Value Creation Meaning, Model & Examples in Business | Guide
Published: 29 September, 2023
Transformation
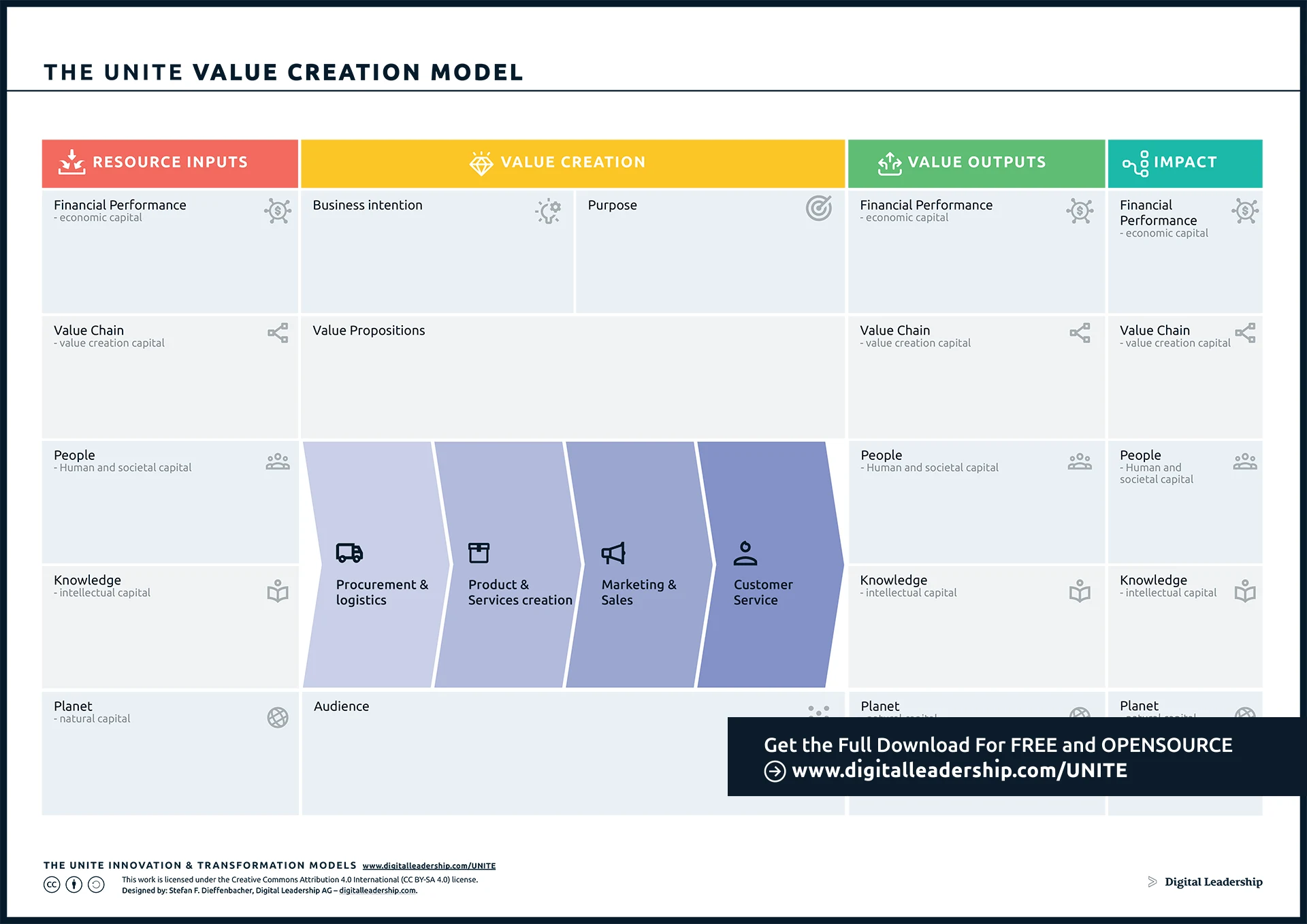
Table of Contents
Value creation is more than a business strategy; it’s a fundamental approach that shapes the direction of organizations and defines their business purpose. It’s the synergy of innovative thinking, unwavering commitment, and an acute understanding of the diverse stakeholders in today’s interconnected world. From the boardroom to the digital frontier, value creation is the compass guiding businesses.
At Digital Leadership, we specialize in digital strategy and execution and use emerging technologies and innovative business models to serve customers better. Our Business Model Strategy service is designed to help organizations create and nurture value for everyone involved.
We will illuminate the path to success by examining the strategies, innovations, and insights that fuel value creation in the business environment. Whether you’re an entrepreneur with a disruptive vision, a leader steering your organization through uncharted waters, or a professional seeking to make a profound impact, this article is your compass to navigate the intricate landscape of value creation, securing investment capital, and crafting a strategic business plan that aligns with your goals and aspirations.
What is Value Creation? Value Creation Meaning
Value creation is at the core of every successful business success. It involves turning resources into something valuable through hard work. In the realm of economics, it’s a comprehensive concept encompassing the creation of tangible products and services. It refers to the process of generating additional value for stakeholders, going beyond the initial investment or input.
It also involves investments in capital goods and intellectual property assets. In essence, value creation is about making more out of what you have, and it’s central to the success of any organization.
It’s important to highlight that the concept of value creation extends beyond just seeking profit. It encompasses a wider range of aspects, such as improving products and services, fostering stronger customer relationships, driving innovation, and making positive contributions to both the community and the environment.
At its core, grasping the meaning of value creation is closely tied to sustainability. Businesses need to continuously innovate and adapt to changing market conditions. This entails streamlining operations, refining products, and promoting a culture of excellence. Organizations must consistently aim to enhance their value creation strategies.
Moreover, Value creation involves aligning with the digital landscape, where data-driven insights, technology integration, and agile decision-making are pivotal. To truly excel in understanding the meaning of value creation, businesses must remain agile and responsive to the evolving needs and expectations of their stakeholders.
The UNITE Value Creation Model:
Value creation lies at the heart of every successful organization’s mission and strategy. It is the fundamental process through which businesses not only generate value for themselves but also contribute positively to society as a whole. The UNITE Value Creation Model serves as a powerful tool to dissect, understand, and harness this crucial process effectively. By meticulously examining the Resource Inputs, Value Creation, Value Outputs, and Impact aspects, organizations gain a holistic view of their operations.
This comprehensive perspective enables them to make informed decisions, enhance their offerings, and ultimately maximize their profitability. Furthermore, it underscores the importance of aligning organizational goals with societal well-being, emphasizing the need for businesses to act responsibly, sustainably, and with a long-term perspective. In a rapidly evolving and interconnected world, the ability to grasp and leverage the nuances of value creation, as outlined in this framework, is paramount for achieving lasting success and significance in today’s business landscape.
The UNITE Value Creation Framework, which comprises four distinct sections—Resource Inputs, Value Creation, Value Outputs, and Impact—provides a structured approach to comprehending and communicating the value creation process. You can download it now.

Designed by: Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, Digital Leadership AG
Let’s delve into each section of the framework:
- Resource Inputs: This section offers an overview of the various inputs contributed by your organization and society as a whole, which play a role in the value-creation process. These resources can encompass financial investments, human capital, technology, and more.
- Value Creation: In this section, the central process of value creation is detailed. It encompasses your value propositions, overarching business intentions and purpose, as well as your target audience. It’s the core engine that drives your organization’s value-creation journey.
- Value Outputs: Here, the results generated through the value-creation process are defined and elaborated upon. These outputs can include products, services, innovations, and customer experiences that resonate with your audience.
- Impact: This section goes a step further by exploring the broader impact your organization has on both itself and society at large. It delves into the consequences of your value creation efforts, considering aspects such as social responsibility, sustainability, and long-term societal benefits.
Understanding and optimizing these value-creation factors empowers organizations to create more value for customers and boost profitability. This versatile framework is applicable in diverse contexts, from startups and business model innovation to corporate communication and boardroom presentations, making it an invaluable and adaptable tool.
Importance of Value Creation
Understanding the importance of value creation reveals its profound impact on businesses. This multidimensional concept extends its influence to various aspects of a company’s success, including customer satisfaction, loyalty, and maintaining a competitive edge. Here, we delve into the crucial dimensions of the importance of value creation:
1) Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Creating customer value lies at the heart of any business’s long-term success. Satisfied and loyal customers not only contribute to revenue but also serve as invaluable brand advocates, attracting new customers through positive word-of-mouth. Here’s a closer look at how customer satisfaction and loyalty are intertwined with value creation:
- Repeat Business:
When a company consistently provides value to its customers, it fosters a sense of trust and reliability. This often results in repeat business, where satisfied customers return for additional products or services. - Brand Advocacy:
Happy customers often become brand advocates. They not only continue to support the business but also actively recommend it to their friends, family, and colleagues. This positive word-of-mouth marketing can significantly expand a company’s customer base. - Reduced Churn:
Customer loyalty, built through value creation, helps reduce churn rates. When customers feel they receive exceptional value, they are less likely to switch to a competitor. - Feedback Loop:
Engaging with customers in the value creation process can lead to valuable feedback. This feedback can be used to further enhance products and services, creating a continuous improvement cycle.
2) Competitive Advantage
Value creation plays a central role in establishing a lasting competitive advantage in today’s ever-changing business environment. When businesses consistently provide greater value to their customers compared to their competitors, they can secure their position in the market and effectively deter rivals. This strategy not only boosts profits but also guarantees sustained viability and expansion in today’s fiercely competitive markets. Let’s explore in more detail how value creation contributes to gaining a competitive edge:
- Market Differentiation:
A business that consistently delivers more value to its customers stands out in the market. This unique value proposition differentiates it from competitors and often leads to a stronger market presence. - Customer Retention:
When customers perceive a business as providing superior value, they are more likely to remain loyal, reducing the risk of switching to competitors. - Price Flexibility:
Businesses with a strong value creation strategy can often maintain higher price points. Customers are often willing to pay more for products or services they perceive as having added value. - Innovation Leadership:
A commitment to value creation drives innovation. Companies focused on creating value are more likely to be at the forefront of industry advancements and trends. - Barriers to Entry:
A business known for value creation can create formidable barriers to entry for potential competitors. It’s challenging for newcomers to replicate the combination of reputation, customer loyalty, and innovation that established value-driven businesses possess.
3) Profitability
Profitability isn’t just a financial metric; it’s a natural consequence of effective value creation. When a business delivers products or services that customers perceive as valuable, several key factors come into play, collectively boosting profitability. Let’s explore these vital aspects:
- Premium Pricing:
Customers are often willing to pay premium prices for products or services they perceive as valuable. This premium pricing not only enhances revenue but also contributes significantly to profit margins. - Cost Efficiency:
Value creation often involves streamlining processes and eliminating inefficiencies. This operational excellence leads to cost savings and higher profitability. - Repeat Business:
Satisfied customers tend to return for additional purchases. The cost of acquiring new customers is higher than retaining existing ones, making repeat business a profitable endeavour. - Cross-Selling and Up-Selling:
Providing value opens opportunities for cross-selling related products or up-selling to higher-value offerings. These strategies can substantially increase the average transaction value and profitability. - Long-Term Growth:
Sustainable profitability resulting from value creation enables businesses to reinvest in research and development, expanding their product or service offerings and fueling long-term growth.
4) Innovation and Adaptation
Innovation stands as the cornerstone of value creation. Companies that embrace innovation and adapt to evolving market conditions are not only better positioned to create value for their stakeholders but also to thrive in a dynamic and ever-changing business environment. Here’s a closer examination of the pivotal role of innovation in value creation:
- Market Responsiveness:
Innovating in response to changing market conditions is a hallmark of value-centric organizations. These businesses not only survive but thrive by adapting their products, services, and strategies to meet shifting customer needs and expectations. - Continuous Improvement:
A commitment to value creation often leads to a culture of continuous improvement. This means refining existing processes, products, or services to make them more efficient and effective, ultimately enhancing their value. - Risk Mitigation:
Being innovative and adaptive allows businesses to mitigate risks associated with market disruptions. By staying ahead of the curve, they are less vulnerable to external shocks and can respond effectively when they occur. - Competitive Edge:
Innovation can result in the development of unique and market-differentiating products or services. This gives businesses a significant competitive edge and strengthens their position in the industry. - Customer-Centricity:
Innovative companies place a premium on understanding and addressing customer needs. This customer-centric approach not only enhances value but also fosters stronger customer relationships. - Investor Confidence:
A track record of creating value for shareholders instils confidence in the company’s leadership and strategy. This confidence attracts new investors and encourages existing ones to stay committed. - Capital Accessibility:
Companies that consistently create shareholder value find it easier to access capital, whether through equity offerings, debt financing, or partnerships. Investors are more willing to invest in companies with a strong history of value creation. - Long-Term Sustainability:
Shareholder value creation is not just about short-term gains; it’s about ensuring the long-term sustainability of the business. Investors are more likely to support companies with a clear vision for sustained growth. - Dividend and Buyback Potential:
As a result of value creation, companies often have the resources to return value to shareholders through dividends or stock buyback programs, further enhancing investor returns. - Alignment of Interests:
When shareholders benefit from value creation, their interests become aligned with the company’s success. This alignment fosters a sense of partnership and collaboration between shareholders and the organization.
5) Shareholder Value Creation
Creating shareholder value is an indispensable element of business achievement. When shareholders witness their investments prosper, they are more inclined to endorse the company’s growth endeavours. Here’s an exploration of the significance of shareholder value creation:
- Investor Confidence:
A track record of creating value for shareholders instils confidence in the company’s leadership and strategy. This confidence attracts new investors and encourages existing ones to stay committed.
