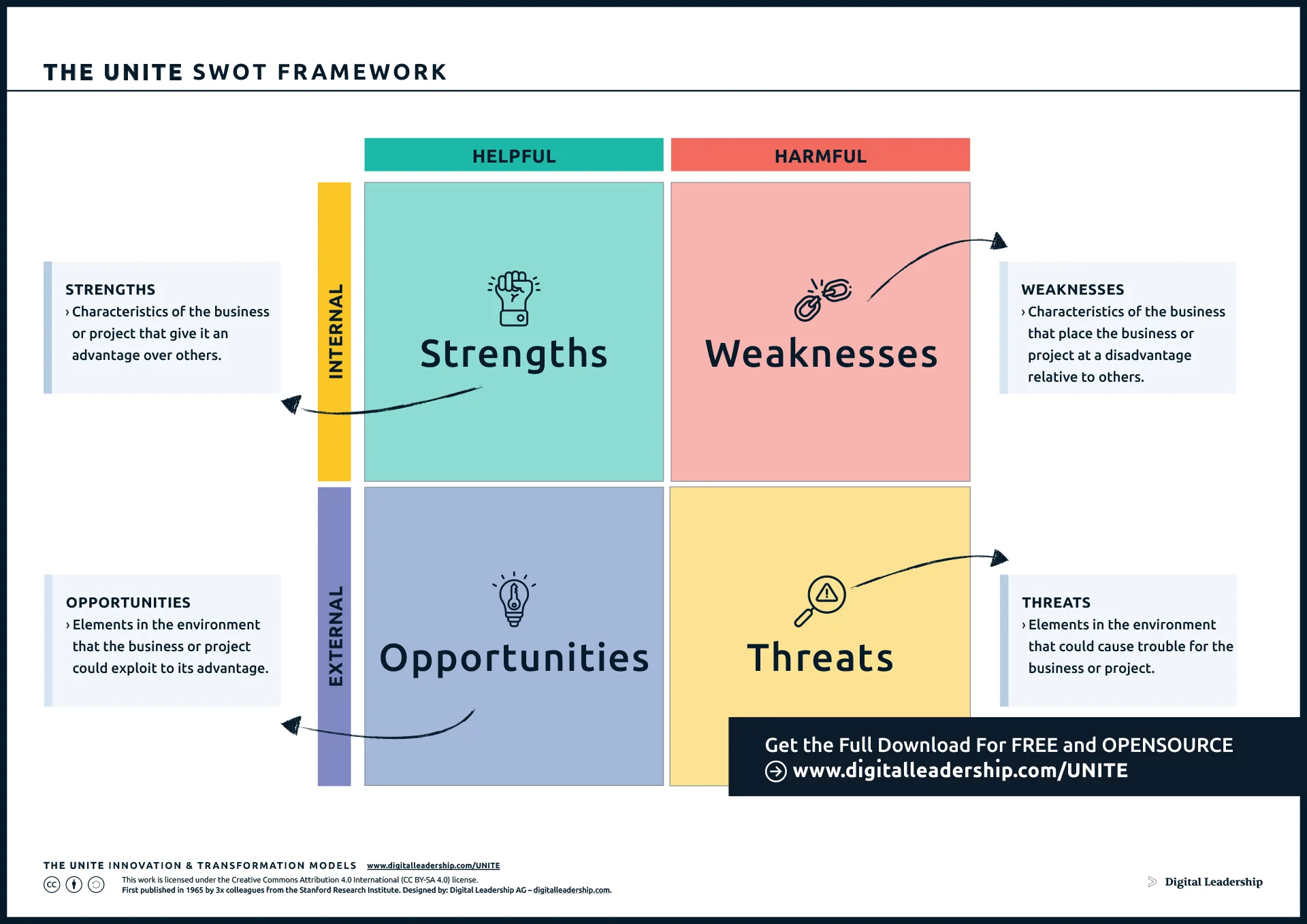
Table of Contents
In the business environment, the choice of an effective strategy can be the decisive factor distinguishing success from stagnation. The business-level strategy serves as the guiding roadmap that steers a company’s endeavours towards securing a competitive advantage in a targeted market or industry. This strategic approach encompasses a series of thought-out decisions and purposeful actions, all with the goal of positioning the business in a distinctive manner relative to its competitors, thereby crafting a unique and compelling value proposition for customers.
In this convergence, business goals align harmoniously with business strategy, allowing a company to compete adeptly within a specific market. The seamless integration of business-level strategy with digital transformation strategy and innovation strategies underscores a contemporary reality: thriving businesses operate within an intricately interconnected strategic framework. This cohesion enhances adaptability and positions businesses to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape successfully.
At Digital Leadership, we are committed to providing innovative solutions that go beyond conventional approaches. Through our Innovation Consulting and Digital Transformation Consulting services, we foster creativity and ensure seamless alignment of technology adoption with business goals. Our approach involves integrating Jobs to be Done into your right business-level strategy, focusing on understanding customers’ fundamental needs and motivations to establish meaningful and lasting connections.
What is Business Level Strategy?
Business level strategy encompasses the deliberate and calculated measures that companies employ to secure a competitive advantage within their designated market segments. This entails making pivotal decisions regarding the allocation of resources, the differentiation of products, and the creation of unique value propositions for customers.
A business level strategy describes a set of intentional and coordinated actions and decisions that a company undertakes to gain a competitive advantage and achieve success within a specific market or industry. It involves defining how a business will position itself relative to its competitors, making choices about the allocation of resources, and determining how to create and deliver value to its customers. A Business level strategy is often concerned with addressing questions such as how the company will differentiate its products or services, what customer needs it will fulfil, and how it will sustain a competitive advantage. Essentially, it outlines the approach a business takes to compete effectively in a particular market segment. The business level strategy definition is the detailed plan and set of actions designed to help a company succeed within its chosen market space.
A business level strategy describes a set of intentional and coordinated actions and decisions that a company undertakes to gain a competitive advantage and achieve success within a specific market or industry. It involves defining how a business will position itself relative to its competitors, making choices about the allocation of resources, and determining how to create and deliver value to its customers. A Business level strategy is often concerned with addressing questions such as how the company will differentiate its products or services, what customer needs it will fulfill, and how it will sustain a competitive advantage. Essentially, it outlines the approach a business takes to compete effectively in a particular market segment. In business level strategy definition, it is the detailed plan and set of actions designed to help a company succeed within its chosen market space.
The Business Model Canvas plays a pivotal role in business level strategy in aligning different elements to ensure that they collectively support the overarching strategic goals. By focusing on customer-centric components and resource allocation, the canvas aids in decision-making crucial to gaining a competitive advantage. Its adaptability allows businesses to innovate and respond to market changes, a vital aspect in executing effective business-level strategies.
