Types of Innovation: Choosing the Right Innovation Type Steps
Published: 15 December, 2023
Innovation
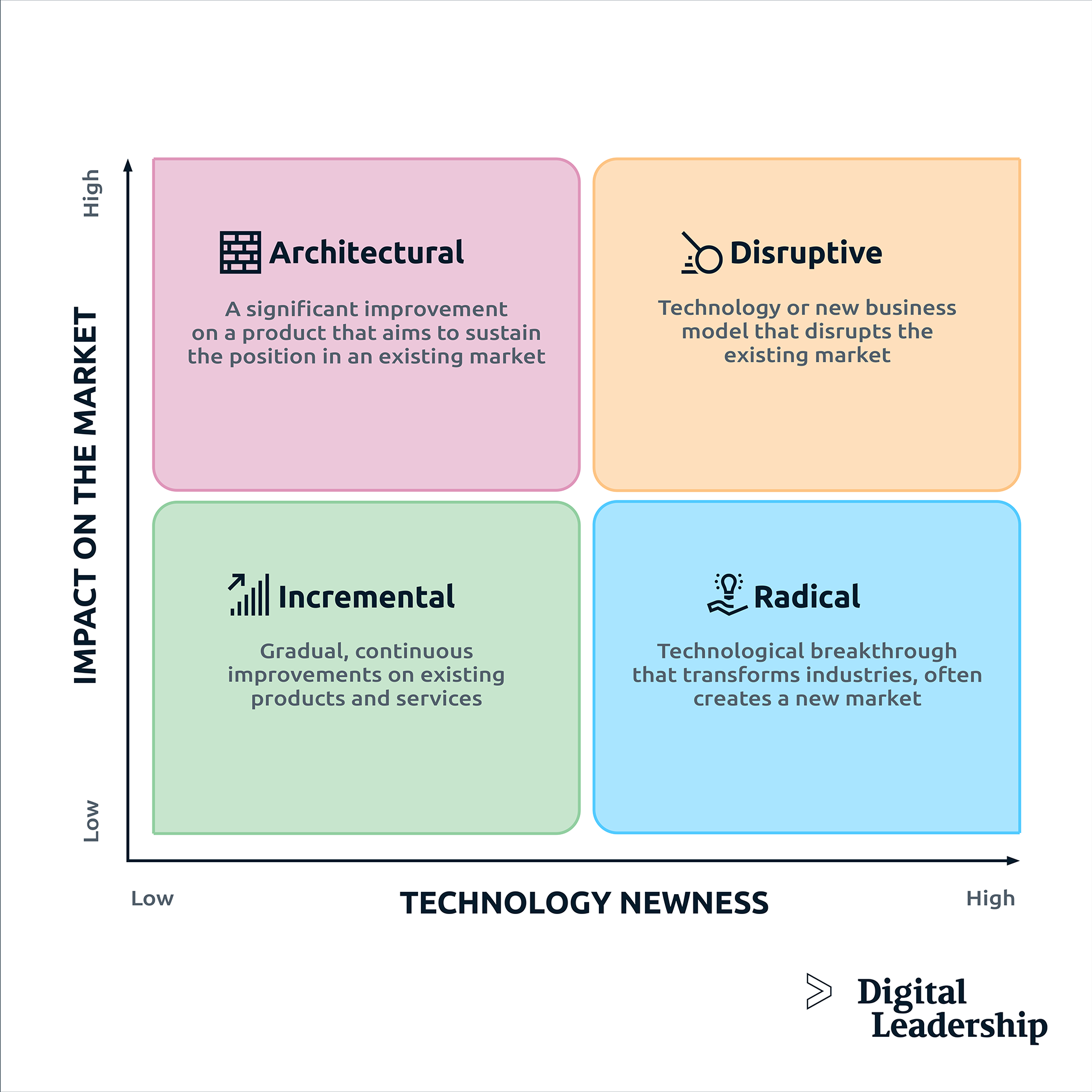
Table of Contents
Understanding the various types of innovation holds significant importance. Innovation extends beyond the creation of new products or services; it encompasses discovering improved ways to assist customers, enhancing operational processes utilizing insights from the jobs to be done theory, crafting innovative business strategies and augmenting organization capacity for value creation and resilience. Armed with knowledge about the four primary types of innovation, businesses can formulate intelligent plans tailored to their Strategic goals and circumstances.
Picking the right innovation type for what a business needs can up their chances of doing well in the market and making customers happy for a long time by Understanding Your Customer Needs. Just focusing on one type of innovation isn’t enough – a really good plan should use all four types of innovation with a well-crafted innovation strategy to grow, work better, and stay ahead of the other businesses.
At Digital Leadership, we understand the significance of continuous innovation for businesses to stay competitive and bring positive change to their customers’ lives, our Innovation blueprint service serves as the starting point, conducting a meticulous evaluation of current innovation practices and integrating them into the overall business plan. This sets the foundation for businesses to choose from our tailored services as Innovation Consulting which aligned with their distinct needs and innovation objectives.
What is Innovation? The Innovation Concept
Innovation entails the methodical practice of creating and promoting groundbreaking products and services with the aim of being adopted by customers, It serves as the driving force propelling organizations forward, enabling them to adapt, thrive, and stay ahead of the curve. In entrepreneurship, defining innovation is crucial—it’s the proactive pursuit of novel ideas, products, or methods, that form the bedrock of transformative change.
So, what are innovations? They are the deliberate and transformative acts of introducing meaningful changes to products, services, or processes. Beyond mere novelty, innovation in entrepreneurship involves enhancing value creation, meeting underserved customer needs, and challenging the status quo. It ranges from incremental improvements to groundbreaking disruptions, each contributing to overall growth and sustainability.
It involves doing so with purpose, relevance, and strategic intent. Innovations become cornerstones upon which businesses build their competitive advantage, shaping industries and carving unique identities in the market. Innovation is all about meeting the evolving needs and expectations of customers and bringing value to society, jobs to be done theory is a popular approach that can help achieve this goal. By identifying the specific jobs customers hire products or services for, businesses can develop more effective and customer-focused solutions.
