What is Innovation in Business: Meaning, Importance, and Characteristics
In the contemporary business environment, the term “innovation” transcends mere rhetoric; it stands as a transformative force shaping the trajectory of organizational success and longevity. Successfully navigating the innovation process within the framework of an innovation strategy and a digital transformation strategy has evolved into a prerequisite for organizations with aspirations to attain their business goals through business strategy by understanding the diverse types of innovation.
But, What is innovation then? Innovation, at its core, is the dynamic process of introducing novel ideas, strategies, and technologies to revolutionize the way organizations operate, enhance value creation, and interact with their stakeholders. Innovation, entwined with the innovation lifecycle and strategically leveraging innovative technology, is the catalyst reshaping the trajectory of progress across diverse fields.
At Digital Leadership, as experts in Innovation Consulting and Digital Transformation Consulting, our mission is to guide organizations from strategy to execution, ensuring a seamless integration of cutting-edge ideas. Our Innovation Blueprint service serves as the initial step, conducting a thorough assessment of existing innovation practices and seamlessly integrating them into the overarching business strategy.
What is Innovation? Meaning of Innovation
The term “innovation” finds its origins in the Latin verb innovare, signifying renewal, a definition that resonates through time. In its essence, innovation conveys the act of improvement or replacement, be it in processes, products, or services. However, within the intricate landscape of business, a more precise definition is requisite.
Innovation is a dynamic and multifaceted concept that encapsulates the process of introducing novel ideas, methods, products, or services to create positive change and enhance value. It goes beyond mere invention, emphasizing the practical application of inventive thinking to bring about tangible improvements in various aspects of business, technology, or society. Innovation involves a continuous and adaptive journey, requiring organizations to foster a culture that encourages creativity, embraces change, and pursues solutions that lead to meaningful advancements.
Innovation differs from invention, Invention refers to the creation of something entirely new, innovation involves the effective application and implementation of inventive ideas to generate practical and impactful outcomes, driving continuous improvement and positive change in the dynamic landscapes of business, technology, and society.
Beyond its fundamental definition, innovation takes on heightened importance through a unified approach. The Unite Innovation Approach amplifies the significance of innovation, making it a collective force driving positive change across the broader spectrum of human endeavor.
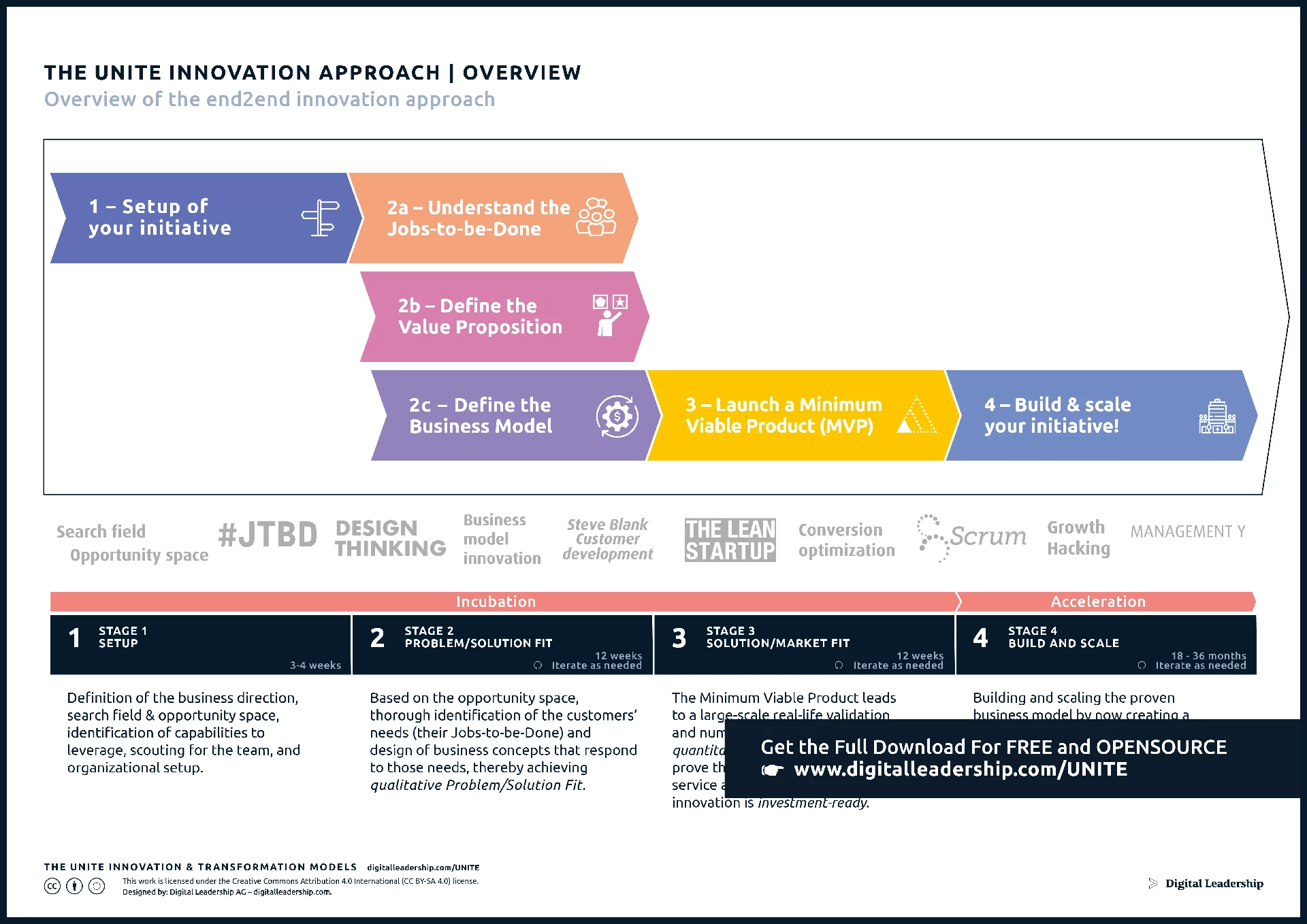
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG
Your download is now available!