- Capital Accessibility:
Companies that consistently create shareholder value find it easier to access capital, whether through equity offerings, debt financing, or partnerships. Investors are more willing to invest in companies with a strong history of value creation. - Long-Term Sustainability:
Shareholder value creation is not just about short-term gains; it’s about ensuring the long-term sustainability of the business. Investors are more likely to support companies with a clear vision for sustained growth. - Dividend and Buyback Potential:
As a result of value creation, companies often have the resources to return value to shareholders through dividends or stock buyback programs, further enhancing investor returns. - Alignment of Interests:
When shareholders benefit from value creation, their interests become aligned with the company’s success. This alignment fosters a sense of partnership and collaboration between shareholders and the organization.
6) Employee Engagement and Retention
Value creation isn’t limited to customers and shareholders; it also extends to employees. Engaged and satisfied employees not only contribute to increased productivity but also tend to remain with the company longer, reducing turnover costs. Here’s a closer look at the pivotal role of employee engagement and retention in value creation:
- Enhanced Productivity:
Engaged employees are more motivated and committed to their work. They take pride in contributing to a company that values their input, leading to higher productivity and better overall performance. - Reduced Turnover:
Value-centric organizations tend to have lower turnover rates. When employees feel their work is meaningful and aligned with the company’s goals, they are more likely to stay, reducing recruitment and training costs. - Knowledge Retention:
Retaining experienced employees means retaining valuable institutional knowledge. This knowledge is often critical for maintaining operational efficiency and competitiveness. - Positive Work Culture:
A focus on value creation fosters a positive work culture. Employees feel a sense of purpose and are more likely to collaborate and contribute to a harmonious and innovative workplace. - Talent Attraction:
Companies known for creating value and fostering employee satisfaction are attractive to top talent. They find it easier to recruit the best candidates, further strengthening their workforce.
Types of Value Creation
Value creation comes in various forms, tailored to meet the diverse needs of stakeholders. These different types of value creation serve as vital strategies for organizations looking to thrive and excel. Let’s explore these types of value creation, beginning with:
1) Customer Value Creation
Customer value creation is a cornerstone of successful businesses. It involves the art of not just selling products or services but providing solutions that genuinely benefit customers. This type of value creation revolves around understanding and addressing customer needs, problems, and desires. Here’s a closer look at the facets of customer value creation:
- Understanding Customer Needs:
Effective value creation starts with a deep understanding of what your customers truly need. This entails market research, customer feedback, and ongoing engagement to uncover pain points and preferences. - Solving Problems:
By identifying and solving specific challenges or problems faced by customers, you create value. This could involve offering innovative solutions, streamlining processes, or enhancing product features. - Enhancing Lives:
Going beyond problem-solving, businesses can create value by improving the overall quality of life for their customers. This can be achieved through products or services that bring joy, convenience, or efficiency to their daily routines. - Customization and Personalization:
Tailoring offerings to individual customer preferences adds significant value. Customization and personalization strategies, often facilitated by data-driven insights, can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. - Exceptional Customer Service:
Providing excellent customer service is a fundamental aspect of value creation. It ensures customers feel supported, valued, and heard throughout their journey with your business. - Anticipating Future Needs:
Forward-thinking companies also focus on anticipating and fulfilling future customer needs. This involves innovation and staying ahead of evolving market trends.
2) Economic Value Creation
In essence, this assessment treats a business as an investment that should yield a specific return on the capital invested in it. If it generates returns exceeding the required threshold, the surplus is the economic value generated or accrued, often referred to as Economic Value Added (EVA). Here’s a closer look at economic value creation:
- Capital Efficiency:
Economic value creation begins with capital efficiency. It involves optimizing the allocation of financial resources, including investments in assets, projects, and operations, to generate the highest possible returns. - Cost of Capital:
Understanding the cost of capital is essential. This represents the rate of return that investors expect to receive on their investment in the company. It typically comprises the cost of equity and debt. - Actual Returns:
The actual returns generated by a business, often measured as profitability and cash flow, are compared to the cost of capital. If the returns exceed the cost of capital, the company is creating economic value. - Risk Management:
Mitigating risks is crucial in economic value creation. Businesses must assess and manage risks associated with their investments to ensure that the expected returns are achieved. - Investment Analysis:
Robust investment analysis is a key component. It involves evaluating potential projects, acquisitions, or initiatives to determine whether they have the potential to create economic value. This analysis considers factors like projected cash flows, risk, and opportunity costs. - Long-Term Perspective:
Economic value creation is often evaluated over the long term. Businesses must sustainably generate returns that consistently exceed their cost of capital to create enduring economic value.
3) Social Value Creation
Social value creation is a dimension of business that transcends profit and delves into the positive impact a company has on society. It encompasses a range of initiatives aimed at promoting environmental sustainability, community development, and social responsibility. Here’s a closer look at social value creation:
- Environmental Sustainability:
Companies engaged in social value creation often prioritize environmental sustainability. This includes efforts to reduce their carbon footprint, minimize waste, conserve resources, and adopt eco-friendly practices. Initiatives like using renewable energy sources, reducing water consumption, and adopting green supply chain practices fall under this category. - Community Development:
Businesses committed to social value creation invest in the communities where they operate. This can involve supporting local education, healthcare, infrastructure, and economic development projects. Building strong relationships with local communities contributes to the long-term success and reputation of the company. - Social Responsibility:
Demonstrating social responsibility goes beyond legal and regulatory compliance. Companies actively engage in activities that benefit society, such as charitable giving, volunteering programs, and philanthropic partnerships. They may also uphold ethical business practices, fair labour standards, and supply chain transparency. - Stakeholder Engagement:
Engaging with a wide range of stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, and the broader community, is integral to social value creation. Companies often seek input and feedback from these stakeholders to shape their social impact initiatives. - Impact Measurement:
Measuring and reporting on the social impact of initiatives is crucial. Companies use key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess their progress in areas like reducing emissions, supporting local businesses, or promoting diversity and inclusion. - Sustainable Innovation:
Companies dedicated to social value creation often focus on sustainable innovation. This involves developing products or services that address societal challenges, such as clean energy technologies, affordable healthcare solutions, or education platforms.
4) Private Equity Value Creation
Within the domain of private equity analysis, the evaluation of value creation often revolves around a company’s enterprise value, which signifies its overall value. Concerning value creation, the key factors influencing enterprise value encompass revenue expansion, the growth of EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) margins, and the elevation of valuation multiples. Let’s delve further into the concept of value creation in the realm of private equity:
- Enterprise Value Focus:
Private equity firms often measure success in terms of enterprise value, which represents the total value of a company. The objective is to increase this value significantly during their ownership. - Revenue Growth:
One of the primary drivers of value creation is revenue growth. Private equity investors work to identify and execute strategies that boost a company’s top-line revenue, such as expanding market share, entering new markets, or launching new products or services. - EBITDA Margin Expansion:
Expanding the EBITDA margin (the profitability margin) is another key element. Private equity firms focus on optimizing operations and cost management to improve the company’s profitability. - Multiple Expansion:
Achieving multiple expansions involves increasing the valuation multiples at which the company is traded. This can result from improved financial performance, reduced risk, or favourable market conditions. It often leads to a higher exit valuation when the private equity firm eventually sells the company. - Operational Efficiency:
Private equity investors typically scrutinize a company’s operations to identify areas for improvement. This can involve streamlining processes, implementing efficiency measures, and upgrading technology infrastructure. - Strategic Initiatives:
Private equity value creation often includes strategic initiatives such as acquisitions, divestitures, or alliances that complement the company’s core business and contribute to overall growth. - Governance and Management:
Restructuring and enhancing governance structures and management teams are common strategies. Private equity firms may bring in experienced executives or work closely with existing leadership to drive value. - Exit Strategy:
Private equity investors also plan for the eventual exit from their investment, aiming to realize substantial returns. This may involve selling the company through various mechanisms, including initial public offerings (IPOs), mergers and acquisitions (M&A), or secondary buyouts.
5) Innovation Value Creation
Innovation value creation is a pivotal driver of growth and competitiveness for businesses. It revolves around the creation of groundbreaking products, services, or processes that not only disrupt existing markets but also open up entirely new opportunities. Here’s a closer look at innovation value creation:
- Market Disruption:
At its core, innovation value creation seeks to disrupt established markets or industries. It involves introducing novel solutions that challenge the status quo and redefine how things are done. - Product or Service Innovation:
Innovation often begins with the development of new and improved products or services. These innovations can be tangible goods, software applications, digital platforms, or even intangible offerings like experiences or content. - Process Innovation:
Beyond products and services, innovation value creation extends to processes. It involves reimagining and optimizing operational processes to boost efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance quality. - Technological Advancements:
Innovation frequently hinges on technological advancements. This can involve harnessing emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, or advanced materials to create unique offerings. - User-Centric Design:
A critical aspect of innovation is designing solutions with the end-user in mind. User-centric design principles ensure that innovations meet real needs and provide a superior user experience. - Continuous Improvement:
Innovation value creation is an ongoing process. Businesses must foster a culture of continuous improvement and encourage employees to contribute their ideas for innovation. - Risk and Experimentation:
Innovation often entails taking calculated risks and embracing experimentation. Not all innovations will succeed, but learning from failures can lead to breakthroughs. - Market Expansion:
Innovations can enable companies to expand into new markets, both geographically and in terms of target demographics. They can also create cross-selling opportunities with existing products or services. - Competitive Advantage:
Companies that excel at innovation value creation gain a competitive edge. They are better positioned to adapt to changing market dynamics, outpace competitors, and secure market leadership. - Sustainability and Responsibility:
Innovations can also address sustainability and social responsibility challenges. They may involve eco-friendly products, responsible supply chain practices, or initiatives that positively impact society.
6) Environmental Value Creation
Environmental value creation is a pivotal dimension of corporate responsibility and sustainability. It centres on adopting practices that are environmentally friendly and aimed at reducing the ecological footprint of business operations. Here’s a closer look at environmental value creation:
- Sustainable Practices:
At its core, environmental value creation entails adopting sustainable practices throughout a company’s operations. This includes reducing waste, conserving natural resources, and minimizing environmental impact. - Carbon Footprint Reduction:
One of the primary objectives is to reduce the company’s carbon footprint. This involves assessing and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions resulting from various aspects of the business, such as energy consumption and transportation. - Resource Conservation:
Companies engaged in environmental value creation often prioritize the efficient use of resources, including water, energy, and raw materials. This can involve adopting technologies that promote resource conservation. - Waste Reduction and Recycling:
Minimizing waste generation and implementing robust recycling programs are key components. Businesses aim to reduce landfill waste and promote the circular economy by recycling materials. - Renewable Energy Adoption:
Switching to renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, is a common strategy. This not only reduces the environmental impact but can also lead to long-term cost savings. - Eco-Friendly Products:
Many companies focus on developing and offering eco-friendly products or services. These may have reduced environmental impact during production, use, and disposal. - Supply Chain Sustainability:
Ensuring that suppliers adhere to sustainability standards is crucial. Companies often work with their supply chain partners to reduce the overall environmental footprint of products and materials. - Environmental Reporting:
Transparency is vital. Companies engaged in environmental value creation often report on their sustainability initiatives, allowing stakeholders to track progress and hold them accountable. - Regulatory Compliance:
Staying in compliance with environmental regulations is a baseline requirement. Companies also aim to go beyond compliance by adopting proactive environmental measures. - Biodiversity Preservation:
In some cases, environmental value creation extends to preserving biodiversity and protecting natural habitats. This can be relevant for businesses operating in sensitive ecosystems. - Stakeholder Engagement:
Engaging with various stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, and environmental organizations, is vital. Collaborative efforts can lead to more effective environmental initiatives.
What Is Value Creation In Business?
Value creation in business involves a multifaceted strategy for attaining enduring success. It goes beyond mere financial aspects, weaving together stakeholder relationships, innovation, efficiency, and distinctiveness. To thrive in the value creation process, businesses should embrace a comprehensive approach that emphasizes crucial strategies and practices, ensuring their continued competitiveness and relevance in a swiftly changing environment. Let’s explore the fundamental components of business value creation:
1) Enhancing Stakeholder Relations for Sustainable Success
In the complex world of modern business, achieving sustainable success goes beyond profit margins and bottom lines. It centres on the art of enhancing stakeholder relations, a concept that extends far beyond financial stakeholders. It encompasses a web of interconnected relationships with customers, employees, suppliers, and the broader community.
- Innovation and Differentiation
Innovation is the driving force behind differentiation and a competitive edge in the market. It involves the creation of unique products, services, or processes that distinguish your business from competitors.
- Product Innovation: Developing new and improved products keeps your offerings fresh and appealing to customers. It can also lead to higher profit margins.
- Service Innovation: Innovative service delivery methods can enhance the customer experience and build loyalty. Think of the convenience introduced by online banking or food delivery apps.
- Process Innovation: Streamlining internal processes improves efficiency and reduces costs. This innovation can translate into better pricing or improved customer service.
- Customer-Centric Approach and Experience
Putting customers at the centre of your business strategy is paramount for long-term success. It involves understanding their needs and delivering exceptional experiences.
- Needs Analysis: Conduct thorough market research to identify customer needs and preferences. This informs product development and marketing strategies.
- Personalization: Tailor your products or services to individual customer preferences when possible. Personalization enhances the customer experience and fosters loyalty.
- Feedback and Improvement: Solicit and act upon customer feedback to continuously improve your offerings. Customers appreciate when their opinions are valued.
- Employee Engagement and Development
Engaging and developing employees is not just a moral imperative; it’s also a strategic advantage. Engaged employees are more productive, innovative, and committed to achieving organizational goals, thus contributing to creating value for customers.
- Training and Development: Invest in ongoing training and development programs to enhance employee skills and knowledge. This not only benefits the individual but also the organization.