The “Jobs-to-be-Done” framework recognizes that customers “hire” a product or service to get a job done in their lives. Understanding these jobs and designing solutions that address them is integral to successful innovation. It shifts the focus from merely improving products to solving specific customer problems, providing a more targeted and customer-centric approach.
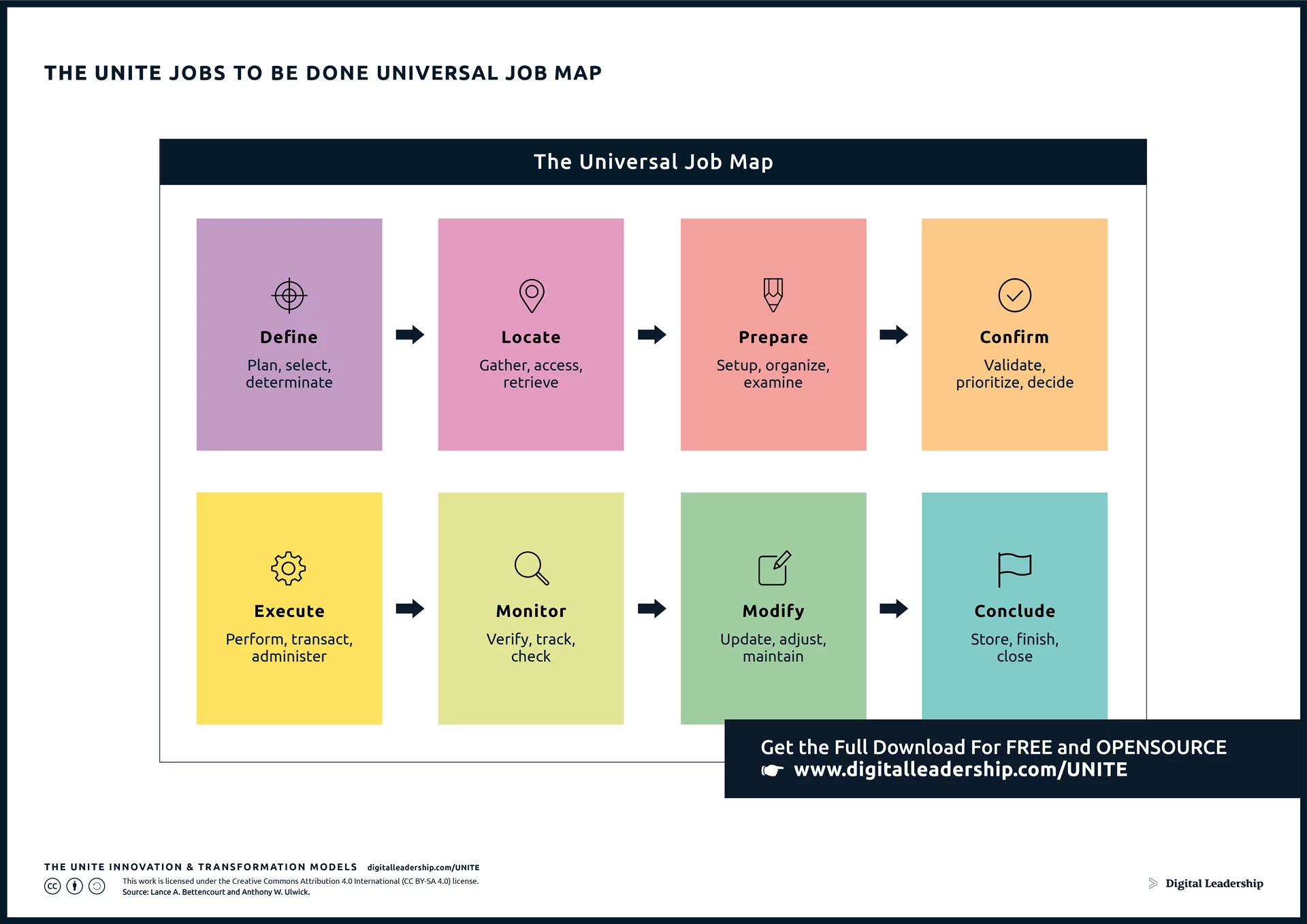
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Source: Lance A. Bettencourt and Anthony W. Ulwick.
Much more about Jobs to be done and innovation approaches, you will find in our book “How to Create Innovation”. Recognizing that innovation is a dynamic process, this guide emphasizes adaptability. Stay ahead of the curve by understanding how innovation strategies evolve with market dynamics, ensuring sustained relevance and competitiveness.
4 Types of Innovation: What are the Main Major Types of Innovation In Business with Examples?

Let’s consider each of the 4 Types of Innovation and how they might fit into the innovation framework of your overall plans.
(1) Architectural Innovation
Architectural innovation happens when new things, like products or services, use existing technology to make new markets or reach new customers who haven’t bought that thing before.
What is Architectural Innovation?
Architectural innovation involves rendering a company’s architectural knowledge obsolete while retaining the knowledge about the components of the firm’s products, which are physically distinct portions representing the core design concept and serving specific functions.
Architectural Innovation Examples
This journey into architectural innovation examples transcends traditional boundaries, unveiling the transformative power of visionary thinking and technological prowess. As we navigate through real-world instances, we’ll witness the fusion of creativity and functionality, where revolutionary ideas materialize into structures that redefine the status quo.
- Product Design: Innovations in the architectural design of a product, such as introducing new features, changing the layout, or enhancing the overall structure to deliver improved performance or user experience.
- System Architecture: Refers to changes in the arrangement and interconnection of components within a system. This can involve adopting new technologies, reconfiguring existing elements, or introducing novel approaches to enhance the system’s capabilities.
- Organizational Structure: In a business context, architectural innovation may involve restructuring the organization’s internal components, processes, or workflows. This could include changes to hierarchical structures, team compositions, or communication channels.
- Information Systems: Within the realm of information technology, architectural innovation often pertains to changes in the design and structure of software and hardware systems. This might involve adopting cloud-based architectures, implementing microservices, or upgrading infrastructure.
Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive Innovation is when a new product or service starts in basic, affordable applications at the lower end of the market. As it becomes more accessible, it gradually moves up the market, eventually displacing established competitors.
What is Disruptive Innovation?
Disruptive innovation involves the transformation of costly or intricately sophisticated products or services once exclusive to a high-end or more skilled consumer segment into offerings that are more economical and accessible to a wider population. This shift disrupts the market by displacing entrenched, longstanding competitors. Over time, the momentum of disruptive innovation gains traction and extends into the primary segments of the industry. When the novel innovation is adopted by the mainstream segment, it is categorized as disruptive innovation.
A compelling illustration of disruptive innovation is found in the trajectory of Netflix. The company initially targeted a less pivotal segment of Blockbuster’s audience, offering a relatively niche service of mailing rental DVDs. Subsequently, Netflix refined its services while maintaining an affordable pricing strategy, ultimately captivating and dominating Blockbuster’s core audience.
Disruptive Innovation Examples
1. Airbnb:
- Airbnb disrupted the traditional hotel industry by creating a platform that allows individuals to rent out their homes or spare rooms to travellers. This decentralized model challenged the traditional hotel business and offered unique, affordable, and often more personalized accommodation options.
- Impact: Airbnb transformed the hospitality industry, providing travellers with alternative lodging choices and enabling hosts to monetize their unused spaces.
2. Uber:
- Uber disrupted the taxi industry by introducing a ride-sharing platform that connects passengers with drivers through a mobile app. This model offers a more convenient, flexible, and often cost-effective alternative to traditional taxi services.
- Impact: Uber transformed urban transportation, changing the way people commute and challenging traditional taxi services worldwide.
3. Netflix:
- Netflix disrupted the home entertainment industry by shifting from a DVD rental-by-mail service to a streaming video-on-demand platform. This allowed users to instantly access a vast library of movies and TV shows over the internet, challenging traditional cable and satellite TV models.
- Impact: Netflix revolutionized how people consume entertainment, leading to cord-cutting trends and influencing the rise of streaming services.
4. Amazon:
- Amazon disrupted the retail industry by pioneering e-commerce and creating an online marketplace. It started as an online bookstore and expanded into selling a wide range of products, challenging brick-and-mortar retailers.
- Impact: Amazon transformed the retail landscape, influencing the shift towards online shopping and setting new standards for customer convenience, fast delivery, and a vast product selection.
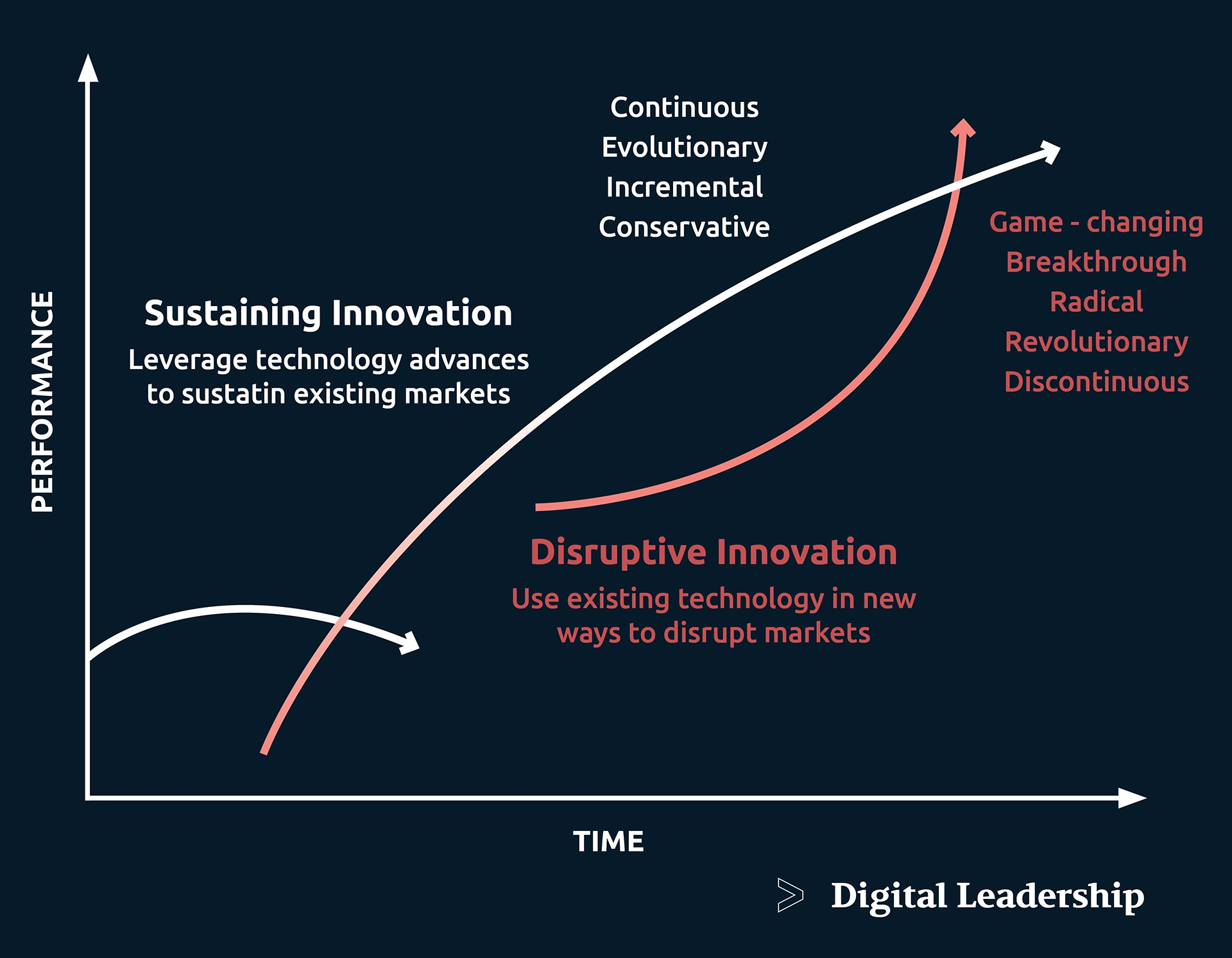
Disruptive vs Sustaining Innovation
disruptive innovation focuses on revolutionary changes, targeting new markets and potentially reshaping industries, while sustaining innovation involves continuous incremental improvements to retain market positions and meet the evolving needs of existing customers. Both strategies are essential components of a comprehensive innovation strategy for organizations.