You can now access the complete Innovation Approach Package, including a full presentation, related models and instructions for use.
For a comprehensive guide to innovation, including various approaches and strategies, explore our latest offering, the FREE book titled “HOW TO CREATE INNOVATION.” This resource is a treasure trove of insights, offering mindsets, structures, and strategies to innovate more efficiently, with fewer resources and greater success. Don’t miss out – register now for a free download!
What is Innovation in Business? Innovation Definition in Business
In the dynamic landscape of business, innovation serves as the linchpin that harmonizes business strategy orchestrating a symphony of positive change and sustained value creation. Beyond the conventional realm of product development, innovation in business is a strategic imperative interwoven with overarching business strategy. It involves leveraging novel ideas, processes, and technologies to gain a competitive edge, explore new markets, and ensure long-term viability. Simultaneously, innovation seamlessly integrates with digital transformation strategy, propelling businesses into the technologically driven future. This strategy becomes the conduit for reimagining processes, enhancing customer experiences, and staying agile in response to evolving consumer expectations.
Business Model Canvas model serves as the blueprint for translating innovative ideas into tangible outcomes. By outlining the processes, structures, and frameworks for fostering creativity and managing innovation initiatives, a well-defined business innovation model becomes a guiding framework.
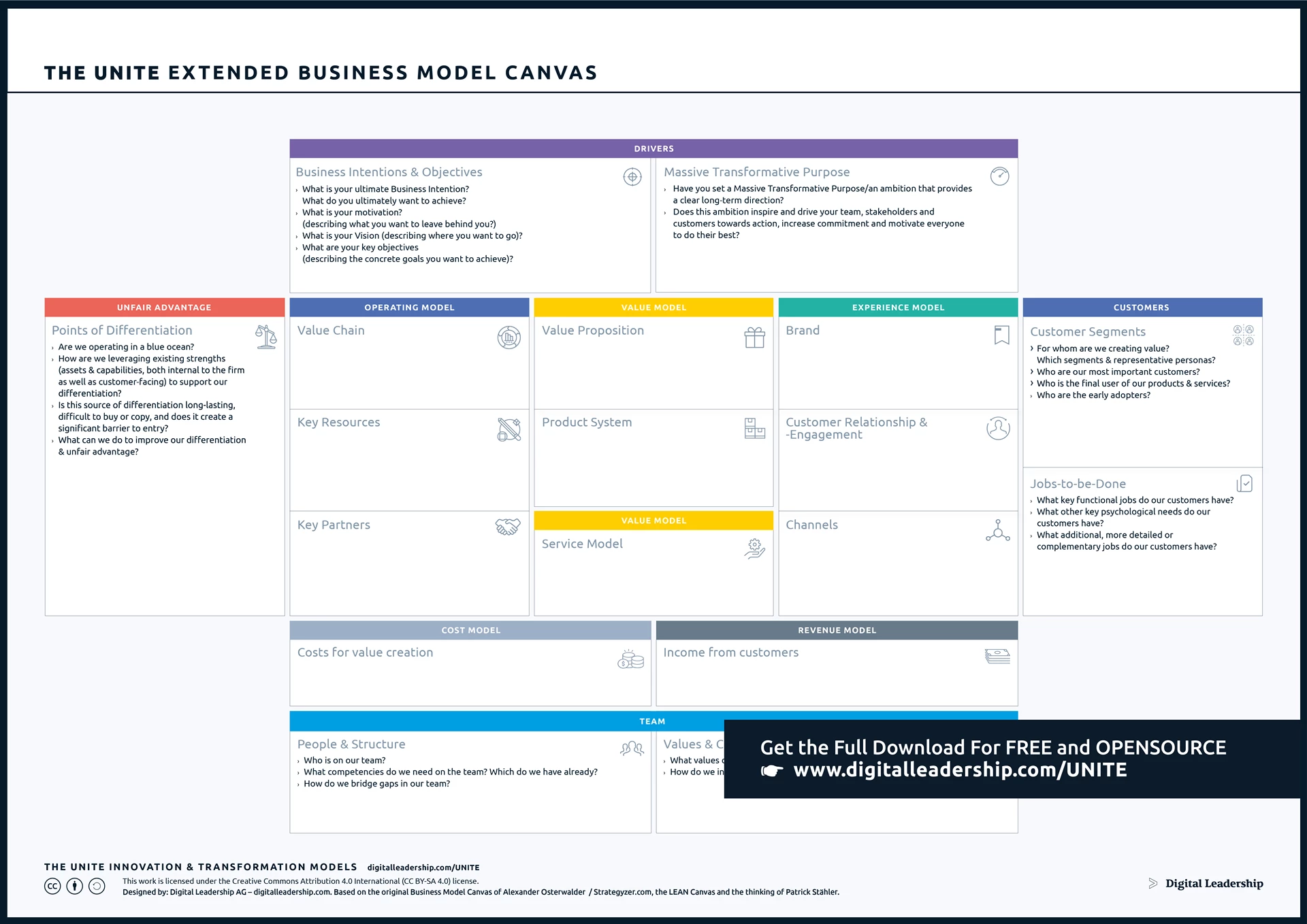
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the work of Alexander Osterwalder, the Lean Canvas and the thinking of Patrick Stahler
Download the Complete eXtended Business Model package, including instructions for putting it to work for you today.
One crucial aspect of fostering innovation is its alignment with the Jobs-to-be-Done” . This framework recognizes that customers “hire” a product or service to get a job done in their lives. Understanding these jobs and designing solutions that address them is integral to successful innovation. It shifts the focus from merely improving products to solving specific customer problems, providing a more targeted and customer-centric approach. You can download it now.
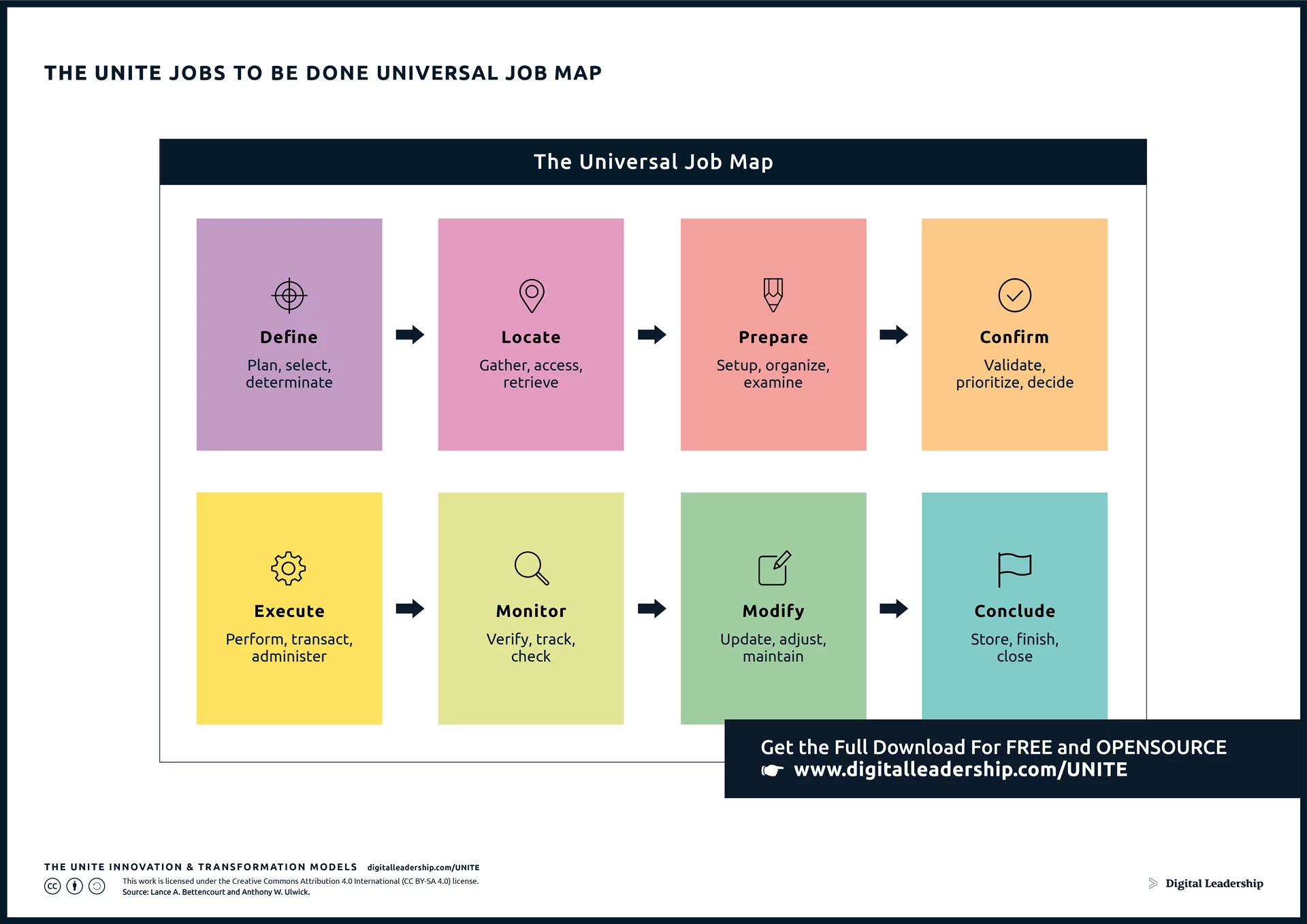
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Source: Lance A. Bettencourt and Anthony W. Ulwick.