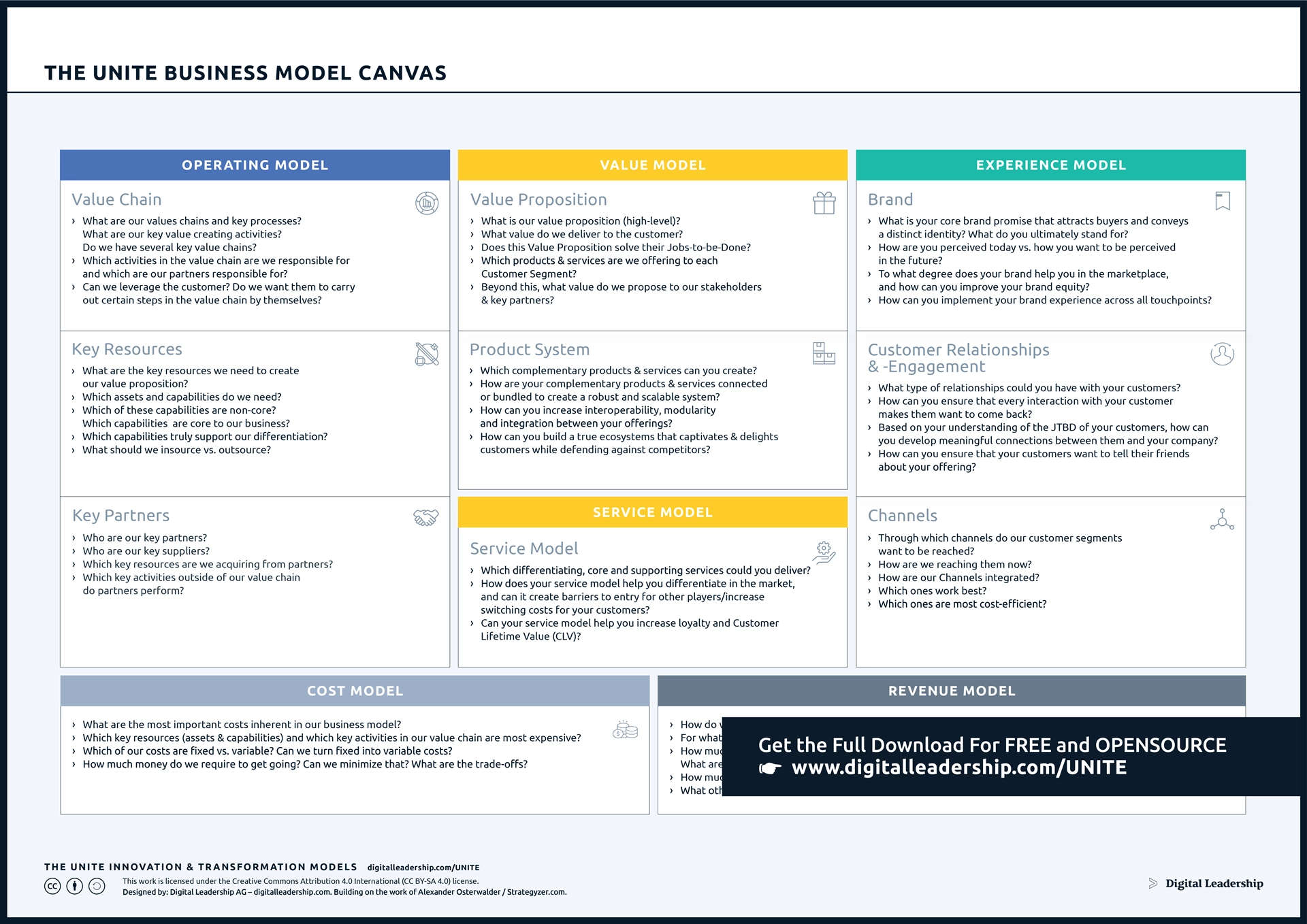
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the work of Alexander Osterwalder
To dig into your Customer Segments and work with data-driven Personas for effective business level strategy. Our book, How to Create Innovation, discusses Personas at length. It’s a system that builds examples, of customers, based on the information you’ve gathered about their habits and identities. Personas help you understand who your customers are as people within their broad segments so you can better reach them and bring them value.
Business Level Strategy within Levels of Strategy
Business level strategy operates within the broader framework of organizational strategy, which consists of multiple levels. These levels include Corporate Level Strategy, Business Level Strategy, and Functional Level Strategy. Business Level Strategy, specifically, is the intermediate layer that focuses on how a company will compete within a particular market or industry.
1- Corporate Level Strategy
Corporate Level Strategy refers to the high-level decisions made by top management to guide the entire organization. It involves determining the scope of the company’s activities, including diversification, mergers and acquisitions, and global expansion. Key aspects include managing the portfolio of business units, resource allocation, and strategic alliances. It sets the overarching direction for the entire organization, ensuring that business units contribute cohesively to achieve corporate goals. It is dynamic, requiring adaptability to changing market conditions and a keen understanding of the organization’s capabilities and competitive landscape.
2- Business Level Strategy
Business Level Strategy is the compass that guides a company’s efforts to distinguish itself within a specific market or industry. It entails a series of strategic decisions and actions aimed at positioning the business uniquely relative to its competitors, ultimately creating a compelling value proposition for customers. Whether through product differentiation, cost leadership, or a focus on specific market segments, Business Level Strategy is about making deliberate choices to gain a competitive advantage. This strategy aligns business goals with actions taken at the operational level, emphasizing resource allocation, market positioning, and adaptation to environmental changes. In the contemporary business landscape, the integration of Business Level Strategy with digital transformation and innovation strategies underscores the interconnected nature of successful organizational
The Value Proposition Canvas empowers organizations to carve out a distinctive identity by honing in on the unique value they offer to customers. By meticulously analyzing customer segments, pains, and gains, businesses can tailor their products or services to stand out in competitive landscapes. This differentiation is pivotal for success in a dynamic market where adapting to changing customer preferences is paramount.