| Criteria | Disruptive Innovation | Sustaining Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Market Focus | Targets new markets or creates entirely new customer segments. | Aims to maintain and improve existing market positions. |
| Degree of Change | Introduces significant, transformative change, often disrupting established industries. | Involves gradual, incremental improvements to existing products, services, or processes. |
| Customer Impact | May initially attract a different set of customers than those served by existing solutions. | Seeks to enhance the experience for existing customers by refining and optimizing current offerings. |
| Timing | Often takes established players by surprise and gains momentum gradually over time. | Is a continuous and ongoing process to stay ahead of market demands and maintain competitiveness. |
Radical Innovation
Radical innovation is like creating something completely new that can replace the way things are done now. It’s different from small improvements or changes – it’s a big, groundbreaking idea that can transform the whole way a business operates.
What is Radical Innovation?
Radical innovation stands as the highlight of our article, and rightfully so, given its nature as the development of an entirely new product or service that defies expectations, often becoming an integral part of users’ lives. Iconic examples of radical innovations altering our daily routines include television and the smartphone.
Not all outcomes of innovation are easily quantifiable. The approach outlined in the Oslo Manual by the OECD involves differentiating the results of innovative activities from the resources invested in their execution.
It’s commonplace, especially in large corporations, for evaluating innovation outcomes to revolve around accounting and financial metrics. Success is measured in profit, revenue growth, shifts in share value, market capitalisation, or enhanced productivity.
For those contemplating the pursuit of radical innovation, two critical considerations come to the forefront. Firstly, a comprehensive understanding, if not anticipation, of the market is imperative. Secondly, the capability to swiftly develop advanced solutions is crucial. Solutions to both prerequisites often emerge from external communities. Agorize, having worked with numerous global clients, has witnessed collaborative solutions crafted through innovation programs based on customer insights. Whether one is in IT, HR, Marketing, or CSR, Agorize provides the flexibility to tailor an innovation program to specific needs.
Radical Innovation Examples
- Smartphones:
- The introduction of smartphones combined communication, computing, and various other functionalities into a handheld device. This radical innovation altered the way people communicate, work, and access information.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- The development and widespread adoption of electric vehicles represent a radical innovation in the automotive industry. EVs aim to revolutionize transportation by reducing dependence on traditional fossil fuels.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- The rapid development of artificial intelligence represents a radical innovation in various sectors. AI has the potential to transform industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing through automation and advanced data analysis.
- Washing Machine
- The transition from manual or semi-automatic washing machines to fully automatic, programmable washing machines represents a radical innovation in the laundry industry. Fully automatic machines handle the entire washing process, including washing, rinsing, and spinning, with minimal user intervention.
- Impact: This innovation significantly transformed household chores, offering users a more convenient and time-saving way to do laundry. Automatic washing machines revolutionized the efficiency and ease of cleaning clothes, leading to increased adoption in households worldwide.
- Cloud Technology:
- The emergence of cloud technology, with companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, represents a radical innovation in computing. Cloud services provide scalable and on-demand access to computing resources, storage, and applications over the Internet.
- Cloud technology has transformed the IT industry, allowing businesses to scale infrastructure more efficiently, reduce
- Personal Computers:
- The development and introduction of the personal computer, exemplified by early models like the IBM PC in the 1980s, marked a radical innovation. These devices brought computing power directly to individuals, enabling tasks such as word processing, spreadsheet calculations, and personal productivity.
Incremental Innovation
Incremental innovation involves making small improvements or upgrades to a company’s current products, services, processes, or methods. The changes made through incremental innovation aim to enhance the development efficiency, productivity, and competitive advantage of existing products.
What is Incremental Innovation?
Incremental innovation termed continuous improvement, involves enhancing an existing product or service, providing a less flashy but effective approach compared to more disruptive innovation types. It proves particularly adept at addressing transformation challenges within a company.
Furthermore, incremental innovation derives its strength from its collaborative and collective essence. Valuable ideas often stem from employees engaging directly with clients, those immersed in daily customer interactions. Additionally, adept leaders in human resource development leverage this approach to cultivate a collective culture of improvement. This article delves into effective methods for fostering such a culture.
Incremental Innovation Examples:
1. Smartphones Incremental Innovation Example: Camera Improvements
- Over successive smartphone models, incremental innovations have been made in camera technology. This includes enhancements in megapixel count, low-light performance, image stabilization, and the introduction of additional lenses (e.g., wide-angle, telephoto).
- Benefits: Improved photo and video quality, and expanded creative possibilities for users.
2. Personal Computers: Incremental Innovation Example: Processor Speed and Efficiency
- In personal computers, incremental innovations have focused on improving processor speed, energy efficiency, and overall performance. Each new generation of processors offers higher clock speeds, better multitasking capabilities, and reduced power consumption.
- Benefits: Faster computing, improved multitasking, and energy efficiency.
3. Analog Processes:
- In analogue audio recording processes, incremental innovation involves the transition to digital recording. This includes the development of analogue-to-digital converters, leading to higher fidelity, ease of editing, and the ability to store recordings in digital formats.
- Benefits: Improved audio quality, ease of editing, and efficient storage and distribution of recordings.
These examples illustrate how incremental innovations in smartphones, personal computers, and analogue processes focus on refining specific features or processes over time, contributing to the overall improvement and evolution of the products or systems.
10 Types of Innovation : Additional Innovation Types for Business Field
1- Product Innovation
Product innovation is a strategic focus on developing novel or enhanced products tailored to address the ever-evolving needs of customers. This process encompasses the refinement of existing features, the introduction of new functionalities, or the creation of entirely new offerings. The aim is to stay responsive to changing market dynamics and consumer preferences, ensuring that the products meet or exceed customer expectations. By continuously adapting and improving, businesses engaged in product innovation seek to maintain a competitive edge, enhance customer satisfaction, and foster sustained growth in the marketplace.