Your download is now available!
You can now access the complete Jobs to be Done Package, including a full presentation, related models and instructions for use.
Importance of Innovation: Why is Innovation Important?
The importance of innovation in the contemporary business landscape cannot be overstated. Innovation serves as a catalyst for organizational growth, competitive advantage, and long-term sustainability. Here are key aspects highlighting the benefits of innovation:
- Competitive Strategies:
- Organizations can enhance their competitiveness through strategies such as price leadership or differentiation.
- Innovation is a crucial element for success in both approaches.
- Price Leadership:
- Companies pursuing price leadership must focus on developing innovative, highly efficient processes.
- Process optimization and continuous cost improvement are vital for ensuring long-term competitiveness.
- Differentiation Strategy: Companies opting for a differentiation strategy rely on innovation to create unique features that distinguish them from competitors.
- Start-ups and Innovation: Many start-ups initiate their operations by introducing innovative products or services.
- Continuous Innovation:
- Continuous innovation is essential for the sustained success of all companies.
- The focus of the innovation strategy varies significantly from one company to another.
- Speed of Change: Collaboration and teamwork methods are increasingly employed to foster digital innovations and address challenges in digital transformation.
- Creativity and Innovation:
- Innovation demands a higher degree of creativity than operational business.
- A clear innovation strategy, especially in the “fuzzy front end of innovation,” is essential.
- Relevant Concepts: Concepts like lean innovation and the establishment of community-based innovation networks are gaining significance.
- Modern Tools for Innovation Management: Companies are adopting modern idea management software and innovation management software to efficiently handle innovation processes.
- Adaptability: In a rapidly changing business environment, innovation enables organizations to adapt to evolving market conditions, technological advancements, and customer preferences. It fosters a culture of agility, allowing businesses to stay relevant and responsive to shifts in the industry.
- Efficiency and Productivity: Innovative processes and technologies often lead to increased efficiency and productivity. Automation, streamlined workflows, and the implementation of cutting-edge tools contribute to optimized operations, reduced costs, and enhanced overall performance.
- Customer Satisfaction: Meeting and exceeding customer expectations is a fundamental aspect of innovation. By understanding and addressing underserved customer needs, businesses can create products and services that resonate with their target audience, leading to higher levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Revenue Growth: Innovative products and services have the potential to open up new revenue streams. Organizations that invest in research and development, introduce novel solutions, and adapt to market demands are better positioned to experience sustained revenue growth.
- Risk Mitigation: Embracing innovation can act as a risk mitigation strategy. By diversifying products, services, or digital business models, organizations become more resilient to external disruptions. This proactive approach helps mitigate the impact of unforeseen challenges.
- Talent Attraction and Retention: A commitment to innovation enhances an organization’s appeal to top talent. Innovative companies often attract skilled professionals who are eager to contribute to cutting-edge projects. Moreover, innovation culture contributes to employee engagement and retention.
- Strategic Evolution: Innovation is integral to strategic evolution. Businesses that continuously innovate can adapt their strategies to align with emerging trends, opportunity identification, and navigate industry shifts, ensuring long-term relevance and success.
Why is Innovation Important in Business
Innovation holds a pivotal role in the success and longevity of businesses in the contemporary landscape. Its significance lies in its ability to drive competitive advantage, providing organizations with the means to stand out in crowded markets. Through innovative practices, businesses can foster growth by expanding their product offerings and exploring new market territories.
Crucially, innovation acts as a compass for navigating the ever-changing business environment, allowing companies to adapt swiftly to evolving customer preferences and industry trends. Beyond market dynamics, innovation enhances the intrinsic value delivered to customers, cultivating loyalty and positive brand perception. Moreover, it boosts operational efficiency through streamlined processes, leading to cost savings and heightened productivity.
A culture of innovation not only encourages entrepreneurial thinking but also attracts top talent, creating a dynamic and engaging work environment. By mitigating risks through diversification and meeting sustainability goals, innovation contributes not only to individual business success but also to broader economic growth. In essence, innovation is not merely a strategic choice; it is the heartbeat of thriving and resilient businesses in the modern world.