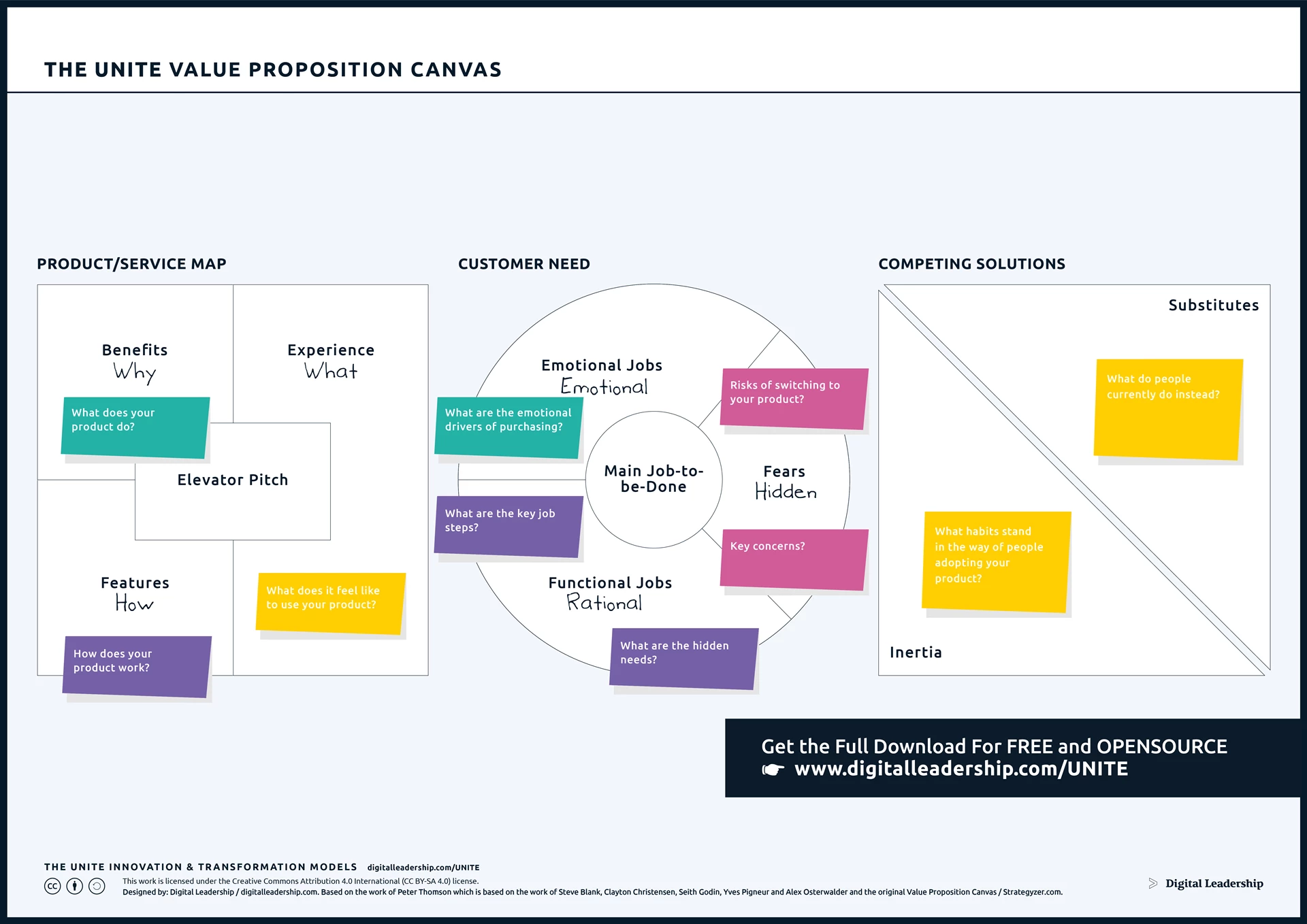
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Based on the work of Peter Thomson which is based on the work of Steve Blank, Clayton Christensen, Seith Godin, Yves Pigneur and Alex Osterwalder and the original Value Proposition Canvas
3- Functional Level Strategy
Functional Level Strategy is the detailed plan of action implemented within specific functional areas of a business to contribute to the overall success defined by higher-level strategies. It focuses on optimizing the performance of individual departments such as marketing, operations, finance, and human resources. Operational excellence, efficient resource allocation, innovation, and technology utilization, human resource management, and targeted marketing and sales strategies are key components of Functional Level Strategy. By aligning the activities of each department with the broader organizational goals set by Corporate and Business Level Strategies, Functional Level Strategy ensures that every aspect of the business operates cohesively. It is the bridge that connects overarching strategic objectives with the day-to-day operations, enhancing the overall effectiveness and competitiveness of the organization.
Importance of Business Level Strategy
A well-defined business level strategy is crucial for several reasons, each contributing to the overall success of an organization.
- Competitive Advantage: Establishing a unique position in the market.
- Resource Allocation: Efficiently distributing resources for maximum impact.
- Customer Value Proposition: Enhance value creation that resonates with the target audience.
- Focus and Alignment: Aligning the entire organization towards common goals.
- Market Positioning: Strategically positioning the business in the market.
- Adaptation to Environmental Changes: Remaining agile in a dynamic business environment.
- Profitability and Sustainability: Ensuring long-term success through profitable operations.
- Decision-Making Framework: Guiding decision-making processes based on strategic goals.
- Brand Image and Reputation: Building a strong brand presence and positive reputation.
- Communication and Coordination: Fostering effective communication and coordination across the organization.
Types of Business Level Strategy
Business Level Strategy encompasses various approaches that companies adopt to gain a competitive edge within their specific market or industry. These strategies guide a company on how to position itself relative to competitors and create a unique value proposition for customers. Porter’s Generic Strategy aligned with business level strategy helps organizations strategically position themselves in the market and secure a lasting competitive advantage.
Integrating Porter’s Value Chain Model into Business Level Strategy enhances organizational efficiency, fosters innovation in value creation, and contributes to the overall success of strategic positioning in the competitive landscape.