The jobs to be done in product management guide the innovation process by focusing on the real needs and motivations of customers. By comprehensively understanding the jobs customers are trying to fulfill, product managers can make informed decisions about which features, improvements, or innovations will be most valuable.
Let’s consider how we might implement Product Innovation:
- New product development: creating entirely new products or services that meet needs not currently being served by existing products
- Product improvement: enhancing existing products or services to improve functionality, quality, or performance
- Line extensions: introducing new variants or versions of existing products to the product line to appeal to different customer segments
- Repositioning: changing the target market or value proposition of an existing product to meet customer needs better
The Value Proposition Canvas is a dynamic tool that ensures your innovation strategy is grounded in a customer-centric approach, enhancing the resonance and effectiveness of your offerings in the market.
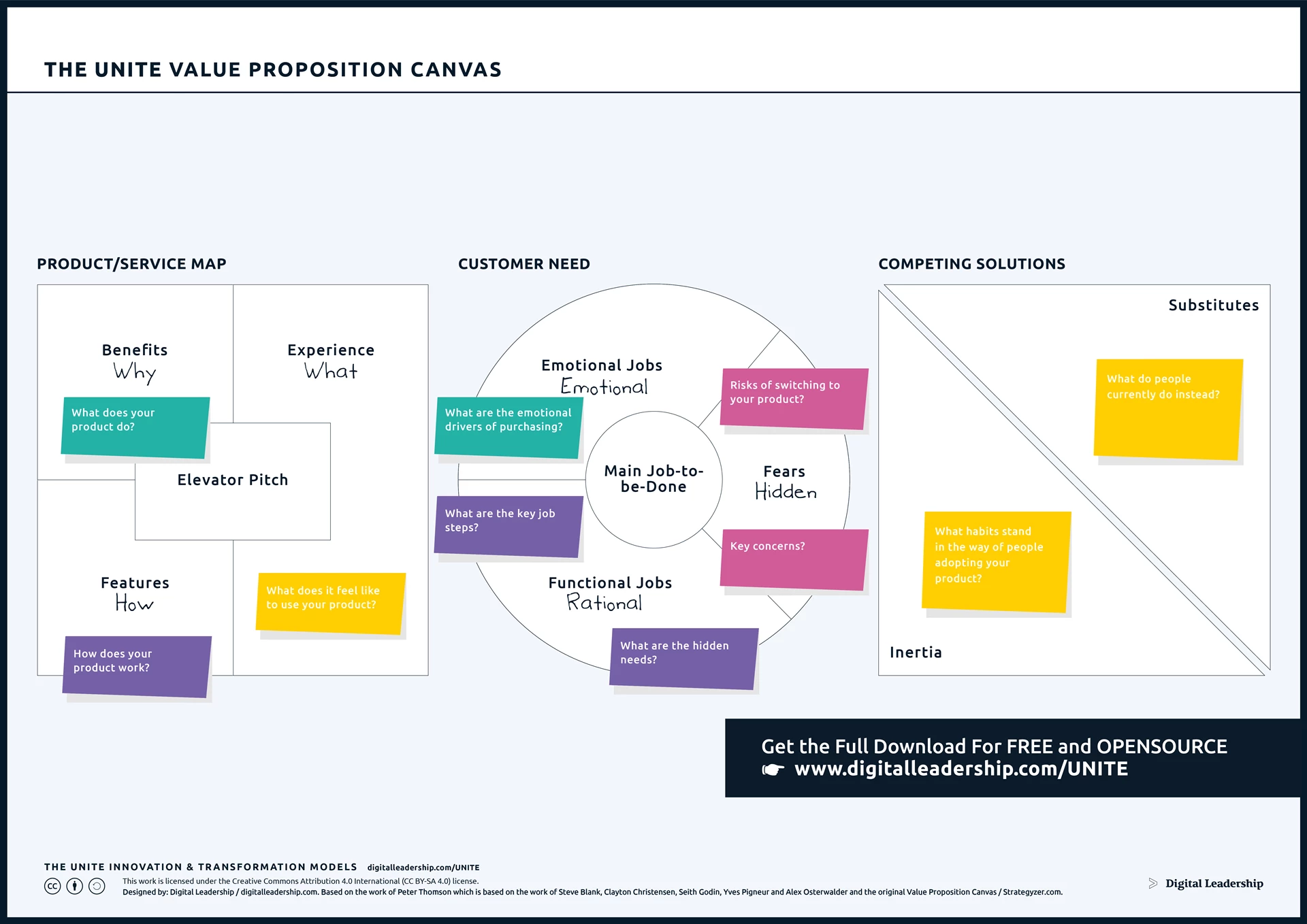
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Based on the work of Peter Thomson which is based on the work of Steve Blank, Clayton Christensen, Seith Godin, Yves Pigneur and Alex Osterwalder and the original Value Proposition Canvas
2- Service Innovation
Service innovation is a strategic initiative aimed at elevating the delivery and quality of services provided by a business. This process involves the introduction of new and innovative service offerings, optimizing existing service processes, and enhancing overall customer experiences. Service innovation recognizes the significance of not only what is offered but also how it is delivered, acknowledging the pivotal role of customer satisfaction in the success of a service-oriented business. By constantly refining and introducing inventive service solutions, businesses seek to stay ahead in the competitive landscape, meet the dynamic demands of consumers, and cultivate enduring relationships with their clientele.
Service Innovation can take many forms:
- Introduction of new services
- Improvement of existing services
- Integration of technology into services
- Customization of services to better meet individual customer needs.