The Value Proposition Canvas which is a key tool in this step of fostering innovation, becomes invaluable. This canvas provides a structured framework for understanding customer needs, pains, and gains, aligning them with your product or service features. It facilitates a deep understanding of customer segments and aids in crafting a value proposition that directly addresses their requirements.
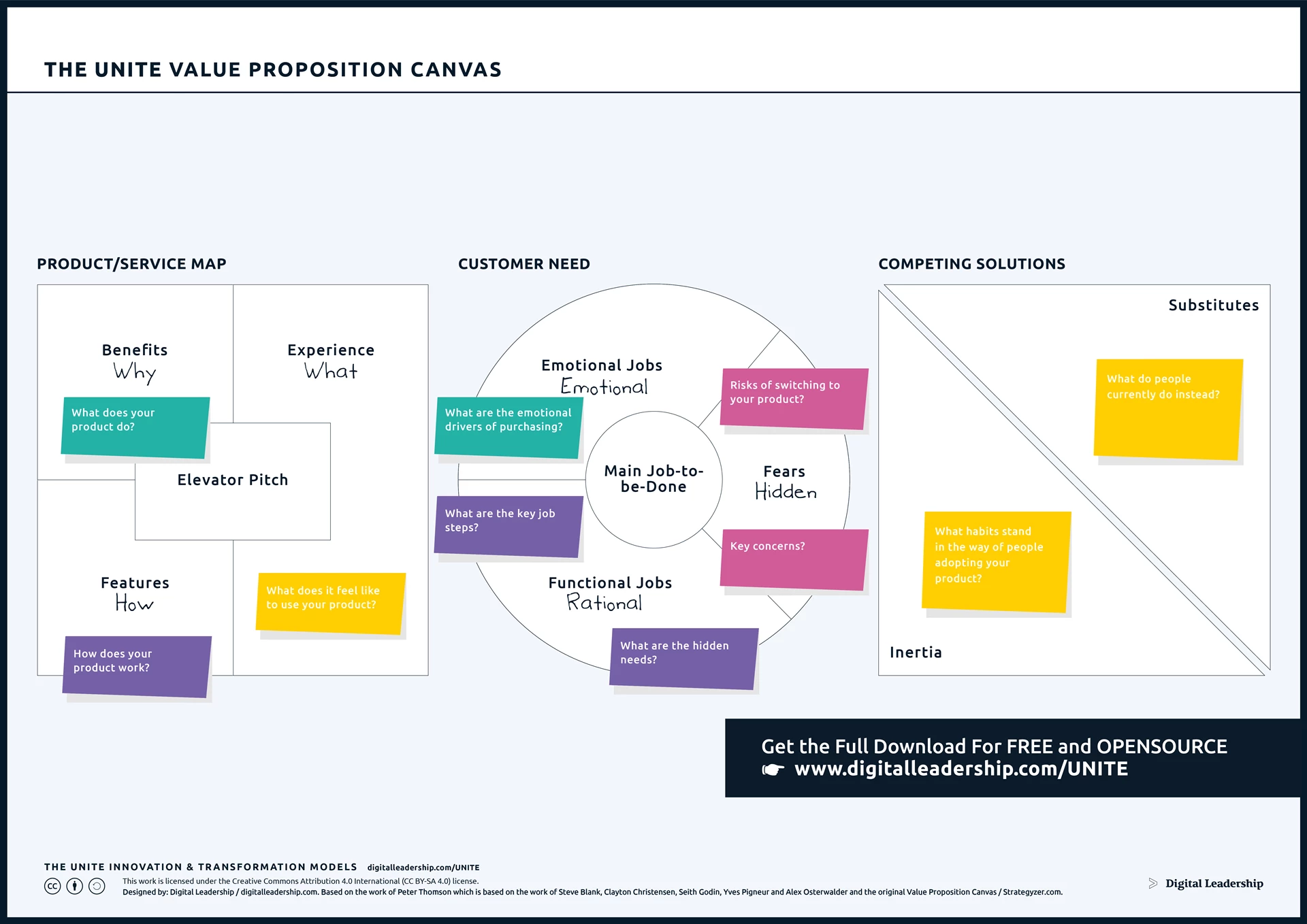
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Based on the work of Peter Thomson which is based on the work of Steve Blank, Clayton Christensen, Seith Godin, Yves Pigneur and Alex Osterwalder and the original Value Proposition Canvas
Download the complete Value Proposition Canvas Package, including instructions for putting it to work for you today.
How Organizations Be Innovative Through Idea Generation
Organizations seeking to stay competitive must continually evolve their approach to innovation. A crucial component of this evolution is mastering the art of idea generation. Here’s a guide on how organizations can become better innovators through effective idea-generation strategies:
1. Cultivate an Innovation Culture
- Encourage Open Communication: Create an environment where employees feel empowered to share their ideas openly. Foster a culture that values diverse perspectives and sees failure as a stepping stone to success.