- Recognition and Rewards: Acknowledge and reward employee contributions. This can boost morale, motivation, and overall job satisfaction.
- Open Communication: Encourage open and transparent communication throughout the organization. This helps foster a culture of collaboration and innovation.
- Wellness Programs: Promote employee well-being through wellness initiatives. Healthy and happy employees are more productive and engaged. contributing to creating value for customers and stakeholders alike.
2) Efficiency and Cost Management
Efficiency and cost management are fundamental pillars of value creation in business. They involve the meticulous optimization of operations and resources to enhance overall profitability. Let’s delve deeper into this critical aspect:
- Resource Allocation: Efficient cost management ensures that resources, including finances, manpower, and time, are allocated judiciously to achieve maximum productivity and minimize waste.
- Improved Profit Margins: By identifying and eliminating inefficiencies, businesses can significantly enhance their profit margins, making every dollar count.
- Competitive Advantage: A company that excels in cost management can often offer more competitive prices in the market, attracting a larger customer base and gaining a strategic advantage.
- Sustainability: Streamlining operations and reducing waste not only bolsters profits but also aligns with sustainability goals, which can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Innovation: Effective cost management encourages innovation as businesses seek creative ways to reduce expenses and enhance processes.
3) Innovation and Differentiation
In today’s fast-paced business environment, innovation and differentiation are critical elements of value creation. They set successful organizations apart by enabling them to not only keep up with changing market dynamics and evolving customer preferences but also lead the way in their respective industries. Let’s explore this concept in greater detail:
- Continuous Innovation: For businesses, innovation should be an ongoing process. It involves identifying opportunities for improvement, both in products and processes, and implementing changes to stay competitive. This may include technological advancements, new product features, or even entirely novel solutions to existing problems.
- Adaptation to Market Dynamics: Markets are dynamic, and what works today may not work tomorrow. Staying attuned to market shifts and emerging trends is essential. Businesses need to adapt quickly to seize new opportunities and mitigate potential risks.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Successful innovation is often customer-centric. Understanding customer needs and preferences is vital in creating products or services that resonate with the target audience. Regular feedback and engagement with customers can guide the innovation process.
- Creating Unique Value: Differentiation is about standing out from the competition. Through innovation, businesses can create unique value propositions that make their offerings more appealing to customers. This could involve superior quality, distinct features, or a one-of-a-kind customer experience.
- Sustainability: Innovation doesn’t just mean short-term improvements; it can also lead to long-term sustainability. Businesses that innovate with sustainability in mind can reduce costs, attract eco-conscious customers, and contribute positively to the environment, thereby enhancing their value creation efforts.
- Market Leadership: Continuous innovation and differentiation can position a business as a leader in its industry. Being at the forefront of change can open up new revenue streams and solidify a company’s reputation as an industry innovator.
4) Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Sustainability and social responsibility are integral facets of value creation in business. These practices not only benefit society and the planet but also bolster a company’s reputation and appeal to a growing base of socially conscious customers. Let’s explore this critical aspect in more detail:
- Environmental Sustainability: Businesses that incorporate environmentally friendly practices contribute positively to the planet. This includes minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and adopting eco-friendly technologies. Sustainability efforts can lead to cost savings, regulatory compliance, and alignment with global sustainability goals, such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Social Responsibility: Beyond environmental concerns, social responsibility involves ethical behaviour and philanthropic initiatives. It includes fair treatment of employees, responsible supply chain management, and community engagement. Companies that prioritize social responsibility often build stronger relationships with employees, suppliers, and local communities.
- Enhanced Reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and social responsibility can significantly enhance a company’s reputation. Customers and stakeholders increasingly prefer to support businesses that align with their values. A positive reputation can lead to customer loyalty, increased market share, and improved brand recognition.
- Appeal to Socially-Conscious Customers: Many consumers today make purchasing decisions based on a company’s social and environmental practices. Businesses that prioritize sustainability and social responsibility can tap into a growing market of socially-conscious customers. This can lead to increased sales and a competitive advantage.
- Long-Term Viability: Sustainability practices aren’t just about short-term gains. They contribute to the long-term viability of a business. By reducing waste, conserving resources, and fostering responsible practices, companies can ensure their operations remain resilient and adaptable in a changing world.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions have implemented environmental and social regulations that businesses must adhere to. By proactively embracing sustainability and social responsibility, companies can avoid legal issues, fines, and negative publicity associated with non-compliance.
5) Measurement and Evaluation
Regularly assess and measure the impact of your value creation efforts to ensure they align with strategic objectives. They serve as a compass that guides organizations toward their strategic objectives. By regularly assessing and quantifying the impact of value creation efforts, businesses can ensure alignment with their overarching goals. Let’s take a closer look at this essential aspect:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Defining clear KPIs is essential for measuring value creation. These indicators should be directly tied to the strategic objectives of the organization. They could include financial metrics like revenue growth and profitability, as well as non-financial metrics such as customer satisfaction, employee engagement, or sustainability targets.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Businesses should establish robust data collection mechanisms to gather relevant information related to their value creation efforts. This data can come from various sources, including customer surveys, financial reports, and operational data. Advanced data analytics tools can help in deriving meaningful insights from this data.
- Regular Reporting: To maintain a proactive approach to value creation, regular reporting is essential. Organizations should have processes in place to compile and analyze data at regular intervals, whether it’s on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis. Reporting ensures that value creation efforts remain on track and are adjusted as needed.
- Benchmarking: Comparing your performance and value creation efforts against industry benchmarks and competitors can provide valuable insights. Benchmarking helps identify areas where improvements can be made and sets the standard for excellence in your industry.
- Feedback Loops: Soliciting feedback from customers, employees, and stakeholders is a valuable part of measurement and evaluation. Feedback can reveal areas of strength and areas in need of improvement. It also fosters a culture of continuous improvement within the organization.
- Strategic Alignment: Perhaps most importantly, measurement and evaluation should always be aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. It ensures that value creation efforts are not just isolated activities but contribute directly to the fulfillment of the organization’s mission and vision.
- Course Correction: When measurement and evaluation reveal discrepancies between desired outcomes and actual results, it provides an opportunity for course correction. Businesses can adapt their strategies, allocate resources differently, or implement changes to optimize value creation.
6) Financial Performance and Adaptation to Market Dynamics
Monitoring financial performance and adeptly adapting to market dynamics is a pivotal aspect of value creation. This practice not only ensures a company’s survival but also its ability to thrive amidst ever-changing economic landscapes. Let’s delve deeper into this crucial element:
- Financial Metrics: The foundation of monitoring financial performance lies in the measurement of key financial metrics. This includes tracking revenue, profit margins, cash flow, and return on investment (ROI). These metrics provide essential insights into the financial health of the organization.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Establishing a sound budget and forecasting system is vital. It allows businesses to set financial goals, allocate resources effectively, and plan for contingencies. Regularly revisiting and adjusting these budgets in response to market changes is essential for agility.
- Risk Management: Navigating market dynamics involves managing various risks. These risks can range from economic downturns to fluctuations in supply chain costs. Developing risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans is integral to maintaining financial stability.
- Competitor Analysis: Keeping a close eye on competitors’ financial performance and market strategies is invaluable. It helps businesses adapt and innovate to stay ahead or pivot in response to shifts in the competitive landscape.
- Customer Insights: Understanding customer behavior, preferences, and spending patterns is another dimension of financial performance. Customer insights can inform pricing strategies, product development, and marketing efforts, ultimately impacting the bottom line positively.
- Capital Allocation: Efficient allocation of capital is essential for value creation. This involves making informed decisions about investing in new projects, expanding into new markets, or optimizing existing operations to maximize returns.
- Adaptation Strategies: Businesses must be nimble and adaptive in the face of market dynamics. This may involve diversifying product offerings, entering new markets, or even pivoting the entire business model to address changing customer needs.
- Technology Integration: Leveraging technology and data analytics is becoming increasingly critical in financial performance monitoring. It allows for real-time data analysis, predictive modeling, and agile decision-making in response to market trends.
- Continuous Improvement: The process of monitoring financial performance should be iterative. Regular reviews, post-mortems, and performance assessments help identify areas for improvement and drive ongoing refinement of financial strategies.
Value Creation Dimensions
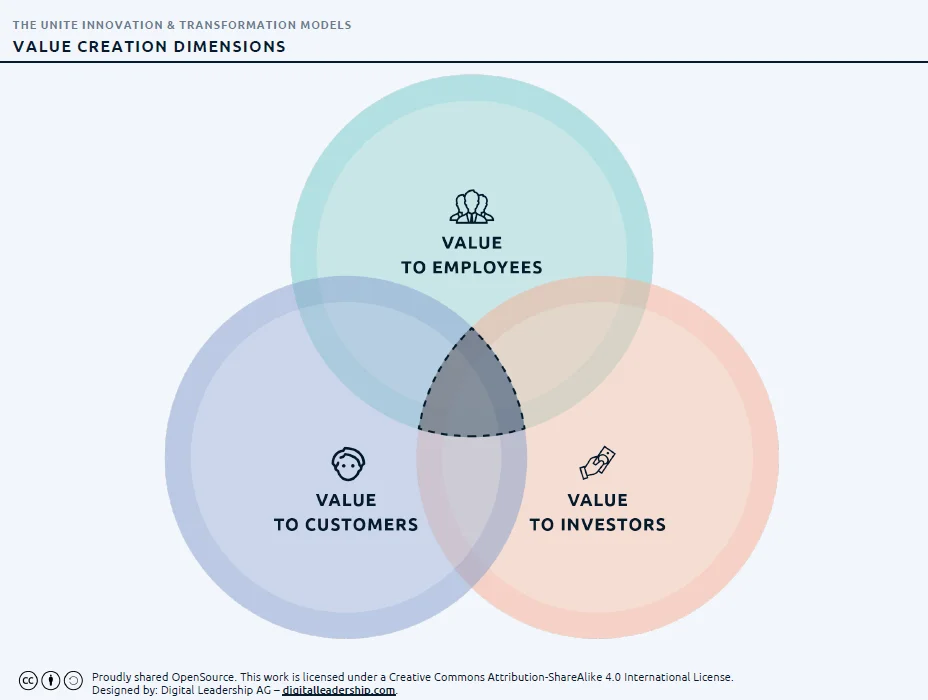
Designed by: Digital Leadership
The value creation model is adaptable, and contingent on factors such as industry, market dynamics, and the specific objectives of a company. In essence, it revolves around crafting a distinctive solution that effectively addresses a particular customer need or problem, surpassing existing alternatives in various aspects.
This achievement is realized through a focus on differentiating factors, which may encompass aspects such as quality, convenience, price, or innovation. Typically, the value created is evaluated by multiple stakeholders, including customers, investors, and internal teams or employees.
As we move towards a more sustainable model, it becomes imperative to extend the value assessment to encompass its impact on the planet and the broader ecosystem.
For a comprehensive exploration of value creation and innovative strategies, we invite you to explore our book, “How to Create Innovation.” In this resource, you’ll find valuable insights, including guidance on developing a business plan and establishing a clear business purpose that aligns with your value creation objectives.
Dimensions of Value Creation Dimension Model:
1) Value Creation for a Customer
Maximizing customer value begins with a thorough understanding of the unique needs and preferences of high-value customers. This entails a multifaceted approach that delves deep into customer data and behavior. By segmenting the customer base, analyzing historical behavior, and conducting in-depth surveys and feedback sessions, businesses can uncover valuable insights.
Additionally, creating customer journey maps, studying competitors, and employing predictive analytics all contribute to a comprehensive understanding. Social listening and cross-functional collaboration enhance this process further. The integration of data from various sources and the establishment of feedback loops ensure that this understanding remains dynamic and up-to-date. Armed with this knowledge, businesses can tailor their offerings and strategies to deliver exceptional value, ultimately fostering long-term customer loyalty and business success.
- Understanding Customer Needs:
The first step in maximizing customer value is understanding the specific needs and preferences of your high-value customers. This involves market research, customer surveys, and feedback analysis to gain insights into what they value.
- Product or Service Quality:
Providing high-quality products or services is essential for value creation. Quality ensures that customers receive what they expect and minimizes the likelihood of dissatisfaction.
- Features and Benefits:
Offering features and benefits that align with customer needs and preferences can enhance the perceived value of your offering. Highlighting how your product or service solves their problems or fulfills their desires is crucial.
- Personalization:
Tailoring your offerings to individual customer preferences can create a unique and personalized experience. This might include customization options, product recommendations, or personalized communication.
- Convenience and Accessibility:
Customers value convenience and accessibility. Make it easy for them to purchase, use, or access your products or services. This can involve user-friendly interfaces, efficient customer service, and multiple distribution channels.
- Competitive Pricing:
While value creation doesn’t solely depend on low prices, offering competitive pricing that aligns with the perceived value of your product or service is important. Customers should feel they are getting a fair deal.
- Customer Service and Support:
Exceptional customer service and support can significantly enhance value creation. Being responsive to customer inquiries, resolving issues promptly, and providing post-purchase support are essential components.
- Trust and Reputation:
Building trust through transparency, reliability, and a positive reputation is crucial for value creation. Customers are more likely to engage with businesses they trust.
- Innovation:
Continuously innovating and staying ahead of competitors can create value by offering customers new and improved solutions that meet emerging needs.
- Sustainability and Social Responsibility:
Many customers today value businesses that demonstrate social and environmental responsibility. Incorporating sustainability into your business practices can enhance value creation.
- Communication and Engagement:
Effective communication with customers, through marketing, social media, and other channels, can help convey the value of your offerings and build relationships. - Feedback and Improvement:
Actively seeking customer feedback and using it to make improvements demonstrates a commitment to customer satisfaction and continuous value creation.