3- Process Innovation
Process innovation is a strategic undertaking that entails the reconceptualization and enhancement of internal operations and workflows within an organization. The primary goal is to achieve increased efficiency, lower costs, and a more streamlined organizational structure. This innovation focuses on optimizing the way tasks are performed, introducing innovative methods, and leveraging technology to drive improvements. By scrutinizing and redefining internal processes, businesses aim to eliminate bottlenecks, enhance productivity, and respond more effectively to market demands. Process innovation is integral to maintaining competitiveness in dynamic environments, as it enables organizations to adapt and thrive in the face of evolving challenges and opportunities.
Process Innovation has several shapes it can take:
- New process development: entirely new processes are created that can be used to solve existing problems or meet new needs
- Process improvement: enhancements made to existing processes to improve their performance, reliability, or efficiency
- Process integration: different processes combined to create new solutions or applications
- Disruptive process: a radically different value proposition is offered by newly developed processes
4- Business Model Innovation
Business model innovation is a strategic initiative that involves the fundamental redesign of a business’s structure to generate new sources of value. This transformative process goes beyond incremental changes and explores alternative approaches to revenue generation, partnerships, and customer engagement strategies. Businesses engaged in business model innovation seek to adapt to changing market dynamics, remain agile, and proactively explore innovative ways to create and capture value. This may involve introducing new business models, exploring different pricing structures, forming strategic alliances, or embracing disruptive technologies. By challenging conventional norms and embracing innovative digital business models, organizations aim to stay competitive, drive growth, and foster long-term sustainability in the marketplace.
This form of innovation helps companies differentiate themselves from competitors, develop new revenue streams, lower their costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Successful Business Model Innovation requires a willingness to experiment, take risks, and iterate on ideas until the optimal solution is found. Successful innovation of this sort requires a keen understanding of markets and the details of how businesses can operate.
The UNITE Business Model Innovation Patterns summarize 95% of all business model innovations. It is a wealth of approaches drawn from some of the most influential companies in the market today and gives you the tools to systematically innovate your Business Model.
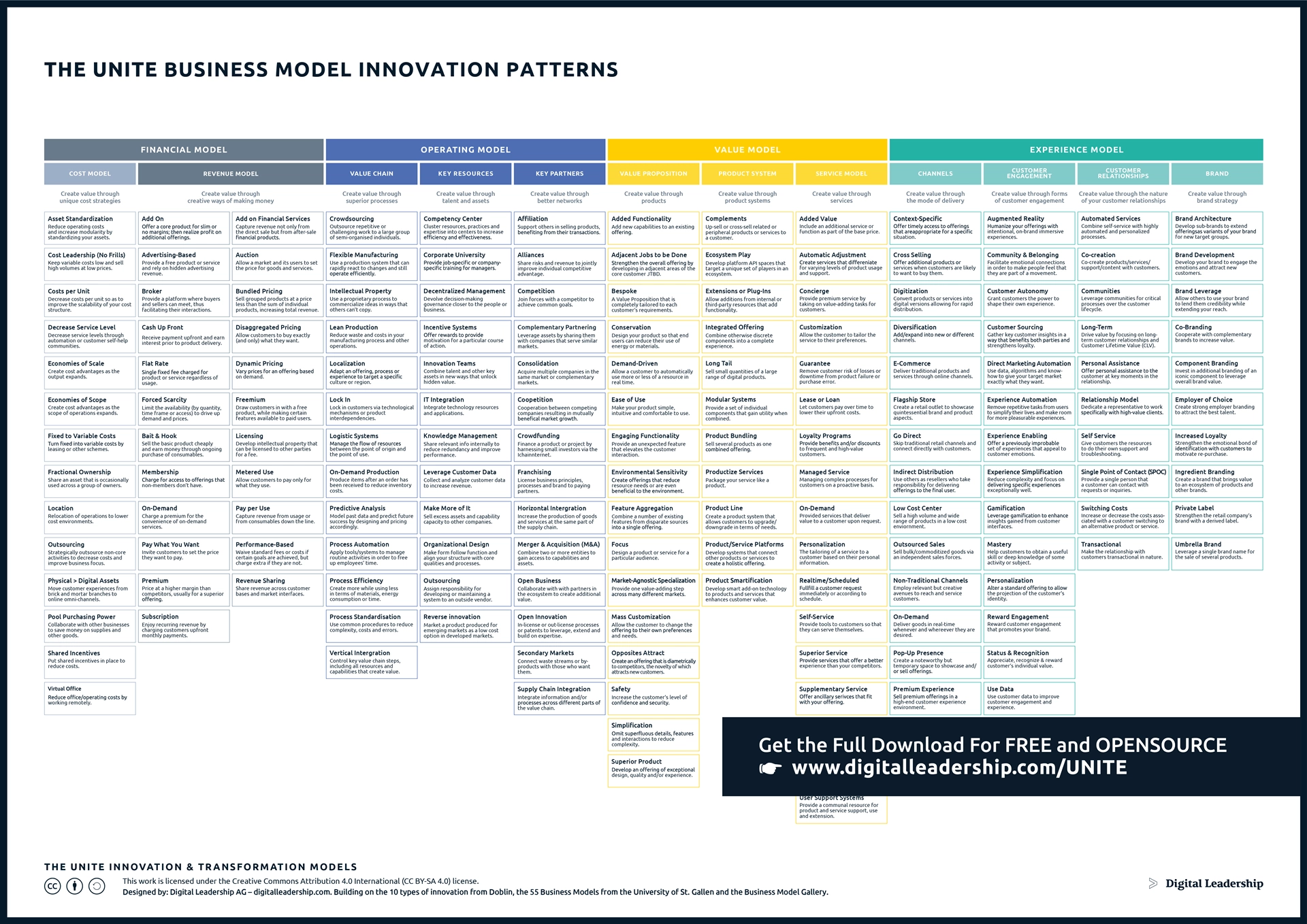
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the 10 types of innovation from Doblin, the SS Business Models from the University of St.Gallen, and the Business Model Gallery
Business model innovation can take several forms:
- New business models: creating entirely new business models that can be used to solve existing problems or meet new needs
- Business model improvement: making enhancements to existing business models, improving their efficiency, effectiveness, or sustainability
- Business model replication: adapting successful business models from one market or industry and applying them somewhere else
- Disruptive business models: creating new business models that offer a radically different value proposition
5- Marketing Innovation
Marketing innovation is a strategic endeavor that focuses on introducing novel approaches to promote products or services. This dynamic process extends beyond traditional marketing methods and embraces creative, cutting-edge strategies to capture the attention of target audiences. This can encompass the adoption of new advertising channels, leveraging digital platforms, exploring unconventional promotional campaigns, and utilizing emerging technologies to enhance overall marketing effectiveness. Marketing innovation recognizes the ever-evolving landscape of consumer behavior and communication preferences, aiming to stay ahead of trends and engage customers in fresh and impactful ways. By fostering creativity and adaptability, businesses can effectively navigate the competitive marketing arena and establish a compelling and contemporary brand presence.