- Leadership Support: Leaders play a pivotal role in shaping organizational culture. When leaders actively support and participate in idea generation initiatives, it sends a powerful message throughout the organization.
2. Implement Structured Idea Generation Processes
- Brainstorming Sessions: Organize regular brainstorming sessions to facilitate creative thinking. Ensure these sessions are inclusive, allowing input from employees across different departments and hierarchical levels.
- Idea Challenges: Pose specific challenges to your teams and encourage them to come up with solutions. This targeted approach can generate innovative ideas focused on addressing particular organizational needs or opportunities.
3. Leverage Technology for Idea Management
- Innovation Software: Invest in innovation management software to streamline the idea generation process. These platforms can help collect, evaluate, and implement ideas efficiently, fostering a more organized and data-driven approach to innovation.
- Collaboration Tools: Utilize digital collaboration tools to connect teams and facilitate idea sharing, especially in the era of remote work. These platforms create virtual spaces for employees to collaborate on innovative concepts.
4. Embrace Diversity in Idea Generation
- Cross-Functional Teams: Form cross-functional teams to bring together individuals with diverse skills and perspectives. This diversity sparks creativity and allows for a holistic approach to problem-solving.
- External Input: Seek external input through partnerships, collaborations, or customer feedback. External perspectives can provide fresh insights and challenge internal assumptions.
5. Recognize and Reward Innovation
- Incentivize Creative Contributions: Implement recognition and reward programs to acknowledge employees who contribute innovative ideas. This not only motivates individuals but also reinforces the importance of innovation within the organization.
- Celebrate Successes: Publicly celebrate successful innovations, showcasing how ideas have translated into tangible outcomes. This builds a positive feedback loop and encourages a culture of continuous improvement.
6. Provide Training on Creative Thinking
- Training Programs: Offer training programs focused on enhancing creative thinking skills. Equip employees with tools and techniques to approach challenges from different angles and think outside traditional boundaries.
- Foster a Growth Mindset: Encourage a growth mindset, where employees believe in their ability to develop and enhance their skills over time. This mindset fosters resilience in the face of challenges and promotes a willingness to explore new ideas.
7. Establish an Idea Review and Implementation Process
- Regular Reviews: Set up a systematic process for reviewing and evaluating ideas on a regular basis. Establish criteria for selecting ideas that align with organizational goals and have the potential for impactful outcomes.
- Pilot Programs: Before full-scale implementation, consider piloting promising ideas. Pilots allow organizations to test the feasibility and effectiveness of ideas in a controlled environment before committing extensive resources.
8. Learn from Failures and Iterate
- Failure as a Learning Opportunity: Acknowledge that not every idea will lead to success. Instead of viewing failures negatively, treat them as learning opportunities. Extract valuable insights from unsuccessful attempts and use them to refine future approaches.
- Iterative Approach: Embrace an iterative approach to idea generation and implementation. Continuously gather feedback, make improvements, and iterate on existing ideas to enhance their effectiveness over time.
By integrating these strategies into their organizational DNA, businesses can foster an innovation culture and consistently generate impactful ideas. Idea generation is not a one-time event but an ongoing innovation process that, when nurtured, becomes a key driver of organizational success and longevity.
Characteristics of Innovation
Innovation, as a dynamic force propelling organizations forward, is characterized by distinct traits that define its nature and impact. Understanding these characteristics is essential for organizations seeking to harness the power of innovation strategically. Let’s delve into the key characteristics that encapsulate the essence of innovation:
1. Creativity and Novelty
- Inherent Creativity: Innovation is inherently tied to creativity. It involves the generation of novel ideas, solutions, or approaches that go beyond conventional thinking. Creative thinking is the spark that ignites the innovation process.
- Novelty in Solutions: Innovative endeavors strive to introduce something new or significantly different, whether it’s a product, service, process, or business model. This novelty is what sets innovation apart from incremental improvements.
2. Problem-Solving Orientation
- Addressing Challenges: At its core, innovation is about solving problems and addressing challenges. It seeks to find inventive solutions to existing problems or anticipates and addresses emerging challenges in a proactive manner.
- Customer-Centric Focus: Successful innovations often arise from a deep understanding of user needs. Innovators keenly observe and analyze problems from the perspective of end-users, ensuring that the solutions align with real-world needs.
3. Continuous Improvement
- Iterative Nature: Innovation is not a one-time event; it’s a continuous and iterative process. Organizations committed to innovation engage in ongoing improvements, learning from experiences, adapting to feedback, and refining their approaches.
- Feedback Loops: Innovative processes incorporate feedback loops that enable organizations to gather insights, measure outcomes, and make necessary adjustments. This iterative approach contributes to the evolution of ideas and solutions.
4. Adaptability and Flexibility
- Adaptation to Change: Innovation thrives in environments that embrace change. Organizations fostering innovation cultivate a culture that welcomes new ideas, adapts to market dynamics, and responds flexibly to evolving circumstances.