2) Value Creation for Employees
Value creation for employees is essential for building a satisfied and engaged workforce, which, in turn, significantly contributes to the overall success and sustainability of a business. Here are some key aspects of value creation for employees:
- Competitive Compensation and Benefits:
Offering competitive salaries and benefits helps attract and retain top talent. Fair compensation demonstrates that the organization values its employees and their contributions. - Career Development Opportunities:
Providing opportunities for skill development, training, and advancement within the company shows a commitment to employees’ professional growth. This can include mentorship programs, tuition reimbursement, and clear career paths. - Work-Life Balance:
Supporting a healthy work-life balance through flexible scheduling, remote work options, and paid time off can improve employee well-being and job satisfaction. - Recognition and Rewards:
Recognizing and rewarding employees for their achievements and contributions boosts morale and motivation. This can include bonuses, awards, and public acknowledgement. - Safe and Inclusive Work Environment:
Ensuring a safe, inclusive, and diverse workplace is crucial for employee satisfaction. A culture that values diversity and inclusion fosters creativity and innovation. - Empowerment and Autonomy:
Allowing employees to have a say in decision-making, encouraging creativity, and providing autonomy in their roles can lead to higher job satisfaction and engagement. - Clear Communication and Feedback:
Open and transparent communication channels, as well as regular feedback sessions, help employees understand their role in the organization and provide opportunities for improvement. - Health and Wellness Programs:
Offering wellness programs, such as gym memberships, mental health support, and health insurance, can promote employee well-being. - Company Culture and Values:
Fostering a positive company culture that aligns with the organization’s values can create a sense of belonging and purpose among employees. - Social Responsibility and Sustainability:
Demonstrating a commitment to social responsibility and sustainability can attract employees who are aligned with these values and create a sense of pride in their work. - Employee Engagement and Feedback:
Actively involving employees in decision-making processes, seeking their input, and acting on their feedback can make them feel more valued and engaged. - Fair and Ethical Treatment:
Treating employees fairly and ethically, addressing concerns promptly, and ensuring a safe and respectful workplace environment is fundamental to value creation for employees. - Team Building and Collaboration:
Encouraging teamwork, collaboration, and a sense of belonging can enhance job satisfaction and create a positive work atmosphere. - Leadership Development:
Investing in leadership development programs can help employees progress into leadership roles within the company, providing a clear path for growth.
3) Value Creation for Investors
Value creation for investors is a fundamental objective for any business, as it directly affects the attractiveness of the company’s investment proposition. Investors, whether they are shareholders, bondholders, or other stakeholders, seek opportunities that offer the potential for sustained value growth. Here are key aspects of value creation for investors:
- Financial Performance:
Investors primarily assess a company’s financial performance and its potential for generating returns on their investment. Consistent revenue growth, profitability, and prudent financial management are essential. - Dividend Payments:
Dividend payments to shareholders provide a direct return on investment. Companies that regularly pay dividends or increase them over time often attract income-oriented investors. - Capital Appreciation:
Investors also seek capital appreciation, which means an increase in the value of their investment over time. A rising stock price or bond value reflects this capital growth. - Transparency and Disclosure:
Maintaining transparent financial reporting and disclosing relevant information ensures that investors have access to accurate data for informed decision-making. - Risk Management:
Implementing effective risk management strategies and providing clear insights into risk factors and mitigation plans is crucial for investor confidence. - Sustainable Growth:
Investors increasingly value companies with strategies for long-term, sustainable growth. This includes considerations for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. - Effective Governance:
Strong corporate governance practices, such as an independent board of directors and executive compensation aligned with performance, can enhance investor trust. - Efficient Capital Allocation:
Investors look for companies that efficiently allocate capital to projects and initiatives that offer the highest returns, rather than wasteful spending. - Clear Strategic Vision:
Companies with a clear and well-communicated strategic vision and execution plan are more likely to attract investors seeking long-term value creation. - Communication with Investors:
Regular communication with investors through financial reports, conference calls, and investor relations teams helps maintain investor confidence. - Return on Investment (ROI):
Providing investors with a competitive return on their investment is the ultimate goal. Demonstrating a track record of delivering solid ROI is vital. - Market Position and Competitive Advantage:
Companies that have a strong market position and a sustainable competitive advantage are often seen as more attractive investment opportunities. - Adaptability and Innovation:
Investors value companies that can adapt to changing market conditions and innovate to stay competitive and grow. - Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensuring compliance with all relevant laws and regulations is critical to avoid legal issues that can erode investor trust.
Principles of Creating Value
In a competitive business environment where options are abundant, the art of creating valuable outcomes is guided by fundamental principles. These principles are actionable strategies that significantly impact an organization’s trajectory. They encompass understanding the target audience, crafting compelling value propositions, leveraging key resources and capabilities, analyzing the competitive landscape, optimizing value creation, continuous evaluation and adaptation, and stakeholder alignment and effective execution.
1) Understanding the Target Audience
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, two fundamental pillars stand as cornerstones of success: understanding your target audience and crafting a compelling value proposition. These principles, far from being abstract concepts, are actionable strategies that can significantly impact your business’s trajectory.
- Customer-Centric Focus
Customer-centricity transcends being a mere buzzword; it forms the bedrock of a business philosophy that places customers at the heart of your strategic endeavors. This philosophy necessitates prioritizing their needs, experiences, and desires. To forge meaningful connections with your audience, consider these effective strategies:
- Actively Listening: Successful customer-centric businesses actively seek feedback from their customers. Utilize surveys, customer support interactions, and social media engagement to capture valuable insights.
- Empathy and Understanding: Empathizing with your customers and comprehending their pain points and challenges are paramount. This insight allows you to develop solutions that directly address their needs, enhancing the relevance and value of your offerings.
- Personalization: Customer-centricity often entails personalization. Tailoring your products, services, and interactions to individual customer preferences enriches their experience and fosters loyalty.
- Compelling Value Proposition
Value proposition serves as a guiding light directing customers towards your offerings. It encapsulates the fundamental commitment you make to those you serve. The process of shaping a captivating value proposition involves a meticulous exploration of essential elements that can set you apart in the market:
- Identifying Unique Benefits: A compelling value proposition hinges on recognizing the distinct advantages your product or service offers. This entails a thorough assessment of your strengths and what sets you apart from competitors.
- Addressing Specific Needs: A robust value proposition directly targets the specific needs of your target audience. It should unequivocally illustrate how your offering resolves their problems, fulfills their desires, or simplifies their lives. This customer-centric approach is pivotal in value proposition creation.
- competitive advantage: Your value proposition should underscore your competitive edge. Articulate why customers should choose your solution over alternatives, highlighting what makes you the superior choice. This facet is central to value proposition creation, as it guides customers toward your offerings.
- Concise Communication: In an era of information overload, keeping your value proposition concise and easily digestible is pivotal. A well-articulated value proposition serves as a potent tool for attracting and retaining customers.
2) Leveraging Key Resources, Capabilities, and Activities
For effective value creation, an essential principle is the strategic utilization of key resources, capabilities, and activities. A fundamental principle for effective value creation involves strategically leveraging key resources, capabilities, and actions. This involves identifying, harnessing, and optimizing the core assets and competencies that distinguish an organization. Here’s a closer look at this principle:
- Identifying Key Resources: Begin by identifying the critical resources within your organization. These can include physical assets like machinery or intellectual resources such as patents and data.
- Harnessing Core Capabilities: Determine what your organization does exceptionally well. These core capabilities might involve technical expertise, unique skills, or a particular approach to problem-solving.
- Optimizing Key Activities: Assess the processes and activities that drive your business. Streamlining and enhancing these operations can lead to greater efficiency and effectiveness.
- Strategic Alignment: Ensure that your resources, capabilities, and activities align with your overall business strategy. They should support your value proposition and the needs of your target audience.
- Continuous Improvement: Recognize that these assets and competencies should not remain static. Continuously evaluate and evolve them to stay competitive and relevant in the ever-changing business landscape.
3) Analyzing the Competitive Landscape and Achieving Differentiation
Analyzing the competitive landscape and striving for differentiation are pivotal aspects of effective value creation. Understanding the market environment and finding ways to set your business apart are essential for long-term success.
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to gain insights into your industry, competitors, and target audience. This data forms the foundation for value creation.
- Competitor Analysis: Identify your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, market positioning, and strategies. This knowledge helps you find gaps and opportunities.
- Unique Value Proposition (UVP): Develop a compelling UVP that clearly communicates what sets your products or services apart from the competition. This could be based on quality, innovation, price, or other factors.
- Innovation: Continuously innovate to stay ahead of the curve. Invest in research and development to create new features, products, or services that resonate with your customers.
- Cost Leadership: Consider cost leadership as a differentiation strategy by offering quality products or services at lower prices than competitors.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Tailor your offerings to meet customer needs and preferences. Provide exceptional customer service and support to build brand loyalty.
- Niche Targeting: Focus on a specific niche within your market. This can help you become a specialist and dominate a smaller segment.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Explore partnerships with complementary businesses or organizations to expand your reach and offerings.
- Sustainability and Social Responsibility: Embrace sustainability and social responsibility practices to differentiate your brand and appeal to conscious consumers.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly assess market dynamics and adjust your strategies accordingly. What sets you apart today may change over time.
4) Optimizing Value Creation
Optimizing value creation is the ongoing process of fine-tuning your strategies and operations to maximize the value delivered to stakeholders while minimizing inefficiencies and waste. This principle is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and ensuring sustained growth.
- Data-Driven Insights: Utilize data analytics and market research to gain a deeper understanding of customer preferences, market trends, and emerging opportunities. This data serves as the foundation for informed decision-making.
- Operational Efficiency: Continuously evaluate and streamline your internal processes to reduce costs, improve productivity, and enhance the quality of products or services.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources judiciously, prioritizing areas that have the most significant impact on value creation. This includes investments in technology, talent, marketing, and innovation.
- Feedback Loops: Establish feedback mechanisms with customers, employees, and other stakeholders to gather insights and identify areas for improvement. Act on this feedback to enhance value delivery.
- Agile Adaptation: Embrace an agile approach to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs. This agility allows you to seize new opportunities promptly.
- Technology Integration: Leverage technology and automation to optimize operations, improve customer experiences, and enhance the scalability of your value creation efforts.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration among different departments and teams within your organization. Cross-functional teams can ideate and implement strategies that maximize value across various facets of the business.
- Cost Management: Implement effective cost management strategies to ensure that resources are used efficiently, thereby freeing up capital for investments that drive value.
- Performance Metrics: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your value creation goals. Regularly monitor and assess these metrics to track progress and make data-driven adjustments.
- Sustainability Focus: Consider sustainability in your value creation process. Sustainable practices can not only reduce costs but also appeal to eco-conscious consumers and investors.
- Continuous Learning: Encourage a culture of continuous learning and improvement within your organization. Invest in training and development to equip your team with the skills needed to optimize value creation.
5) Continuous Evaluation and Adaptation
The ability to continuously evaluate and adapt is paramount for effective value creation. This principle emphasizes the importance of staying agile and responsive to evolving circumstances, market trends, and customer preferences.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Base your decisions on data and analytics. Regularly collect and analyze information about your market, customers, and competition.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define KPIs that align with your business goals. These metrics help you assess your progress and make informed adjustments.
- Feedback Loops: Establish feedback mechanisms with customers, employees, and stakeholders. Their insights can provide valuable guidance for improvements.
- Market Trends: Stay informed about industry trends and emerging technologies. Anticipate shifts in customer behavior and adapt your strategies accordingly.
- Competitor Monitoring: Continuously monitor your competitors to identify new threats and opportunities. Learn from their successes and failures.
- Agility and Flexibility: Build an organizational culture that values agility and flexibility. Be prepared to pivot when necessary to seize emerging opportunities or address challenges.
- Strategic Planning: Regularly review and update your strategic plan. Ensure it remains aligned with your long-term vision and adapts to changing circumstances.
- Innovation Culture: Foster a culture of innovation within your organization. Encourage employees to contribute ideas and solutions that drive value.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources based on performance and potential. Focus investments on areas that have the greatest potential for value creation.
- Risk Management: Assess and mitigate risks proactively. Develop contingency plans to navigate unforeseen challenges.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Continually refine your understanding of customer needs and preferences. Adjust your offerings and strategies to meet their evolving expectations.
- Testing and Experimentation: Experiment with new ideas and approaches. A/B testing and pilot programs can help you identify what works best.
6) Stakeholder Alignment and Effective Execution
Achieving value creation requires not only careful planning and strategy but also the alignment of various stakeholders within and outside the organization. Effective execution of your plans is crucial to turning strategies into tangible results.
- Identifying Key Stakeholders: Begin by identifying all relevant stakeholders. These may include employees, customers, investors, suppliers, regulatory bodies, and the local community.
- Understanding Stakeholder Needs: Once identified, understand the unique needs, expectations, and interests of each stakeholder group. This insight will guide your value creation efforts.
- Alignment of Interests: Seek common ground among stakeholders and align their interests with your business goals. This alignment fosters collaboration and support.
- Clear Communication: Maintain transparent and open communication with stakeholders. Convey your goals, progress, and how their involvement contributes to value creation.
- Employee Engagement: Ensure that employees are engaged and motivated to contribute to value creation. Recognize their role as crucial stakeholders.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Place customers at the center of your value creation efforts. Continuously gather feedback and adapt your offerings to meet their evolving needs.
- Investor Relations: Maintain a positive relationship with investors by delivering on promises and demonstrating your commitment to creating value for them.
- Supply Chain Collaboration: Collaborate closely with suppliers to ensure a seamless supply chain, quality products, and cost-effectiveness.
- Regulatory Compliance: Understand and adhere to relevant regulations and compliance standards. This builds trust with regulatory stakeholders.