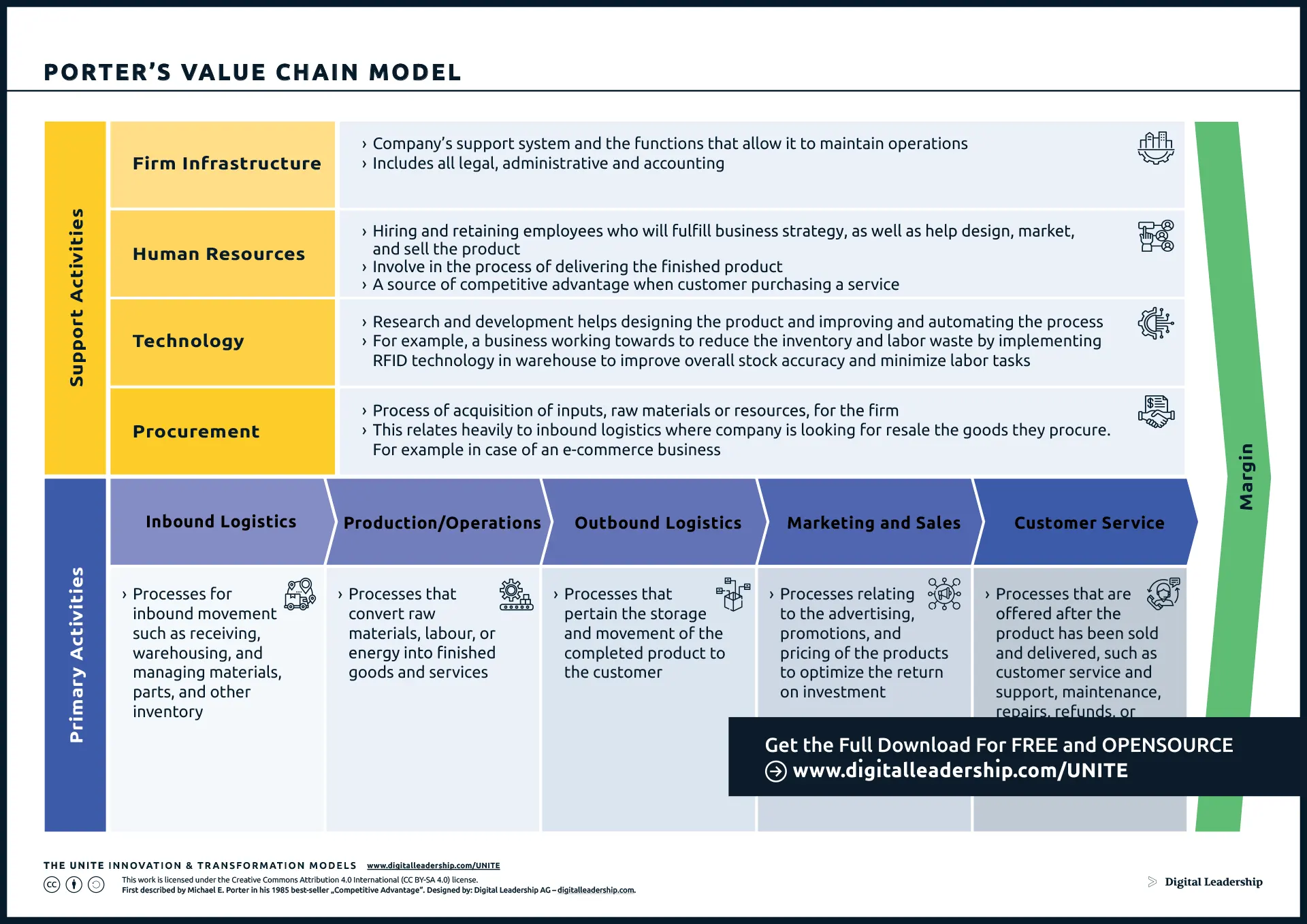
First described by Micheal E.Porter in his best-seller “Competitive Advantage”, Designed by: Digital Leadership AG
Here are some common types of different Business Level Strategies:
Cost Leadership Strategy
Cost leadership revolves around efficient cost management, allowing businesses to offer competitive prices and potentially gain market share. Success requires maintaining a balance between cost reduction and delivering quality products or services.
Key Elements:
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining processes and controlling production costs.
- Economies of Scale: Capitalizing on larger production volumes for cost advantages.
- Technological Investments: Embracing automation and digital technologies for efficiency.
- Supply Chain Management: Negotiating favorable deals, and minimizing inventory costs.
- Product Standardization: Simplifying production through standardized offerings.
Benefits:
- Competitive Pricing: Attracting price-sensitive customers with lower prices.
- Market Share Expansion: Gaining a larger market share in price-sensitive markets.
- Barriers to Entry: Creating obstacles for competitors due to cost-efficient processes.
Risks:
- Imitation: Competitors replicating cost leadership strategies.
- Quality Perception: Risk of being seen as a low-quality provider.
- Market Changes: Vulnerability to disruptions or rapid market shifts
Differentiation Strategy
Differentiation strategy centers on offering unique value to stand out in the market, commanding premium prices and fostering brand loyalty. The challenge lies in sustaining distinctiveness amidst evolving customer preferences.
Key Elements:
- Innovative Products: Introducing unique features and creativity.
- Quality Excellence: Emphasizing superior product and service quality.
- Brand Image: Building a strong brand through effective marketing.
- Customer Experience: Providing exceptional service and personalized interactions.
- Exclusive Distribution: Controlling product access through unique channels.
Benefits:
- Premium Pricing: Charging higher prices due to perceived added value.
- Brand Loyalty: Cultivating strong customer loyalty with unique offerings.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: Customers may accept higher prices for distinctiveness.
Risks:
- Imitation: Competitors may replicate successful differentiators.
- Costs of Innovation: Investments in uniqueness may lead to higher production costs.
- Market Changes: Shifting customer preferences can impact differentiation effectiveness.
Focused Differentiation Strategy
Businesses zoom in on a specific market segment, delivering highly differentiated products or services tailored to its unique needs.
Key Characteristics:
- Targeted Market: Focusing efforts on a well-defined segment.
- Unique Value: Offering distinct products aligned with segment-specific needs.
- Deep Understanding: Grasping preferences and requirements of the chosen market.
- Specialized Brand Image: Creating a brand that resonates with the targeted audience.
Benefits:
- Premium Pricing: Charging more for unique offerings.
- Loyalty: Cultivating strong loyalty within the focused market.
- Reduced Competition: Operating in a niche minimizes direct competition.
Risks:
- Limited Market Size: The segment may be small.
- Changing Preferences: Shifts in preferences can impact success.
- Dependency: Success relies on sustained satisfaction within the chosen market.
Focused Low-Cost Strategy
Focused low-cost strategy directs businesses to a specific market segment, prioritizing cost leadership to deliver products or services at a lower price point.
Key Characteristics:
- Targeted Market: Concentrating efforts on a specific and well-defined market segment.
- Cost Leadership: Prioritizing efficiency and cost reduction in production and operations.
- Simplified Offerings: Streamlining product or service features to minimize costs.
- Value for Price: Providing affordability as a primary selling point within the chosen market.
Benefits:
- Competitive Pricing: Offering products at lower prices compared to competitors.
- Market Accessibility: Attracting budget-conscious consumers within the focused segment.
- Cost Efficiency: Streamlining operations for optimal cost-effectiveness.
Risks:
- Quality Perception: Balancing cost savings without compromising perceived quality.
- Limited Market Size: The segment may be restricted in size.
- Dependency: Success heavily relies on sustaining cost advantages.
Integrated Low-Cost Differentiation
Integrated low-cost differentiation strategy represents a dual focus on achieving both cost leadership and product differentiation concurrently.
Key Characteristics:
- Cost Leadership Emphasis: Prioritizing cost efficiency in production and operations.
- Product Uniqueness: Offering differentiated products or services with unique features.
- Operational Optimization: Streamlining processes to reduce costs while maintaining distinctiveness.
- Value Proposition Balance: Striking a harmonious balance between affordability and unique offerings.
Benefits:
- Competitive Edge: Combining cost advantages with unique product features.
- Broad Market Appeal: Attracting a diverse customer base with varied preferences.
- Resilience: Navigating market changes by having a dual advantage.
Risks:
- Complex Execution: Balancing cost and differentiation can be challenging.
- Operational Strain: Maintaining efficiency while innovating requires careful management.