6- Organizational Innovation
Organizational innovation is a strategic initiative centered on optimizing internal structures, fostering cultural enhancements, and refining employee workflows within a business. The primary objective is to create a more adaptive, collaborative, and dynamic work environment. This innovation recognizes that organizational success is not solely dependent on external factors but also hinges on the internal capabilities, efficiency, and adaptability of the workforce. Businesses engaged in organizational innovation often explore new management practices, leadership models, and collaborative tools to enhance employee engagement and productivity. By cultivating a work environment that encourages innovation, continuous learning, and adaptability, organizations can position themselves to navigate change effectively and capitalize on emerging opportunities in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
7- Tehnology Innovation
Technology innovation refers to the process of creating, developing, and implementing new technologies or improving existing ones to address specific needs, solve problems, or enhance efficiency in various fields. This type of innovation plays a pivotal role in advancing industries, driving economic growth, and improving overall quality of life. Technology innovation is not limited to the creation of hardware or software; it also encompasses the integration and application of cutting-edge solutions in diverse sectors.
Technology Innovation includes several potential approaches:
- New technology development: creating entirely new technologies that can be used to solve existing problems or meet new needs
- Technology improvement: making enhancements to existing technologies to improve their performance, reliability, or efficiency
- Technology integration: combining different technologies to create new solutions or applications
- Disruptive technology: creating new technologies offering a radically different value proposition
8- Value Innovation
Value innovation is a strategic approach that concurrently pursues both differentiation and cost-effectiveness, challenging the conventional trade-off between these two factors. This strategy involves identifying innovative ways to create unique value for customers while optimizing operational efficiencies. By breaking away from the traditional mindset that assumes a trade-off between cost and differentiation, organizations can achieve a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Value innovation encourages businesses to rethink and redesign their products, services, or processes to deliver exceptional value at a lower cost. This transformative strategy not only enhances customer satisfaction but also positions organizations as industry leaders capable of delivering high-quality offerings with operational efficiency.
9- Breakthrough Innovation
Breakthrough innovation represents a transformative leap forward, marked by the development of revolutionary ideas or advancements that surpass existing norms. This form of innovation goes beyond incremental improvements and introduces groundbreaking concepts, technologies, or solutions that have the potential to reshape entire industries and establish new standards. Breakthrough innovations often represent a paradigm shift, challenging established practices and introducing novel approaches that significantly impact the way businesses operate. Organizations that engage in breakthrough innovation are at the forefront of driving change, pioneering new technologies, and influencing the future trajectory of their respective industries. This type of innovation is characterized by its ability to bring about substantial and unprecedented advancements, setting the stage for transformative shifts in the business landscape.
10- Digital Innovation
Digital innovation is a strategic initiative that revolves around the integration and application of digital technologies to transform various aspects of products, services, or processes. This innovation encompasses leveraging emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, and automation to enhance efficiency, connectivity, and user experiences within the digital realm. Businesses engaged in digital innovation recognize the transformative power of technology in shaping the way they operate and interact with customers. By adopting and adapting to the latest digital advancements, organizations can streamline operations, improve decision-making processes, and offer innovative solutions that meet the evolving needs of a digitally connected world. Digital innovation is instrumental in staying competitive in today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Choosing and Implementing the Right Type of Innovation to Your Business Steps
Selecting the appropriate innovation type is paramount. It cannot be overstated, because It serves as the compass guiding your company through the ever-changing currents of the business world.
This careful selection is not merely a business decision; it’s a strategic move that reverberates across every facet of your organization. It’s about future-proofing your business, staying relevant, and ensuring that innovation becomes a driving force for sustained success. The choice of the right innovation strategy aligns seamlessly with your overall business objectives, optimizing the allocation of resources, providing a unique competitive edge, and fostering a culture of creativity and continuous improvement.
The right innovation strategy is the key to enhanced problem-solving, satisfied customers, and a business that thrives amid the challenges and opportunities of the ever-evolving market. Understanding the dichotomy between open and closed innovation cultures is the first crucial step in navigating this journey effectively.”
| Step Number | Step Name | Step Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Define Your Business Objectives | Clearly articulate overarching business goals: growth, efficiency, market expansion, or customer satisfaction. |
| 2 | Assess Your Current Innovation Landscape | Conduct a thorough evaluation of existing innovation practices, capabilities, and organizational culture. Identify challenges. |
| 3 | Familiarize Yourself with Types of Innovation | Gain an understanding of various innovation types, align each with specific business goals and understand how each type can contribute to specific business goals. |
| 4 | Prioritize Based on Impact and Feasibility | Prioritize innovation types based on potential impact and feasibility within the organizational context. Consider short-term and long-term implications. |
| 5 | Consider Customer Needs and Market Trends | Incorporate a customer-centric approach by understanding current and future customer needs. Stay informed about market trends and emerging technologies. |
| 6 | Define Innovation Culture | – Understand nuances between open and closed innovation cultures. Consider benefits and challenges in the business context. – Consider adopting an open innovation culture, emphasizing collaboration and external partnerships. – Explore implementing open innovation within the organization. Leverage internal dynamics for fresh perspectives and ideas. – Recognize that the choice between open and closed innovation is not binary. Explore a hybrid approach based on unique needs and strategic goals. |
| 7 | Implement a Mix of Innovation Types | Recognize that a comprehensive innovation strategy often involves a mix of different types. For example, combining product innovation with process innovation or business model innovation can create synergies and amplify the overall impact. |
| 8 | Embrace Digital Transformation | Consider integrating a digital transformation strategy into your overall innovation business plan. Leverage digital technologies to enhance products, streamline processes, and improve customer experiences. |
| 9 | Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Define measurable KPIs aligned with innovation goals: time-to-market, customer satisfaction scores, or revenue growth. |
| 10 | Foster Collaboration Between Companies | Delve into collaborative open innovation partnerships. Understand how synergies can amplify creativity and drive innovative initiatives. |
| 11 | Engage with External Experts | For businesses seeking external expertise, navigate engaging with industry specialists and subject matter experts. |
| 13 | Emphasize Internal R&D | Understand the dynamics of relying on an internal Research and Development (R&D) department. Cultivate innovation from within. |
| 14 | Continuous Assessment and Adaptation | Regularly review and reassess the innovation strategy. Iterate and adapt based on feedback, market changes, and evolving business needs. |
Measuring Innovation for Different Types of Innovation
Measuring innovation involves assessing both quantitative and qualitative indicators. Key metrics include:
- Return on Innovation Investment (ROII): Evaluate the financial returns compared to the investment made in innovation initiatives.