- Community Engagement: Actively engage with the local community and demonstrate corporate social responsibility (CSR) to create goodwill.
- Execution Excellence: Develop a robust execution plan that translates your value creation strategies into tangible actions. Assign responsibilities, set milestones, and monitor progress.
- Agility and Adaptability: Be prepared to adapt your execution plan as circumstances change. Agility is essential in responding to market shifts.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish clear KPIs to measure the effectiveness of your value creation initiatives. Regularly assess and adjust your strategies based on KPI outcomes.
Organizations utilize value creation models to gain insights into and strategize on how to generate value for customers, stakeholders, and shareholders. Employing a value creation framework enhances comprehension of the critical elements and mechanisms involved in the value creation journey.
Value Creation Through Growth and Innovation
Achieving sustainable growth and maintaining competitiveness requires a proactive approach that embraces fresh ideas, emerging technologies, and innovative processes.
The growth through innovation value creation model focuses on achieving growth and competitiveness by identifying and harnessing fresh ideas, technologies, and processes. This model places a strong emphasis on ongoing enhancement, experimentation, and collaboration across various organizational functions. You can download it now.
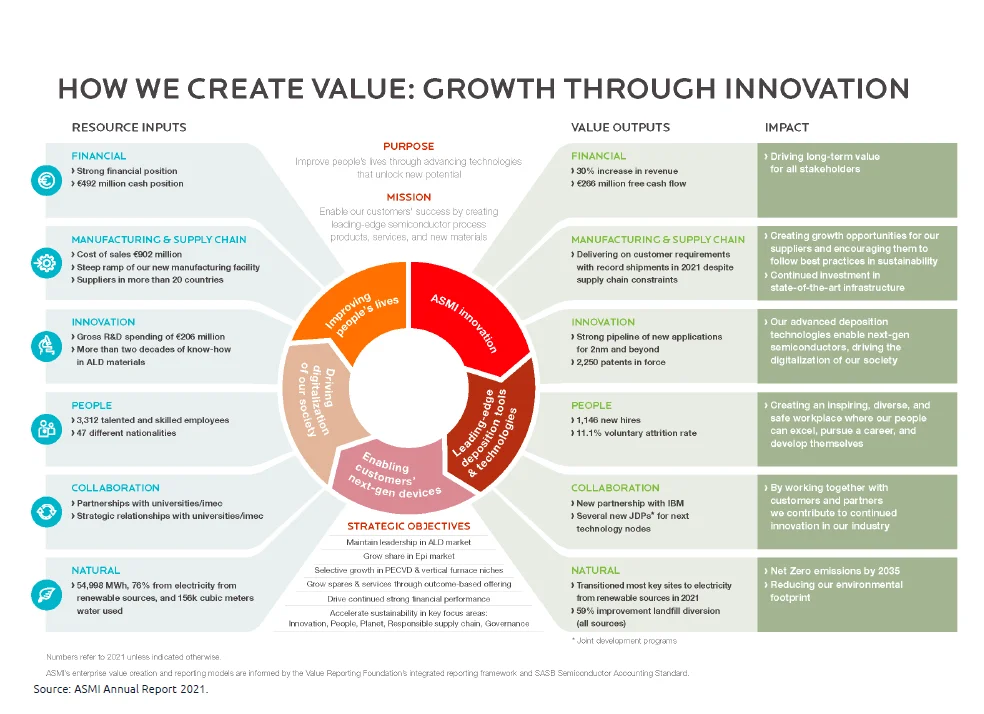
Source: ASMI Annual Report 2021
Its core elements involve conducting thorough market research, nurturing an innovative culture, allocating resources to research and development, and establishing strategic alliances with suppliers, customers, and stakeholders. Embracing growth through an innovation approach enables organizations to introduce novel products and services, enhance existing ones, and gain a distinct competitive advantage in the market. You can download it now.
Key Elements of the Growth Through Innovation Model:
- Market Research:
Conducting thorough market research is fundamental to identifying opportunities for growth and innovation. It involves studying market trends, customer needs, and emerging technologies. - Innovative Culture:
Nurturing an organizational culture that values innovation is essential. Encouraging employees to generate and implement creative ideas fosters a fertile ground for innovation. - Research and Development:
Allocating resources to research and development (R&D) is crucial for innovation. This includes investing in the exploration of new technologies, processes, and product/service enhancements. - Strategic Alliances:
Establishing strategic partnerships with suppliers, customers, and stakeholders can provide access to valuable resources and expertise. Collaborative relationships often lead to innovative solutions. - New Products and Services:
Embracing growth through an innovation approach allows organizations to introduce novel products and services to the market. These innovations can attract new customer segments and revenue streams.
Our Approach to Value Creation: Growth and Innovation
1) Innovation as a Catalyst
Innovation stands as a powerful catalyst for value creation within organizations. It drives growth, enhances competitiveness, and fosters sustainability by introducing novel ideas, processes, and technologies. Let’s explore how innovation fuels value creation:
- Product Innovation: Introducing new or improved products can capture fresh markets and customer segments, boosting revenue and market share.
- Process Innovation: Streamlining internal processes leads to cost reductions and increased efficiency, contributing to higher profitability.
- Customer-Centric Innovation: Tailoring products or services to customer needs not only strengthens customer loyalty but also attracts new clientele.
- Market Expansion: Innovations can open doors to new markets and geographic regions, broadening an organization’s reach.
- Competitive Advantage: Staying at the forefront of innovation helps organizations outshine competitors and maintain a strong market position.
2) Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in modern business environments, acting as a catalyst for value creation in numerous ways. These innovations continually reshape industries and market dynamics. Let’s delve into how technological advancements drive value creation:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Adopting cutting-edge technologies streamlines processes, reduces operational costs, and improves overall efficiency.
- New Revenue Streams: Technological innovations often lead to the development of new products or services, tapping into previously unexplored markets.
- Improved Customer Experience: Advanced tech solutions can enhance the customer experience, resulting in increased satisfaction and loyalty.
- Data-Driven Insights: Big data analytics and artificial intelligence empower organizations to make informed decisions, identify trends, and optimize strategies.
- Competitive Edge: Staying updated with the latest technologies ensures a competitive advantage, attracting both customers and investors.
3) Cross-Functional Collaboration
Cross-functional collaboration within organizations is a fundamental strategy for value creation. It involves breaking down silos between different departments or teams to work together seamlessly toward common goals. Here’s how cross-functional collaboration contributes to value creation:
- Diverse Expertise: By bringing together individuals with diverse skills and knowledge, organizations can approach challenges and opportunities from multiple angles.
- Innovation Incubator: Collaborative environments often breed innovation, as the exchange of ideas and perspectives can lead to creative solutions and breakthroughs.
- Efficient Problem-Solving: Cross-functional teams can address complex issues more efficiently, drawing upon a broader range of resources and expertise.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Collaboration helps ensure that all departments align their efforts with the goal of meeting customer needs and delivering exceptional value.
- Strategic Alignment: When various functions collaborate, they are better positioned to align their activities with the organization’s strategic objectives, leading to more effective value creation.
4) Risk and Experimentation
To create value, one often overlooked yet crucial factor aspect is the willingness to take calculated risks and engage in experimentation. Here’s an exploration of how risk and experimentation can drive value:
- Innovative Solutions: Embracing risk allows organizations to experiment with new ideas and approaches, potentially leading to groundbreaking innovations.
- Market Leadership: Companies that are willing to take calculated risks often become market leaders, as they are more likely to seize opportunities and navigate uncertainties.
- Adaptability: A culture of experimentation fosters adaptability, helping organizations respond effectively to changing market conditions and consumer preferences.
- Learning and Growth: Even if an experiment doesn’t yield the desired results, it offers valuable insights and learning opportunities that can inform future strategies.
- Competitive Advantage: Bold experimentation can set organizations apart from competitors, attracting customers who value innovation and risk-taking.
5) Sustainability and Responsible Innovation
Sustainability and responsible innovation are integral to value creation. These principles not only contribute to ethical and environmental responsibility but also drive long-term success. Let’s explore how sustainability and responsible innovation play a crucial role in value creation:
- Environmental Stewardship: Sustainable practices minimize environmental impact, reduce waste, and lower resource consumption, ultimately cutting costs and enhancing reputation.
- Long-Term Viability: Responsible innovation takes into account the long-term consequences of decisions, ensuring that actions taken today do not compromise future value.
- Consumer Demand: Increasingly, consumers prioritize products and services that align with sustainable and ethical values, creating opportunities for businesses to meet this demand.
- Regulatory Compliance: Complying with environmental and ethical regulations not only mitigates risks but can also lead to cost savings and improved public perception.
- Reputation and Brand Equity: Organizations that champion sustainability and responsible innovation often enjoy stronger brand loyalty and trust among consumers.
6) Measuring Innovation Success
In the process of value creation through innovation, measuring success is essential to ensure that efforts align with strategic objectives and provide a return on investment. Here’s how organizations can effectively measure the success of their innovation endeavors:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establishing KPIs specific to innovation initiatives helps track progress and evaluate outcomes. These might include metrics like revenue growth from new products, the number of successful product launches, or customer satisfaction scores related to innovations.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculating the ROI for innovation projects is crucial. It involves comparing the gains, such as increased revenue or cost savings, to the costs associated with the innovation, including research and development expenses.
- Market Impact: Assessing how an innovation impacts the market, such as gaining market share or expanding into new customer segments, provides insights into its success.
- Customer Feedback: Soliciting feedback from customers who have experienced the innovation can provide valuable qualitative data on its perceived value and effectiveness.
- Time-to-Market: Measuring the time it takes to move from ideation to product launch can indicate the efficiency and success of the innovation process.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Comparing the innovation’s performance to competitors in the market can help organizations gauge their relative success.
- Innovation Portfolio Analysis: Organizations can assess the overall health and performance of their innovation portfolio by categorizing innovations as incremental improvements or disruptive breakthroughs and tracking their impact over time.
7) Adaptability and Agility
To create value, adaptability, and agility are indispensable qualities that enable organizations to respond effectively to changing circumstances and seize emerging opportunities. Here’s how adaptability and agility contribute to value creation:
- Responsive Decision-Making: An adaptable organization can quickly assess changing market conditions and make informed decisions, maximizing the potential for value creation.
- Innovation Facilitation: Agility fosters an environment where new ideas can be tested and implemented swiftly, driving innovation and staying ahead of competitors.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Adaptability allows organizations to align their strategies with evolving customer needs and preferences, ensuring that they continue to deliver value.
- Risk Management: An agile organization is better equipped to manage and mitigate risks, safeguarding against potential value erosion.
- Operational Efficiency: Adaptable processes and structures enable organizations to streamline operations and reduce costs, contributing to overall value creation.
- Scalability: The ability to adapt and scale resources and operations as needed ensures that organizations can seize growth opportunities when they arise.
8) Long-Term Perspective
Taking a long-term perspective is a fundamental aspect of value creation, ensuring that organizations not only thrive in the present but also lay the groundwork for sustained success in the future. Here’s how adopting a long-term view contributes to value creation:
- Strategic Planning: Long-term thinking guides strategic planning, enabling organizations to set clear objectives and develop comprehensive strategies that align with their mission and vision.
- Investment in Research and Development: Organizations that prioritize the long term are more likely to invest in research and development, leading to innovation and the creation of new value streams.
- Customer Relationships: A long-term perspective fosters the cultivation of enduring customer relationships, which can result in continued revenue streams and brand loyalty.
- Risk Mitigation: It allows organizations to anticipate and mitigate potential risks and challenges that may arise in the future, safeguarding against value erosion.
- Corporate Responsibility: Organizations committed to the long term often embrace corporate social responsibility, contributing positively to society and the environment, which can enhance their reputation and long-term value.
- Adaptability: A long-term view encourages adaptability and flexibility, ensuring that organizations can weather changing market dynamics and remain relevant.
Steps for Formulating a Value Creation
The value creation process is a deliberate and structured journey that begins with defining your purpose and extends to crafting a detailed plan for execution. These steps, encompassing both strategy and planning, serve as the backbone for organizations striving to create value effectively and efficiently. Here, we explore these crucial steps for formulating a value creation strategy and plan.
1- Creating Value Creation Strategy
- Define Your Business Purpose
To embark on a journey of value creation, the first step is to establish a clear and compelling business purpose and mission. This sets the foundation for all your subsequent efforts.
- Define your business’s overarching purpose and mission.
- Clearly articulate what your organization aims to achieve in the long term.
- Ensure that your purpose aligns with the values and aspirations of your stakeholders.
- Comprehend Your Target Audience
Understanding your target audience is vital for creating value that resonates with them. It forms the basis for tailoring your products or services to meet their specific needs and preferences.
- Conduct thorough research to comprehend the needs and preferences of your target audience.
- Segment your audience to better tailor your value creation efforts.
- Identify pain points and challenges your audience faces that your business can address.
- Analyze the Market and Competitors
A deep understanding of the market and your competitors is crucial to position your business effectively and identifying opportunities for value creation.
- Conduct a comprehensive analysis of the market in which you operate.
- Study your competitors to identify gaps in their offerings and areas where you can excel.
- Recognize emerging trends and market dynamics that may impact your value creation strategy.
- Leverage Core Competencies
Identifying and utilizing your organization’s core competencies and strengths is key to creating a sustainable competitive advantage.
- Identify the unique strengths and capabilities that set your business apart.
- Determine how these strengths can be harnessed to create additional value.
- Explore opportunities for further developing and leveraging these competencies.
- Craft a Compelling Value Proposition
A well-crafted value proposition is the cornerstone of effective value creation. It should clearly communicate the benefits you offer to your target audience.
- Create a value proposition that addresses the specific needs and pain points of your audience.
- Highlight what makes your products or services unique and superior.
- Ensure that your value proposition resonates emotionally with your customers.