- Market Perception: Ensuring customers recognize and appreciate the dual value.
Integrated Cost Leadership/Differentiation Strategy
Integrated cost leadership/differentiation strategy is a hybrid approach that amalgamates elements of both cost leadership and differentiation, establishing a distinctive market position.
Key Characteristics:
- Cost Efficiency: Prioritizing cost control in operations and production.
- Product/Service Uniqueness: Offering differentiated features or attributes.
- Strategic Positioning: Carving out a unique market space by combining cost and differentiation.
- Comprehensive Value Proposition: Providing value through both affordability and unique offerings.
Benefits:
- Competitive Advantage: Possessing a dual edge in cost and uniqueness.
- Market Flexibility: Appealing to a broad audience with diverse preferences.
- Innovation Capability: Balancing innovation with operational efficiency.
Risks:
- Resource Intensity: Managing the demands of both cost control and innovation.
- Strategic Alignment: Ensuring seamless integration of cost and differentiation strategies.
- Market Recognition: Communicating the dual value proposition effectively.
Business Level Strategy Examples
Business level strategies are foundational frameworks that guide organizations in navigating the competitive landscape within their industries. These strategies determine how companies position themselves, compete, and enhance value creation for their target audiences. Let’s delve deeper into notable examples that highlight diverse approaches to achieving success, exploring business level strategies examples across various industries.
Cost Leadership: Walmart Business Level Strategy
Walmart’s business level strategy example revolves around cost leadership, positioning itself as a retail giant committed to providing goods at the most competitive prices. Through the strategic execution of economies of scale, operational efficiency, and the implementation of an Everyday Low Prices (EDLP) strategy, Walmart has secured its status as a market leader. The company’s relentless focus on negotiating favorable deals with suppliers, optimizing supply chain management, and embracing technological advancements has not only contributed to consistent low pricing but also enabled Walmart to dominate the global retail landscape.
While the cost leadership strategy has garnered a diverse customer base and a wide product range, challenges such as potential imitation by competitors and the delicate balance between low prices and quality perception require ongoing attention. In the face of evolving consumer preferences and the rise of e-commerce, Walmart looks to the future with continued investments in digital strategies and a commitment to sustainable business practices to maintain its position as a cost leader in the retail industry.
Differentiation: Apple Business Level Strategy
Apple’s business level strategy centers on differentiation, positioning the company as a premier brand through a relentless focus on innovation, design, and an unparalleled Customer experience. The hallmark of Apple’s success lies in its commitment to introducing groundbreaking technologies, and distinctive product designs, and fostering a seamless ecosystem across its devices. This emphasis on differentiation enables Apple to command premium prices for its products, cultivating strong brand loyalty among consumers. Despite challenges such as market saturation and the rapid pace of technological advancements, Apple remains a leader in various product categories.
Looking ahead, the company may explore diversification into new product areas, further emphasize its services, and integrate sustainability initiatives to continue setting industry standards and maintaining its distinctive edge in the market. Apple’s differentiation strategy not only solidifies its market leadership but also contributes to its enduring status as a symbol of innovation, quality, and customer-centric excellence.
Another examples for companies have employed business level strategies to differentiate themselves and establish unique market positions.
Starbucks Business Level Strategy
Starbucks excels in creating a unique and premium brand image through its business level strategy. The company’s differentiation is evident in its ambiance, high-quality coffee offerings, and overall customer experience. Prioritizing these elements has allowed Starbucks to position itself as more than just a coffee provider, becoming a destination for those seeking an immersive and high-quality coffeehouse experience.
Tesla Business Level Strategy
Tesla’s business level strategy revolves around innovation in the automotive industry. Renowned for producing high-quality electric vehicles, Tesla stands out by prioritizing technological advancements, sustainable practices, and sleek design. This differentiation has positioned Tesla as a leader in the competitive automotive landscape, attracting consumers who value innovation and environmental consciousness.
Netflix Business Level Strategy
Netflix disrupted the entertainment industry with a distinctive business level strategy focused on streaming services. By offering a unique and convenient platform for on-demand content consumption, Netflix differentiates itself from traditional media. The company’s vast library of accessible content has transformed how audiences experience entertainment, showcasing the power of differentiation in a rapidly evolving industry.
Google Business Level Strategy
Google’s dominance is grounded in a business level strategy centered on innovation in search solutions. The company consistently provides user-friendly and efficient search services, differentiating itself by improving search algorithms, offering relevant results, and exploring new technologies. This commitment ensures that Google remains a leader in the online search space, catering to users seeking a seamless and effective search experience.
Integrated Cost Leadership/Differentiation Strategy: Amazon Business Level Strategy
Amazon’s triumph in the realm of e-commerce can be traced back to its astute employment of an Integrated Cost Leadership/Differentiation Strategy. At its core, this strategy revolves around two fundamental pillars: operational efficiency and customer-centric innovation. Amazon’s commitment to operational efficiency is manifested in its revolutionary supply chain management, leveraging cutting-edge technologies and an expansive distribution network. This enables the company to minimize costs and provide competitive pricing to consumers.
Amazon stands out through its unwavering dedication to customer-centric services, introducing initiatives like Prime memberships and same-day delivery. This commitment enhances the overall customer experience, creating a unique value proposition. What sets Amazon apart is the seamless integration of these two aspects – cost leadership and differentiation. While operational efficiency keeps costs in check, the focus on customer experience fosters loyalty, leading to a continuous cycle of satisfaction and business expansion. Amazon’s culture of continuous innovation ensures the strategy remains dynamic, allowing the company to adapt to evolving market demands. In essence, Amazon’s Integrated Cost Leadership/Differentiation Strategy serves as a paradigm for businesses seeking success in the ever-evolving landscape of digital commerce.
Focused Differentiation Strategy: Ferrari Business Level Strategy
Ferrari’s business level strategy revolves around a Focused Differentiation Strategy, positioning the company as a pinnacle in the realm of luxury sports cars and precision engineering. By exclusively targeting a niche market segment that values unparalleled performance, craftsmanship, and brand prestige, Ferrari commands premium prices for its iconic vehicles. This focused approach allows the company to concentrate resources on continuous innovation, pushing the boundaries of automotive excellence. Ferrari’s commitment to exclusivity and high performance has cultivated a devoted customer base, reinforcing its status as a symbol of automotive aspiration. The brand’s limited production runs and meticulous attention to detail further contribute to its aura of rarity and desirability. In essence, Ferrari’s Focused Differentiation Strategy not only ensures a distinctive market position but also encapsulates the essence of automotive luxury and performance.