- Agility in Implementation: Innovative organizations exhibit agility in implementing new ideas. They are quick to pivot, experiment, and adjust strategies based on the dynamic nature of their industries and customer expectations.
5. Risk-Taking and Tolerance for Failure
- Risk-Taking Culture: Innovation involves a degree of risk-taking. Innovative organizations create a culture that encourages calculated risks, empowering individuals to explore uncharted territories and challenge the status quo.
- Learning from Failure: Failure is viewed as a valuable source of learning in the innovation process. Innovators understand that not every idea will succeed, and failures provide insights that contribute to future successes.
6. Collaboration and Cross-Functional Teams
- Cross-Pollination of Ideas: Innovation thrives on collaboration. Successful innovators actively foster collaboration among individuals with diverse skills and perspectives. Cross-functional teams bring together different expertise to enrich the creative process.
- Breaking Silos: Innovative organizations break down silos that can stifle the flow of ideas. They encourage open communication across departments, fostering a collaborative spirit that transcends organizational boundaries.
7. Vision and Strategic Alignment
- Strategic Intent: Innovation is guided by a clear vision and strategic intent. Organizations articulate their innovation goals, aligning them with broader strategic objectives. This ensures that innovation efforts contribute directly to organizational success.
- Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Goals: Innovative organizations strike a balance between short-term gains and long-term strategic objectives. They invest in both incremental improvements and disruptive innovations that have the potential to reshape the industry landscape.
8. Technology Integration and Digital Transformation
- Harnessing Technology: Innovation often involves leveraging cutting-edge technologies. Forward-thinking organizations actively explore and adopt technological advancements to enhance their products, services, and operational processes.
- Digital Transformation Initiatives: Innovative organizations embark on digital transformation journeys, integrating digital technologies into various aspects of their operations. This enables them to stay competitive in the digital era.
9. Ethical Considerations and Social Impact
- Ethical Innovation: Innovation is increasingly guided by ethical considerations. Organizations recognize the importance of responsible innovation, ensuring that their endeavors contribute positively to society and align with ethical standards.
- Socially Impactful Solutions: Innovators are mindful of the broader societal impact of their creations. Socially responsible innovation involves developing solutions that not only meet market needs but also contribute to the well-being of communities.
10. Leadership Commitment and Support
- Leadership as Champions: Innovation requires strong leadership commitment. Successful innovators have leaders who champion innovation, actively support idea generation, and provide the necessary resources and encouragement for innovative initiatives.
- Empowering Teams: Innovative leaders empower their teams, fostering a sense of ownership and autonomy. This empowerment encourages individuals to take initiative, explore new ideas, and contribute to the innovation agenda.
In essence, the characteristics of innovation encompass a blend of creativity, adaptability, collaboration, strategic alignment, and ethical considerations. Organizations that embody these traits not only navigate the complexities of today’s business landscape but also position themselves as drivers of positive change and continuous progress.
How to Measure and Manage Innovation In Innovation Process for Innovation Strategy Success
Successfully measuring and managing innovation within the innovation process is crucial for the overall success of an organization’s innovation strategy. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to achieve this synergy for innovation success:
- 1. Define Clear Business Objectives: Clearly articulate the objectives of your innovation strategy. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Having well-defined goals provides a basis for measuring progress.
- 2. Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Identify and establish key performance indicators that align with your innovation objectives. These KPIs can include metrics such as the number of new ideas generated, time-to-market for innovations, cost-effectiveness, and customer satisfaction. Tailor KPIs to reflect both quantitative and qualitative aspects of innovation.
- 3. Implement an Innovation Process: Develop a structured innovation process that guides idea generation, evaluation, and implementation. This process should incorporate stages from ideation to execution, ensuring that innovative concepts are systematically nurtured and brought to fruition.
- 4. Foster Innovation Culture: Cultivate an organizational culture that encourages creativity, risk-taking, and continuous improvement. Ensure that employees feel empowered to contribute ideas, experiment, and challenge the status quo. A supportive culture is essential for the success of any innovation strategy.
- 5. Provide Resources and Support: Allocate the necessary resources, including budget, time, and expertise, to innovation initiatives. Leadership support is critical to overcoming challenges and ensuring that innovative projects have the backing required for success.
- 6. Regularly Assess Progress: Regularly assess and analyze progress against established KPIs. Use data-driven insights to evaluate the effectiveness of innovation initiatives. Identify successful practices and areas for improvement, adjusting strategies accordingly.
- 7. Encourage Cross-Functional Collaboration: Facilitate collaboration among diverse teams and departments. Cross-functional collaboration brings varied perspectives to the innovation process, fostering a rich environment for creativity and problem-solving.
- 8. Embrace Continuous Learning: View setbacks and failures as opportunities for learning and improvement. Encourage a mindset that values experimentation and views failures as stepping stones to success. Continuous learning enhances adaptability and resilience in the face of challenges.
- 9. Integrate Feedback Loops: Establish feedback loops that allow for ongoing communication between different stages of the innovation process. This ensures that adjustments can be made promptly based on insights gained during implementation.