- Set Strategic Objectives
To guide your value creation efforts, establish clear and measurable strategic objectives. These objectives will serve as benchmarks for your progress.
- Define strategic objectives that align with your business purpose and value proposition.
- Ensure that these objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Use these objectives to track your progress and make adjustments to your value creation strategy as needed.
2- Creating Value Creation Plan
- Detailed Execution:
- Creating a value creation plan begins with a clear and comprehensive execution strategy.
- This step involves laying out the specific actions and tasks required to bring your value creation concept to life. It includes defining roles and responsibilities, setting deadlines, and establishing a detailed workflow.
- Budgeting and Resource Allocation:
- Effective resource management is crucial for value creation success.
- Here, you determine the financial and non-financial resources needed for your plan. It includes budgeting for expenses and allocating personnel, technology, and other assets required to execute your strategy efficiently.
- Timeline and Milestones:
- A well-defined timeline and milestones are essential for tracking progress.
- This step involves creating a timeline that outlines when specific tasks and milestones should be achieved. Milestones serve as checkpoints to ensure your value creation plan stays on track.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Measuring success requires establishing key performance indicators.
- Identify and define KPIs that will gauge the effectiveness of your value creation efforts. These metrics could include customer satisfaction scores, revenue growth, market share, or any other relevant benchmarks.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation:
- Anticipating and managing risks is vital to avoid setbacks.
- This step involves identifying potential obstacles or challenges that could hinder your value creation plan’s progress. Develop strategies to mitigate these risks and establish contingency plans.
- Communication, Alignment, and Feedback:
- Effective communication and feedback loops ensure everyone is aligned with the value creation plan.
- Implement communication channels to keep stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the execution process. Regularly gather feedback and make necessary adjustments to optimize your value creation strategy.
Value Creation Examples
Value creation is a multifaceted concept that finds application across various industries and sectors. Organizations continually seek innovative ways to generate value for their customers, stakeholders, and shareholders. Here, we explore examples of industries demonstrating value creation models and delve into some prominent value creation frameworks employed by successful companies.
1) Industries Demonstrating Value Creation Models
Various industries have harnessed value creation models to drive their success. These models encompass strategies and practices that go beyond traditional approaches, resulting in enhanced outcomes and stakeholder satisfaction. Here, we delve into some key industries and their value creation examples:
Technology and Software Industry
The technology and software industry thrives on continuous innovation and adaptation, exemplifying value creation in its purest form.
Value Creation Examples in Technology and Software:
- Developing cutting-edge software solutions that streamline processes and boost productivity.
- Introducing new features and updates to meet evolving customer needs.
- Leveraging data analytics for informed decision-making and personalized user experiences.
Retail and E-commerce
Retail and e-commerce have witnessed a transformative shift, largely driven by digitalization and customer-centric approaches.
Value Creation Examples in Retail and E-Commerce
- Implementing user-friendly online shopping experiences with intuitive interfaces.
- Utilizing customer data to provide tailored product recommendations.
- Efficient supply chain management to ensure prompt deliveries and minimize costs.
Healthcare Sector
The healthcare sector places immense importance on value creation, as it directly impacts patient care and overall well-being.
Value Creation Examples in Healthcare
- Telehealth services that enhance accessibility to medical consultations.
- Developing innovative medical devices and treatments to improve patient outcomes.
- Cost-effective healthcare management systems that optimize resource allocation.
Financial Services:
Financial institutions are adopting value creation models to provide better financial products and services.
Value Creation Examples in Financial Services
- Offering digital banking solutions for convenient and secure transactions.
- Personalized financial advice and investment strategies.
- Implementing robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard customer assets.
Environmental Services:
Environmental services focus on sustainable practices, aligning with the broader goal of preserving our planet.
Value Creation Examples of Environmental Services
- Renewable energy solutions to reduce carbon footprints.
- Waste management innovations, such as recycling and waste-to-energy technologies.
- Conservation efforts and eco-friendly product development.
Transportation and Logistics:
Transportation and logistics are crucial for the global movement of goods and people, and value creation plays a pivotal role.
Value Creation Examples of Transportation and Logistics
- Efficient route optimization to reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
- Real-time tracking systems for enhanced supply chain visibility.
- Adoption of electric and autonomous vehicles to improve sustainability.
2) Value Creation Models And Frameworks
In the business environment, numerous value creation models and frameworks provide organizations with structured approaches to articulate and enhance their value creation strategies.
These models serve as invaluable tools for businesses of all sizes and across various industries, helping them communicate their value creation narratives effectively and align their efforts with the expectations of stakeholders.
Here, we explore some notable value creation models and frameworks that guide businesses in their journey to create value and thrive in the marketplace.
Value Creation Model Examples in Business
Integrated Reporting Framework Example
Source: IIRC, 2013
- The Integrated Reporting Framework aims to establish a conceptual foundation for linking the IFRS Accounting Standards with the emerging IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards. One of its key focal points is the inputs and outputs within an organization’s value creation process, although the structure of this process is less defined.
- At its core, the framework strives to foster a more coherent and streamlined approach to corporate reporting. Its primary objective is to enhance the quality of information accessible to those who provide financial capital. By achieving this, the framework aims to facilitate a more efficient and effective allocation of capital resources, ultimately benefitting both businesses and investors.
Dutch Post (PostNL) Value Creation Model Example
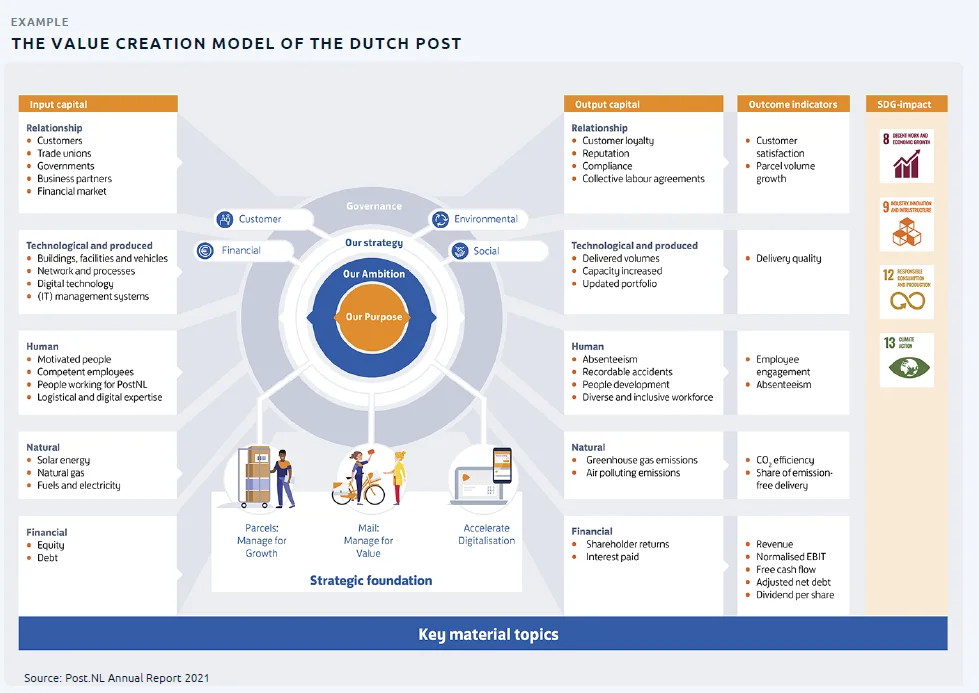
Source: Post NL Annual Report 2021
- The Dutch Post’s value creation model provides a structured overview of key elements within its value creation process, allowing stakeholders to grasp its fundamental components. However, it falls short of providing detailed explanations for these components, which can make it feel somewhat abstract and challenging to fully comprehend.
- While the model may appear somewhat disconnected due to its high-level nature, it does offer a noteworthy feature. It establishes a link between the outputs and outcomes of the value creation process and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set forth by the United Nations. This alignment demonstrates the company’s commitment to addressing global sustainability challenges and contributing to broader societal goals through its operations.
Bekaert Value Creation Model Example
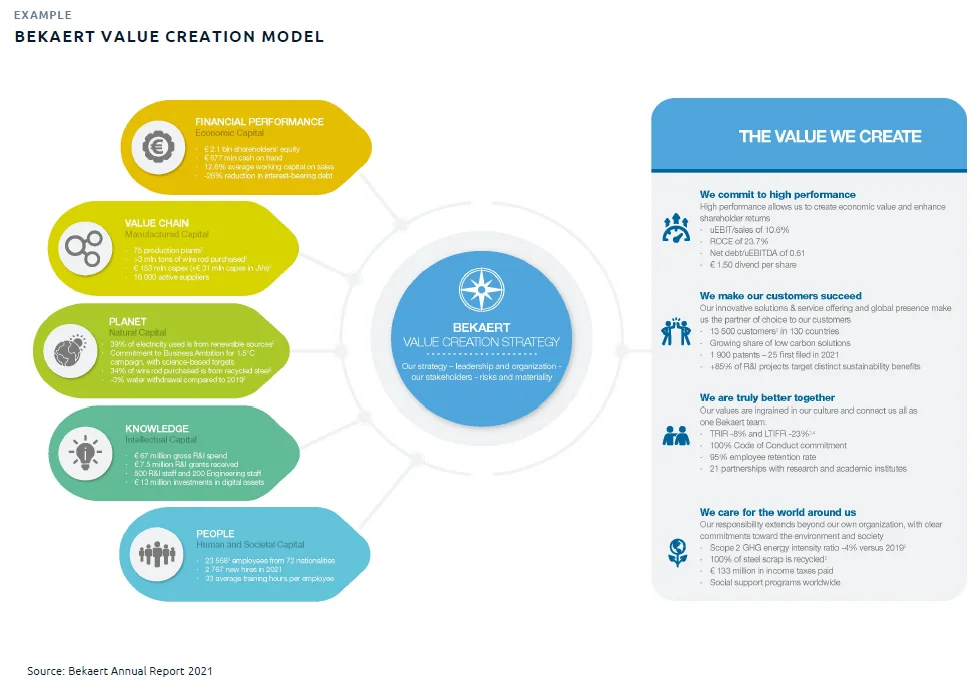
Source: Bekaert Annual Report 2021
- Bekaert, headquartered in Belgium, operates as a prominent global player in the steel wire transformation and coating industry. With a rich history dating back to its establishment in 1880, the company has continuously evolved and expanded its operations to become a leading innovator in its field.
- Bekaert’s value creation model delves into a detailed analysis of inputs and outputs, emphasizing a quantitative approach. This focus allows the company to meticulously measure and evaluate various aspects of its operations, from resource utilization to product outcomes. By doing so, Bekaert strives to achieve greater efficiency and sustainability in its processes.
- The company’s commitment to quantifying and optimizing resource utilization aligns with its dedication to responsible business practices and environmental stewardship. Bekaert’s efforts in value creation extend beyond merely economic considerations to encompass environmental and social aspects, contributing to a more holistic and sustainable approach to its operations.
Westpac Value Creation Model Example
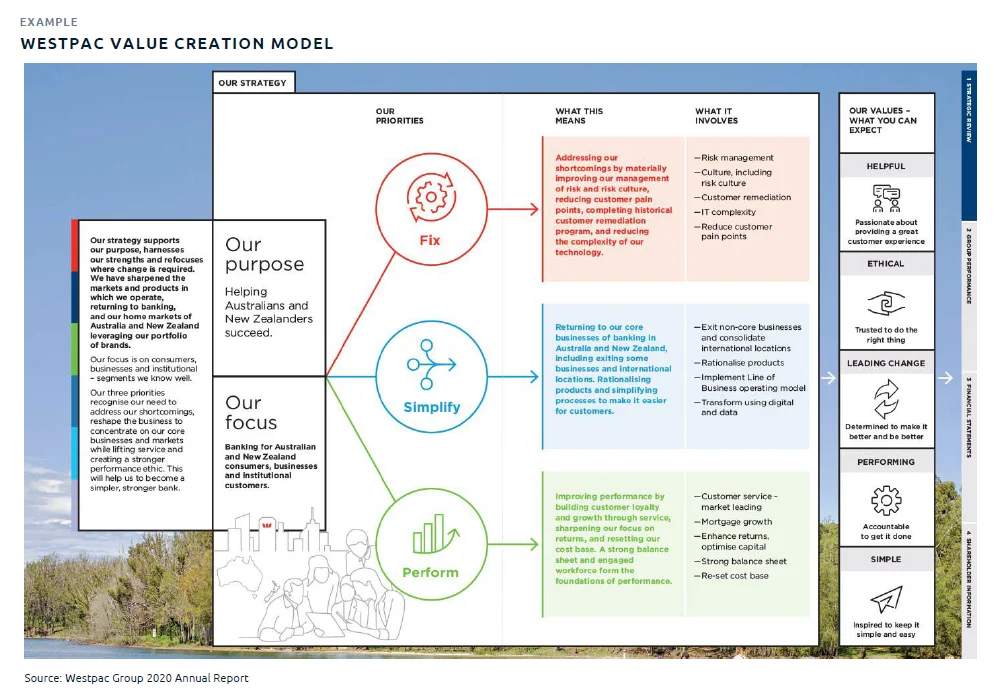
Source: Westpac Group 2020 Annual Report
- Westpac, headquartered in Sydney, Australia, is a prominent multinational banking and financial services corporation. With a global presence, the company serves a wide range of customers and offers various financial products and services.
- Westpac’s value creation model places a strong emphasis on the clear communication of its high-level strategic vision. It delves into how this overarching strategy aligns with and is reinforced by a set of core values that are deeply ingrained in the company’s culture. These values guide Westpac in its day-to-day operations, decision-making processes, and interactions with stakeholders.