Focused Low-Cost Strategy: Dollar General Business Level Strategy
Dollar General adopts a Focused Low-Cost Strategy as its core business level strategy, positioning itself as a go-to destination for budget-conscious consumers seeking essential products. By concentrating on providing a wide array of necessities at competitive prices, Dollar General appeals to a specific market segment that prioritizes affordability without compromising quality. The company’s strategic focus on cost efficiency in operations enables it to maintain low prices, further attracting price-sensitive consumers. Dollar General’s extensive network of stores, streamlined supply chain, and emphasis on in-house brands contribute to its ability to offer budget-friendly options. This strategic alignment with the needs of cost-conscious shoppers has propelled Dollar General to establish a prominent presence in the retail landscape, reflecting the success of its Focused Low-Cost Strategy.
Integrated Low-Cost Differentiation: Toyota Business Level Strategy
Toyota’s business level strategy is characterized by an Integrated Low-Cost Differentiation approach, blending cost leadership and product differentiation to create a unique market position. The company focuses on producing reliable and affordable vehicles while incorporating innovative features that set its products apart. By integrating cost-effective manufacturing processes with a commitment to technological advancements and quality, Toyota ensures that its vehicles cater to a broad consumer base.
The strategic combination of cost efficiency and product innovation allows Toyota to provide value to customers, offering them reliable transportation options with added features. This approach has been instrumental in establishing Toyota as a global automotive leader, with a diverse product lineup that appeals to a wide range of consumers seeking both affordability and advanced features in their vehicles. Toyota’s Integrated Low-Cost Differentiation Strategy exemplifies a harmonious balance between cost-consciousness and product excellence.
Choose and Implement the Right Business-Level Strategy Steps
Choosing and implementing the right business-level strategy is a crucial step for organizations aiming to achieve sustainable success in their respective industries. The following steps provide a structured guide for this strategic process:
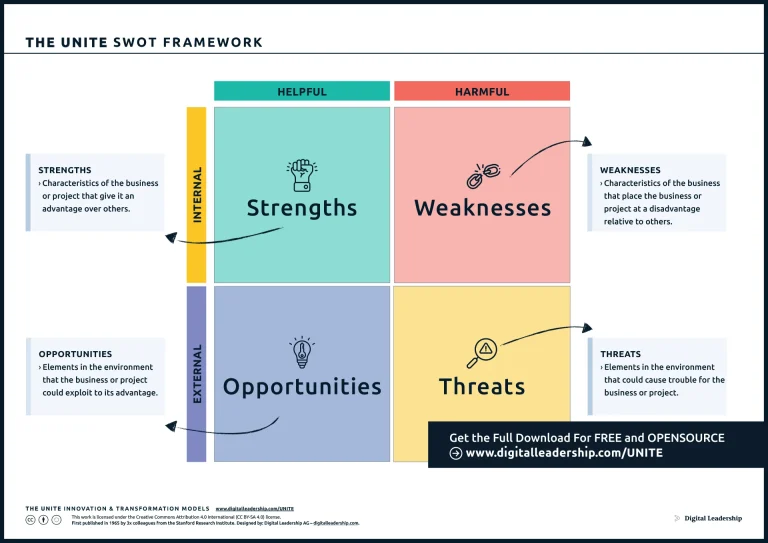
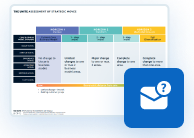
1- Conduct a SWOT Analysis:
Conducting a SWOT analysis is a fundamental step in strategic planning, providing a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s internal and external factors. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Identify and list internal factors contributing positively to the organization, such as a strong brand, skilled workforce, or advanced technology.
- Examine internal factors posing challenges, including areas where the organization may lag behind competitors or weaknesses in processes and infrastructure.
- Explore external factors for potential growth, considering emerging market trends, technological advancements, or collaboration opportunities.
- Recognize external factors that may pose risks, including competitive pressures, regulatory changes, or economic uncertainties.
- Highlight distinctive capabilities and competencies that give the organization a competitive advantage.
- Pinpoint specific areas for performance enhancement by evaluating gaps in skills, technology, or processes.
- Consider strategic actions like employee training, process optimization, or investments to address identified areas.
The integration of the SWOT framework ensures that business-level strategies are well-informed and aligned with the internal and external factors identified through the analysis, contributing to effective strategic decision-making and sustainable success.

First Published in 1965 by 3x colleagues from the Stanford Research Institue. Designed by: Digital Leadership AG
2. Define Your Core Competencies
Defining your core competencies is a pivotal step in crafting a business-level strategy that aligns with your organization’s strengths and positions you competitively in the market. Here’s how to navigate this crucial aspect:
- Conduct an internal audit to pinpoint the unique strengths and capabilities that set your organization apart.
- These strengths could be in areas such as technology, human resources, innovation, or operational efficiency.
- Evaluate how these identified strengths contribute to a competitive advantage.
- Consider aspects like cost efficiency, product differentiation, or superior customer service.
- Analyze how your strengths translate into value for your customers.
- Identify aspects of your products or services that resonate with customer needs and preferences.
- Compare your competencies with those of key competitors.
- Determine where you excel and where you may need to enhance or differentiate your offerings.
- Prioritize the core competencies that align most closely with your strategic objectives.
- Focus on those competencies that offer a sustainable advantage and are challenging for competitors to replicate.
- Recognize that core competencies often involve cross-functional collaboration.
- Integrate expertise from different areas of your organization to leverage comprehensive strengths.
- Commit to a culture of continuous improvement in your core competencies.
- Regularly reassess and enhance these competencies to stay ahead of market changes.
- Confirm that your core competencies align with the overall business-level strategy you’ve chosen.
- Ensure coherence between your strengths and the strategic direction you aim to pursue.
- Clearly, communicate identified core competencies to internal stakeholders.
- Foster a shared understanding of these strengths and their significance in achieving organizational goals.
3. Understand the Competitive Environment
Understanding the competitive environment is a pivotal step in crafting a business-level strategy that capitalizes on opportunities and mitigates threats. Here’s a detailed guide on how to navigate this crucial aspect:
- Conduct a Comprehensive Market Analysis
- Identify Key Competitors
- Supplier and Partner Analysis
- Competitive Positioning
- Risk Assessment
4. Identify Target Customer Segments
- Gather Data through Market Research
- Define segmentation criteria
- Develop detailed customer personas
- Evaluate Segment Attractiveness
- Competitor Analysis
- Consider Behavioral Insights
- Align with Value Proposition
- Evaluate the accessibility and reach of each segment
- Test and Validate the appeal of your offerings within selected segments.
- Segmentation Flexibility into your strategy to adapt to shifts in consumer behavior or market trends.
- Customized Marketing Mix (product, price, place, promotion) to suit the preferences and expectations of each segment.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your segmentation strategy.
5. Select the Right Business-Level Strategy
Selecting the right business-level strategy is a critical decision that determines how your organization will compete in the market. Follow these steps to make an informed choice:
- Evaluate Strategic Options
- Consider Market Positioning
- Choose a strategy that leverages your organization’s core competencies.