- Time to Market: Measure the speed at which innovations are developed and brought to market.
- Customer Feedback and Satisfaction: Assess customer reactions, feedback, and satisfaction levels regarding new products or services.
- Employee Engagement: Evaluate the level of employee engagement in innovation activities and their perception of the organization’s commitment to innovation.
Measuring innovation entails evaluating the effectiveness and impact of innovation initiatives within an organization. Understanding the correlation between measuring innovation and the types of innovation implemented is crucial for comprehending how diverse strategies contribute to overall success. Here’s an exploration of how innovation measurement is linked to various types of innovation:
- Product Innovation:
Measurement Metrics: Keep track of metrics like new product launches, revenue generated from new products, and market share gains.
Success Indicators: Achieve increased sales, positive customer feedback, and a growing market presence. - Service Innovation:
Measurement Metrics: Monitor enhancements in service delivery, customer satisfaction scores, and the adoption rate of new service offerings.
Success Indicators: Attain higher customer loyalty, improved customer experiences, and increased service revenue. - Process Innovation:
Measurement Metrics: Evaluate changes in operational efficiency, cost reduction, and time savings through streamlined processes.
Success Indicators: Realize reduced production costs, improved resource allocation, and faster time-to-market. - Business Model Innovation:
Measurement Metrics: Assess the impact on revenue streams, profitability, and market positioning.
Success Indicators: Experience diversification of revenue sources, increased profit margins, and enhanced competitive advantage. - Marketing Innovation:
Measurement Metrics: Analyze the effectiveness of new marketing strategies, campaigns, and channels.
Success Indicators: Witness increased brand awareness, higher customer engagement, and improved conversion rates. - Organizational Innovation:
Measurement Metrics: Evaluate changes in internal structures, employee satisfaction, and collaboration metrics.
Success Indicators: Attain enhanced employee morale, improved teamwork, and increased adaptability to change. - Social Innovation:
Measurement Metrics: Assess the social impact of innovative solutions on communities and societal well-being.
Success Indicators: Achieve positive social change, community engagement, and contributions to sustainable development goals. - Value Innovation:
Measurement Metrics: Evaluate the simultaneous pursuit of differentiation and cost reduction.
Success Indicators: Realize increased customer value perception, improved operational efficiency, and competitive advantage. - Breakthrough Innovation:
Measurement Metrics: Track revolutionary advancements, patents filed, and industry recognition.
Success Indicators: Witness industry disruption, creation of new markets, and establishment of new industry standards. - Digital Innovation:
Measurement Metrics: Analyze the impact of digital technologies on products, services, or processes.
Success Indicators: Experience improved digital experiences, increased efficiency through automation, and enhanced connectivity.
In measuring innovation, organizations should align their metrics with the specific goals of each innovation type. A comprehensive approach involves considering both financial and non-financial indicators to capture the multifaceted nature of innovation’s impact on business success. Regular assessments and adjustments to measurement strategies ensure that innovation efforts remain aligned with organizational objectives and market dynamics.
Conclusion
Innovation is not a one-size-fits-all concept; it encompasses a rich tapestry of possibilities that organizations can explore to stay resilient, relevant, and visionary. By understanding the diverse types of innovation, embracing the innovation process, fostering a culture of creativity, and strategically measuring and protecting innovations, businesses can position themselves as pioneers in an ever-evolving business landscape. As we navigate the intricacies of the innovation journey, remember that innovation is not just about change—it’s about shaping a future where possibilities are limitless and success is defined by continuous evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions
1- Which type of innovation applies to existing markets and existing technologies?
In existing markets with established technologies, sustaining innovation is often the most applicable. This type of innovation involves incremental improvements and optimisations to existing products, services, or processes, ensuring their relevance and competitiveness in the current market landscape.
2) How to Measure Innovation?
Measuring Innovation is an essential part of evaluating the success of innovation initiatives. While each business is different, there are some general ways of measuring Innovation that you could consider:
- Number of patents filed: a good measure of the level of innovation within the organization, as patents are an indication of the development of new products, processes, or technologies.
- Research and development (R&D) investment: the amount of resources devoted to innovation. This can include investments in new product development, technology research, or process improvements.
- Revenue from new products or services: a good indicator of successful innovation. Through tracking revenue from new offerings, you can measure the impact of Innovation on your company’s bottom line.
- Customer satisfaction: indications of whether the new products or services are meeting customer needs and expectations. Implement tools like surveys, focus groups, and other customer feedback mechanisms.
- Time to market: indicates the speed at which the company can develop and launch new offerings.
- Employee engagement: engaged employees are more likely to contribute to innovation efforts and share their ideas and perspectives.
- Collaboration and partnerships: collaborations and partnerships with other companies, research institutions, or startups can be a good measure of the level of innovation within an organization.



























 Book How to Create Innovation
Book How to Create Innovation