- The model further illustrates how these values are translated into actions and initiatives that drive value creation for both the company and its stakeholders. It may encompass aspects such as responsible banking practices, customer-centricity, sustainability efforts, and community engagement.
- Westpac’s approach to value creation underscores not only financial performance but also its commitment to ethical and responsible business practices, contributing to its reputation as a socially responsible financial institution.
Alliander Value Creation Model Example
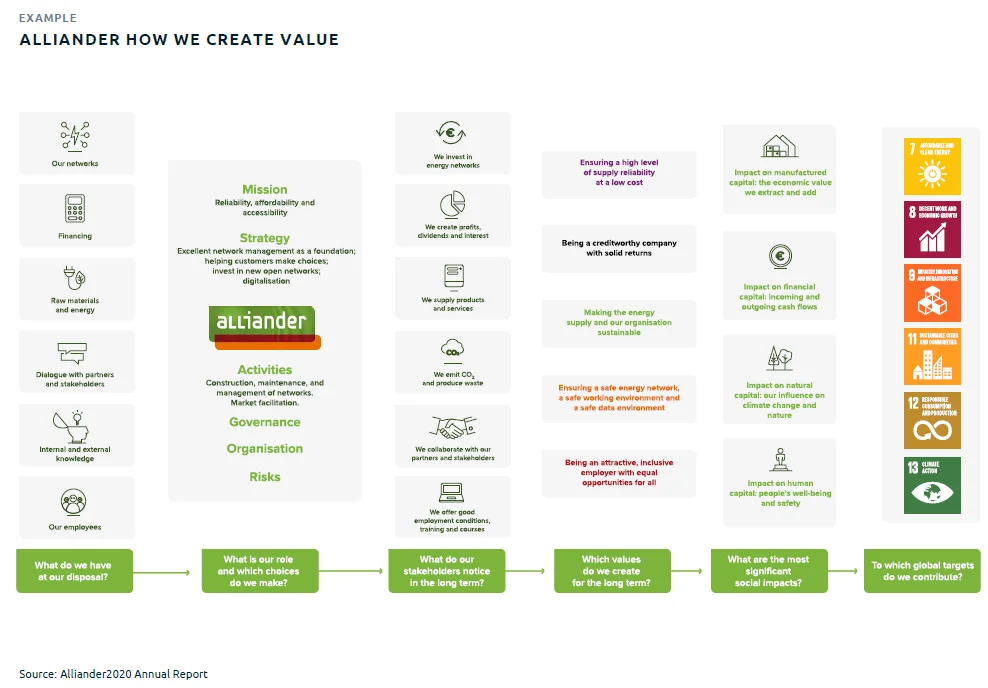
Source: Alliander 2020 Annual Report
- Alliander, a Dutch energy network company, is dedicated to value creation through a three-fold approach: sustainability, innovation, and customer-centricity. The company harnesses the power of technology and data analytics to enhance the efficiency and optimization of its energy network. Simultaneously, it commits to investing in renewable energy sources, thereby lessening its environmental footprint.
- Moreover, Alliander places a significant emphasis on elevating customer service standards. It accomplishes this by providing an array of digital tools and services designed to enhance the overall customer experience.
- By making sustainability, innovation, and customer satisfaction its focal point, Alliander successfully generates enduring value that benefits both its customers and shareholders in the long run.
Van Lanschot Kempen Value Creation Model Example
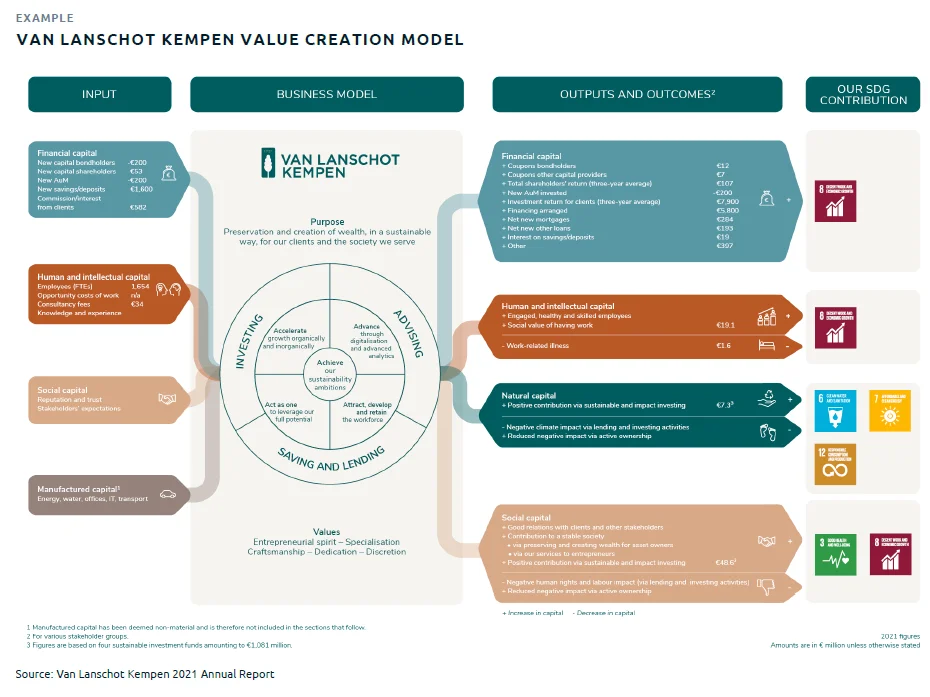
Source: Van Lanschout Kempen 2021 Annual Report
- Van Lanschot Kempen, a renowned Dutch wealth management and investment firm, employs a value creation model rooted in a deep understanding of customer needs and the delivery of personalized solutions through a blend of expertise and innovation.
- This model prominently features sustainability, emphasizes long-term investment strategies, and upholds an unwavering commitment to delivering exceptional customer service. By harnessing its profound financial industry knowledge and adopting a forward-looking approach to investment opportunities, Van Lanschot Kempen consistently generates value for its clients.
- These endeavors forge enduring relationships grounded in trust and transparency. Furthermore, the firm’s steadfast focus on sustainability aligns seamlessly with the burgeoning trend of socially responsible investing, solidifying Van Lanschot Kempen’s position as an industry trailblazer.
Related UNITE Models: Driving Business Value Creation Success
At Digital Leadership, we provide a range of related models and frameworks that empower organizations to navigate the complexities of today’s dynamic landscapes.
These models are designed to enhance your understanding of the business environment and uncover opportunities for value creation. One such model is:
THE UNITE BUSINESS MODEL ENVIRONMENT CANVAS
In the dynamic realm of business evolution, organizations cannot afford to operate in isolation. To thrive and succeed, it’s imperative for businesses to have a keen awareness of their external environment. This is where the UNITE Business Environment Canvas emerges as an invaluable tool. It empowers organizations to gain profound insights into their business environment, offering a deep understanding of emerging trends and disruptive forces that could significantly impact their operations. You can download it now.
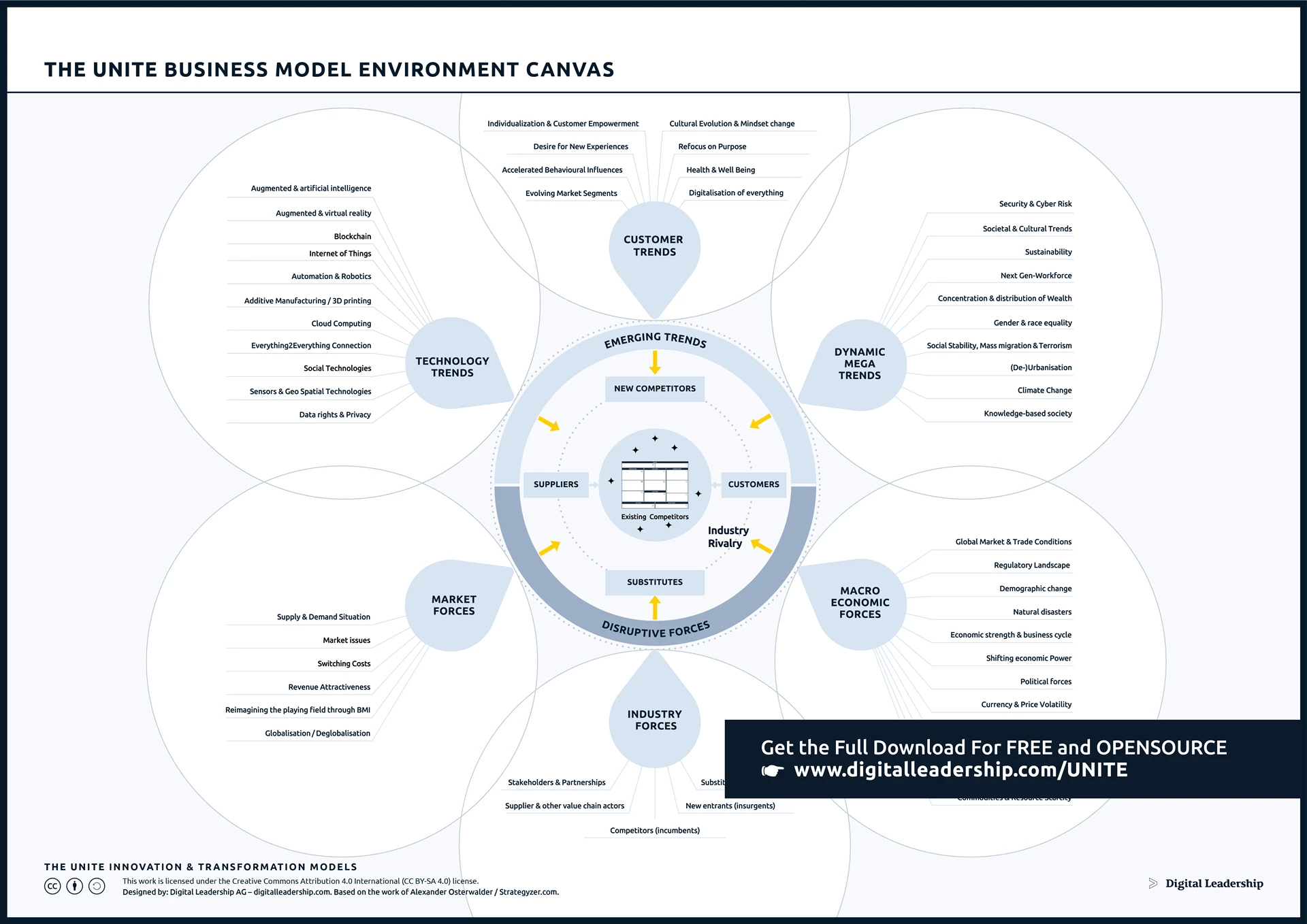
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Based on the work of Alexander Osterwalder
It enables you to collaboratively identify and dissect the pivotal factors that will mold your organization’s future. By discerning these critical dynamics, you can proactively strategize and innovate your value creation structure. This proactive approach positions your organization to not only adapt but thrive in the fiercely competitive business landscape, ensuring long-term success and relevance.
The UNITE Business Environment Canvas is crucial for creating value in:
- Aligning strategies with the external environment.
- Fueling innovation by identifying trends.
- Mitigating risks proactively.
- Providing a competitive edge.
- Optimizing resource allocation.
- Enhancing adaptability and resilience.
- Promoting stakeholder engagement.
THE UNITE STRATEGY-EXECUTION FRAMEWORK
The UNITE Strategy-Execution Framework is a vital tool for businesses, offering a structured approach to navigate the complexities of strategy and execution. It plays a pivotal role in aligning an organization’s capabilities with its strategic objectives and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
It offers a structured approach to understanding and optimizing your organization’s capabilities. It ensures that you allocate resources wisely, focus on what truly matters, and communicate your unique value effectively in the competitive business landscape.