- Evaluate the resources required to implement the chosen strategy
- Assess the level of risk associated with each business-level strategy
- Define how the chosen strategy will create value for your customers.
- Evaluate the sustainability of the chosen strategy over the long term
- Ensure alignment between the chosen business-level strategy and your overall organizational strategy.
- Assess how the selected strategy will confer a competitive advantage
- Choose a strategy that allows for flexibility and adaptation
- Clearly communicate the chosen business-level strategy
6. Align Functional Areas with the Strategy
Aligning functional areas with the chosen business-level strategy is crucial for effective implementation. Follow these steps to ensure seamless alignment:
- Clearly communicate the chosen business-level strategy to all departments and functional teams.
- Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each functional area in supporting the chosen strategy.
- Provide training and development programs to equip teams with the necessary competencies.
- Align KPIs with the objectives of the chosen business-level strategy to track performance effectively.
- Implement regular feedback mechanisms to assess the alignment of functional areas with the strategy.
- Encourage a culture of adaptation and flexibility, allowing functional areas to respond to changing circumstances.
- Introduce incentives and recognition programs tied to the successful execution of the strategy.
- Align software, tools, and systems with the requirements of the chosen strategy.
- Conduct Regular Review Meetings:
- Provide strategic leadership that emphasizes the importance of cross-functional alignment.
7. Develop Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Developing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is a crucial step in ensuring the effective implementation and monitoring of your chosen business-level strategy. Follow these guidelines to establish meaningful and measurable KPIs:
- Ensure that each KPI Align with Strategic Objectives
- Formulate KPIs using Quantifiable Metrics
- Consider the interests and concerns of various stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, and management.
- Balance Leading and Lagging Indicators to provide a comprehensive view of performance.
- Ensure that each KPI meets the SMART criteria
- Establish a Regular Review and Adjustments
- Benchmark your KPIs against industry standards or competitors where applicable.
- Consider adopting a Balanced Scorecard Approach
- Define a clear reporting structure for KPIs
- Integrate KPI tracking with existing data systems and analytics tools
- View the establishment of KPIs as an iterative process that allows for continuous improvement.
8. Implement Operational Changes
Once you’ve selected the appropriate business-level strategy, the next crucial step is to implement operational changes effectively. Here’s a guide to implementing operational changes aligned with your chosen strategy:
- Develop an Implementation business Plan
- Engage Leadership and Employees:
- Identify and allocate the necessary resources
- Provide training programs to equip employees with the skills required for the new operational model.
- Review existing processes and workflows to identify areas that need modification.
- Integrate or upgrade technology systems to align with the chosen strategy.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics
- Implement feedback mechanisms
- Identify potential risks and Monitor any challenges
- Embrace a culture of continuous improvement.
- Document changes and updates to standard operating procedures (SOPs) and policies.
- Ensure that the organizational culture aligns with the new operational model.
The Unite Organizational Culture Canvas encompasses the shared values, beliefs, and practices that define how employees interact and work together toward common goals within the framework of Business Level Strategy. It becomes instrumental in aligning the internal cultural aspects of a company with its strategic objectives.
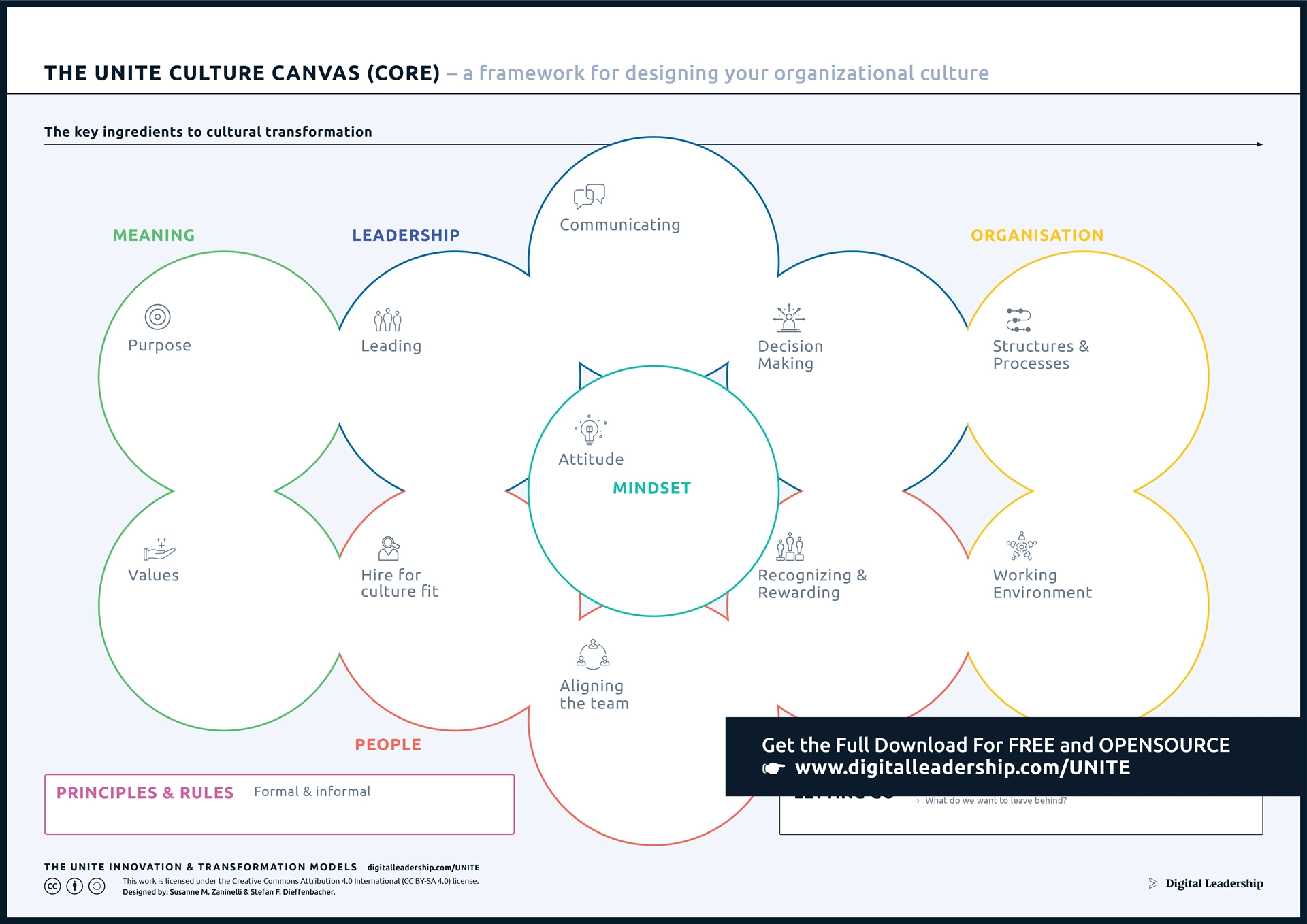
Designed by: Susanne M.Zaninelli & Stefan F.Dieffenbacher
9. Communicate the Strategy Internally and Externally
Effective communication of the chosen business-level strategy is crucial for its successful implementation. Follow these steps to ensure clear and comprehensive communication both internally and externally:
- Develop a Communication Plan:
- Craft Clear and Concise Messages:
- Ensure that top leadership actively participates in communication efforts.