- 10. Align with Business Strategy: Ensure that innovation efforts align with the broader business strategy. A cohesive integration of innovation into the organizational strategy ensures that innovative endeavours contribute directly to long-term business goals.
By conscientiously integrating these measures into the business purpose organizations can effectively measure, manage, and enhance their innovation strategies, fostering an environment conducive to continuous growth and success.
Types of Innovation and Strategic Selection for Business Strategy Success
In the pursuit of organizational growth and competitiveness, understanding the various types of innovation and strategically selecting the right one is paramount. Here’s an exploration of different types of innovation and a guide on how to choose the most fitting for your business strategy:
- Incremental Innovation:
- Description: Making small improvements to existing products, processes, or services.
- Benefits: Low-risk, continuous improvement, often well-received by existing customers.
- When to Choose: Suitable for steady progress without radical changes, maintaining market share, or refining existing offerings.
- Disruptive Innovation:
- Description: Introducing new products or services that significantly alter existing markets.
- Benefits: Opens new markets, and can lead to industry transformation.
- When to Choose: Ideal for revolutionizing industries, entering new markets, or challenging existing business models.
- Radical Innovation:
- Definition: Involves the development of entirely new products, services, or processes that significantly disrupt and reshape existing markets or industries.
- Characteristics:
- Transformational impact.
- High level of risk.
- Shift in customer expectations.
- Examples:
- The introduction of the personal computer in the 1970s.
- The advent of smartphones combines communication, computing, and entertainment.
- Architectural Innovation:
- Definition: Involves making significant changes to the underlying design or structure of a product, system, or organization.
- Characteristics:
- Structural modification.
- Integration of components.
- Optimization of interactions.
- Examples:
- The transition from traditional landline telephony to Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology.
- The development of hybrid electric vehicles that combine traditional combustion engines with electric propulsion.
- Open Innovation:
- Description: Collaboration with external partners, customers, or even competitors to generate ideas and solutions.
- Benefits: Access to diverse expertise, accelerates innovation cycles.
- When to Choose: Ideal for organizations looking to tap into external creativity, leverage external resources, and foster a collaborative ecosystem.
- Platform Innovation:
- Description: Creating a foundation (platform) that allows others to build upon and contribute.
- Benefits: Enables ecosystem growth, and fosters third-party innovations.
- When to Choose: Suitable for businesses aiming to create ecosystems, expand service offerings, and leverage external contributions.
- Process Innovation:
- Description: Optimizing internal operations and workflows.
- Benefits: Increased efficiency, cost reduction, improved productivity.
- When to Choose: Ideal for enhancing operational effectiveness, streamlining workflows, and reducing costs.
- Product Innovation:
- Description: Focusing on creating new or significantly improved products.
- Benefits: Appeals to customer preferences, potentially opens new markets.
- When to Choose: Suitable when there’s a need for differentiated offerings, entering new markets, or responding to changing customer demands.
- Service Innovation:
- Description: Introducing new or enhanced services to meet customer needs.
- Benefits: Improved customer experience, and differentiation in the market.
- When to Choose: Appropriate for enhancing customer satisfaction, creating new revenue streams, or standing out in a service-oriented market.
Choosing the Right Type of Innovation for Your Business Strategy:
By carefully considering the following factors, organizations can strategically select the type of innovation that best suits their business context, ensuring sustainable growth, and maintaining a competitive edge in the dynamic business landscape.
- Assess Business Objectives:
- Align the choice of innovation with overarching business goals and objectives.
- Analyze Market Dynamics:
- Consider the competitive landscape, market trends, and customer needs to identify opportunities for innovation.
- Evaluate Resources and Capabilities:
- Assess the organization’s internal capabilities, resources, and readiness for different types of innovation.
- Consider Risk Tolerance:
- Evaluate the organization’s risk tolerance and choose an innovation type that aligns with the acceptable level of risk.
- Customer-Centric Approach:
- Prioritize innovation types that resonate with customer needs and preferences.
- Long-Term Strategy:
- Choose innovations that align with the organization’s long-term strategic vision and positioning.
- Collaboration Potential:
- Assess the potential for collaboration and determine if open innovation or platform innovation aligns with the organizational culture.
- Monitor Industry Trends:
- Stay abreast of industry trends to identify emerging opportunities and disruptive forces that may influence the choice of innovation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the meaning, importance, and characteristics of innovation is paramount for businesses striving to thrive in today’s competitive environment. Whether incremental or disruptive, innovation is the driving force behind sustained success.
Recent Posts
Business Level Strategy Examples, Types, Definition and Implementing Steps For Successful Strategy
Social ShareIn the business environment, the choice of an effective strategy can...
View Full article
Radical Innovation Meaning, Examples and Characteristics
Social ShareRadical innovation is a main type of innoavtion that involves the...
View Full article
























 Book How to Create Innovation
Book How to Create Innovation