- Conduct interactive sessions with internal teams to explain the strategy in detail.
- Utilize Multiple Communication Channels:
- Create visual aids, infographics, and documentation
- Implement training programs to equip teams with the skills and knowledge required for strategy execution.
- Establish a feedback mechanism for employees
- Develop an external communication plan for stakeholders outside the organization.
- Ensure consistency in messaging across all communication platforms.
- Celebrate achievements and milestones related to the strategy.
- Recognize that communication is an ongoing process.
10. Monitor and Adjust: Ensuring Strategic Agility
Implementing a business-level strategy is not a one-time effort; it requires continuous monitoring and adaptability. Here’s a structured approach to effectively monitor and adjust your chosen strategy:
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) aligned with the objectives of your business-level strategy.
- Conduct regular assessments to measure performance against established KPIs.
- Establish feedback mechanisms from customers, employees, and other stakeholders.
- Stay attuned to changes in the market environment
- Conduct scenario analyses to anticipate potential challenges or opportunities.
- Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration across departments to gather diverse perspectives.
- Schedule Regular Strategy Reviews:
- Compare your organization’s performance and strategic outcomes with industry benchmarks.
- Emphasize data-driven decision-making in adjusting the strategy.
- Design the strategy implementation with built-in flexibility.
- Promote a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability by actively seeking feedback from employees engaged in strategy execution.
- Document lessons learned during the monitoring and adjustment process.Document lessons learned during the monitoring and adjustment process.
11. Learn from Feedback and Results:
After implementing your chosen business-level strategy, the journey doesn’t end; it evolves. Actively seek feedback and closely monitor the results of your strategy’s execution. Here’s how you can leverage this ongoing learning process:
- Implement feedback systems that gather insights from customers, employees, and other relevant stakeholders.
- Analyze Performance Metrics and Regularly assess key performance indicators (KPIs) associated with your strategy.
- Conduct Customer Surveys and Reviews:
- Engage with employees at various levels to gather insights into the strategy’s implementation.
- Cultivate a culture of adaptability within the organization.
- Compare actual results against the goals and objectives
- Embrace a mindset of continuous improvement for Iterative Strategy Refinement:
- Stay attuned to changes in market dynamics
- Conduct regular strategic reviews and meetings
Business Level Strategy VS Corporate Level Strategy
Business level strategy and corporate level strategy are distinct yet interrelated concepts that play crucial roles in shaping an organization’s overall direction and success. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between these two strategic dimensions:
| Aspect | Business Level Strategy | Corporate Level Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Focus | Specific industry or market segment | Entire organization and its overall direction |
| Decision-Making Level | Operational or business unit level | Top executive and board level |
| Focus on Competitive Advantage | Achieving competitive advantage within a segment | Achieving competitive advantage for the organization |
| Resource Allocation | Specific to the needs of a business unit level strategy | Allocating resources across different business units |
| Risk and Return | Associated with the performance of a specific unit | Risks and returns spread across the entire portfolio |
| Examples | Cost leadership, differentiation, focus strategies | Diversification, mergers and acquisitions |
Linking Business-Level Strategy to Organizational Success
The seamless integration of a well-crafted business level strategy plays a pivotal role in determining organizational success. It serves as the guiding framework that aligns internal processes, allocates resources judiciously, and orchestrates activities to achieve sustainable growth and a distinct competitive edge. A robust business level strategy not only outlines the direction a company should take but also ensures that every facet of the organization works in harmony towards common objectives.
This strategic alignment enhances operational efficiency, fosters innovation, and enables businesses to adapt to dynamic market conditions. Ultimately, the successful implementation of a business level strategy becomes the cornerstone for organizational success, empowering companies to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and carve a meaningful impact within their respective industries.
The integration of business-level strategy, digital transformation strategy, and innovation strategy is imperative for organizations seeking sustained success. Digital transformation is no longer a mere buzzword but a strategic imperative that reshapes the way businesses operate. A robust digital transformation strategy enables organizations to harness the power of emerging technologies, streamline operations, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. Concurrently, an innovation strategy serves as the engine of growth, driving organizations to explore new ideas, reimagine processes, and pioneer solutions that set them apart.
The synergy of these elements creates a dynamic and resilient organizational framework. A well-crafted business-level strategy, when aligned with digital transformation and innovation, positions organizations to navigate the challenges of the digital age effectively. The integrated approach ensures that digital initiatives are not isolated endeavors but integral components contributing to overarching business objectives. This synergy cultivates agility, adaptability, and a proactive stance, enabling organizations not only to respond to industry disruptions but to lead them.
Conclusion
Business level strategies are concerned specifically with the ways a company seeks to gain a competitive advantage within its specific market or industry. These strategies focus on the methods and approaches a business employs to differentiate itself from competitors, achieve cost leadership, or target a specific market segment. Crafting and implementing a robust business level strategy is a multifaceted process that requires careful analysis, decision-making, and execution. By understanding the nuances of different business level strategies and following a systematic approach, entrepreneurs can position their businesses for long-term success in dynamic markets. This comprehensive guide serves as a roadmap for entrepreneurs seeking to navigate the complexities of business level strategy, providing actionable insights and examples for strategic success.
Frequently Asked Questions
1- What is the significance of business level strategy?
Business level strategy is crucial for establishing a competitive advantage, allocating resources effectively, creating customer value, and ensuring profitability and sustainability.
2- Business-level strategy addresses which overarching question?
A business-level strategy addresses the overarching question of how a company will compete in a specific market or industry. It involves making choices about how the business will position itself relative to competitors, what customer needs it will fulfill, and how it will achieve a sustainable competitive advantage. In essence, the business-level strategy answers the fundamental question of how the company intends to distinguish itself and create value for its customers within a defined market segment.
3- What is the role of differentiation in business level strategy?
Differentiation involves offering unique products or services that distinguish a business from competitors, allowing it to command premium prices.
4- How often should a business level strategy be reassessed?
Business level strategies should be regularly reassessed in response to changes in the market, competition, and internal capabilities.
5- Why is alignment with functional areas important in strategy implementation?
Alignment with functional areas ensures that every aspect of the organization supports and contributes to the chosen business level strategy.
6- How can a business achieve cost leadership?
Cost leadership can be achieved through operational efficiency, economies of scale, and strategic cost management.




























 Book How to Create Innovation
Book How to Create Innovation