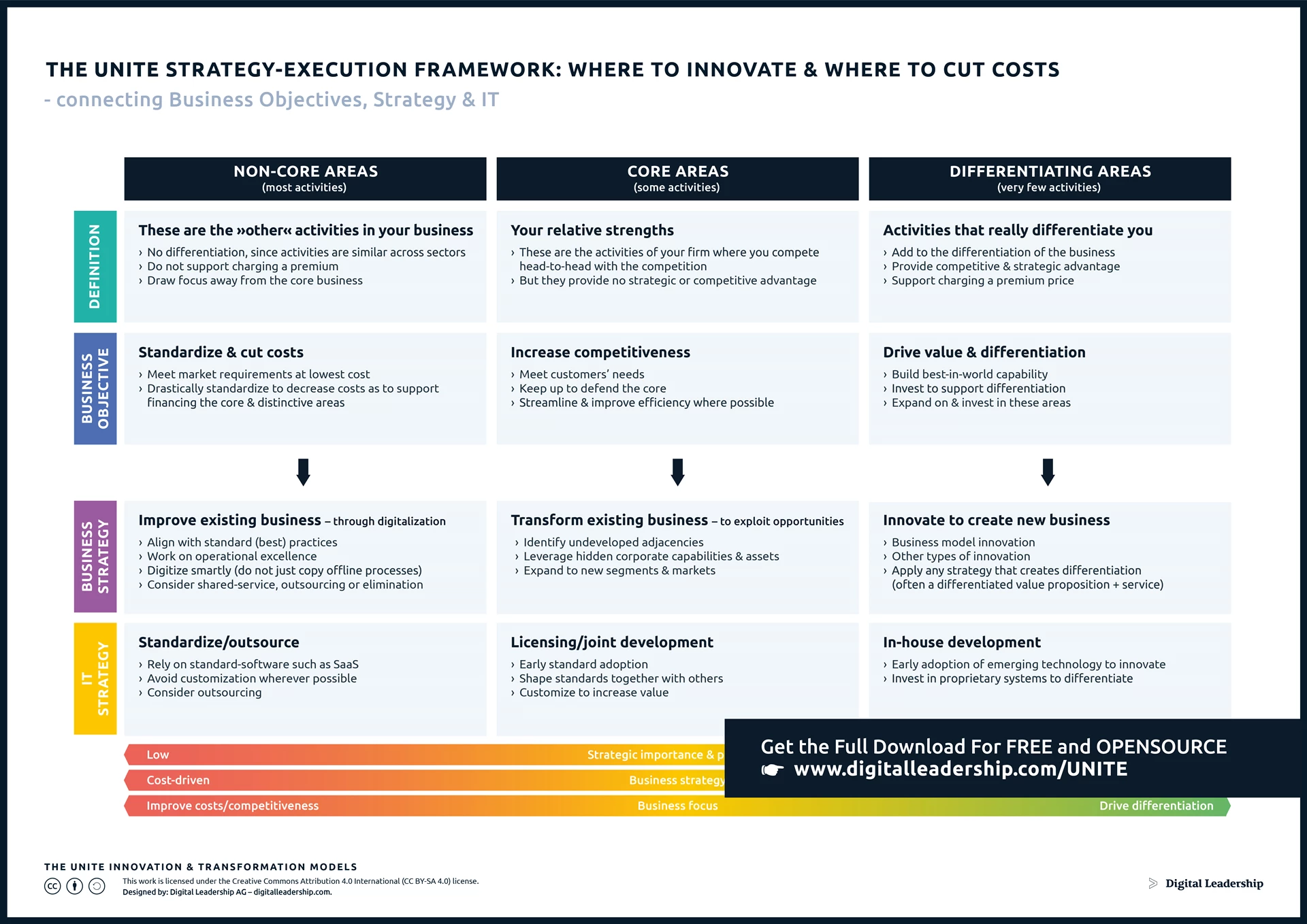
Designed By: Digital Leadership AG
The UNITE Framework comprises the following components:
- Non-Core Capabilities: These are aspects of your business that are necessary but do not provide a competitive advantage. They are the foundational elements that keep the business running but are not the focal points of your strategy.
- Core Capabilities: Core capabilities are those that are essential for competing effectively in your industry. While they may not be unique, they are necessary for the business to operate successfully.
- Differentiating Capabilities: These are the few areas where your organization truly stands out. These capabilities are your competitive advantage, setting you apart from others in the market. Emphasizing them is key to communicating your unique value to customers.
THE UNITE OPERATING MODEL CANVAS
It is a visual representation of how an organization operates and creates value. At its core is the Value Chain, a concept central to both the Operating Model Canvas and the UNITE Value Creation Framework. The Value Chain outlines the primary activities and processes involved in delivering a product or service to customers.
The Operating Model Canvas serves as a comprehensive tool for organizations to analyze, plan, and optimize their operating model. It is especially valuable when used in conjunction with the UNITE Value Creation Framework.
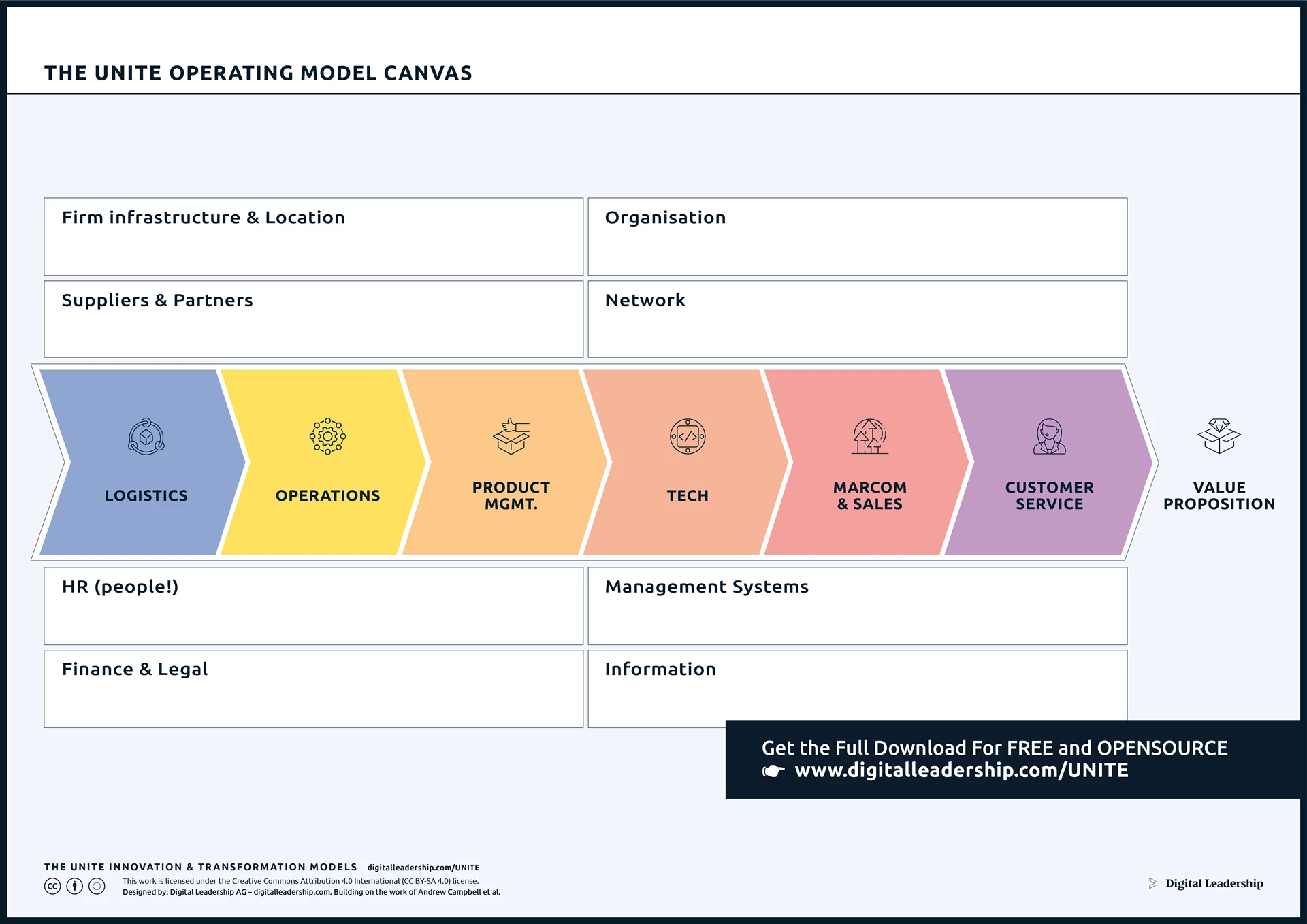
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the work of Andrew Campbell at Al.
the Operating Model Canvas, particularly when integrated with the UNITE Value Creation Framework, is an invaluable asset for organizations seeking to optimize their operations, allocate resources effectively, and communicate their value creation strategy. It plays a pivotal role in achieving clarity, alignment, and competitiveness in today’s dynamic business environment.
THE UNITE BUSINESS MODELS CANVAS
The UNITE Business Model Canvas serves as a vital tool for organizations striving to fine-tune their operational strategies and revenue generation processes. It provides a structured framework to dissect and visualize the fundamental building blocks that drive value creation within a company. You can download it now.
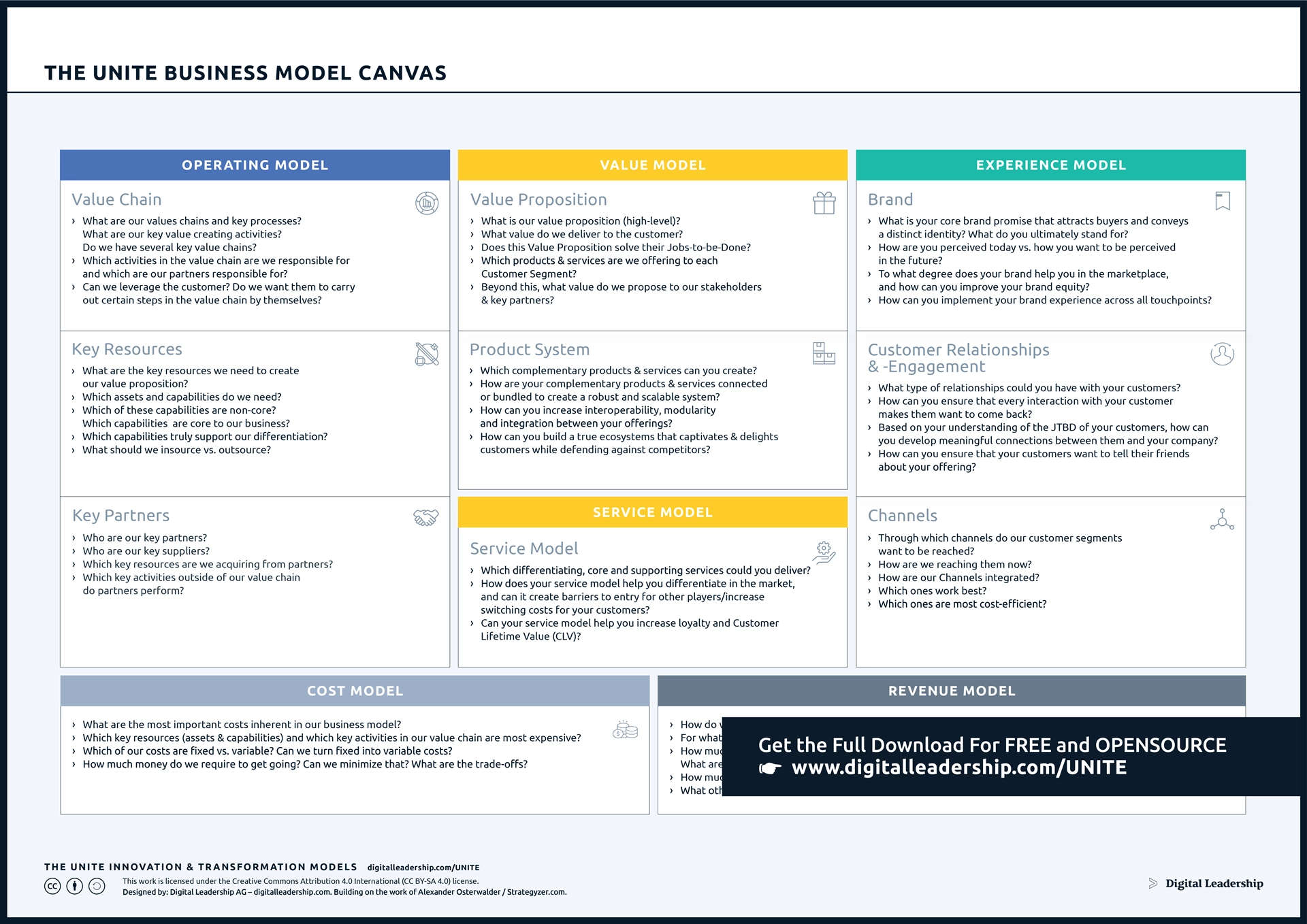
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Building on the work of Alexander Osterwalder
The UNITE Value Creation Framework and the UNITE Business Model Canvas share a common goal: to enhance the understanding and refinement of how a company creates value. While the business model primarily delves into the internal mechanisms of the organization, the value creation framework places greater emphasis on the inputs, outputs, and the overall impact it generates.
Incorporating the UNITE Business Model Canvas into your strategic planning process can lead to more streamlined operations, improved profitability, and a sharper focus on what truly drives value within your organization. It complements the broader perspective offered by the UNITE Value Creation Framework, ensuring a well-rounded approach to understanding and enhancing value creation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) How is value creation measured?
Value creation can be measured through various metrics, providing a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s performance. These metrics include:
- Revenue Growth: Increasing revenue over time indicates the creation of economic value.
- Return on Investment (ROI): ROI measures the profitability of investments, reflecting the value generated compared to the resources invested.
- Customer Satisfaction: High customer satisfaction scores often correlate with value creation, as satisfied customers are more likely to continue doing business with an organization.
- Social Impact: Assessing the positive social impact of a company’s activities, such as community development or environmental stewardship, contributes to understanding value creation’s broader implications.
2) What are the key components of value creation?
The key components of value creation form the foundation of a successful business strategy. To thrive in today’s competitive landscape, organizations must grasp these fundamental elements.
- Understanding Customer Needs: Value creation begins with a deep understanding of customer needs, allowing organizations to tailor their offerings effectively.
- Leveraging Core Competencies: Organizations identify and leverage their core strengths and competencies to create value.
- Innovation: Innovation fuels value creation by introducing new products, services, or processes that address evolving market demands.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Optimizing the allocation of resources, including financial, human, and technological, is crucial for value creation.
3) What are the six capitals of value creation?
The six capitals of value creation encompass various forms of resources and assets that contribute to value generation:
- Financial Capital: The monetary resources a company possesses.
- Human Capital: The skills, knowledge, and expertise of an organization’s workforce.
- Social Capital: The relationships and networks a company builds with stakeholders, contributing to reputation and trust.
- Intellectual Capital: Intellectual property, patents, copyrights, and proprietary knowledge.
- Natural Capital: Environmental resources, such as clean air, water, and ecosystems.
4) What is the difference between Value Co-Creation and Value Creation?
In the realm of business and innovation, two closely related concepts, Value Creation and Value Co-Creation, play a pivotal role in shaping organizational success. These terms may sound similar, but they represent distinct approaches to delivering value to stakeholders. Let’s explore the key differences between them:
- Value Creation: This term refers to the process of generating value for stakeholders through an organization’s activities, products, or services. It primarily focuses on how an organization produces and delivers value.
- Value Co-Creation: Value co-creation extends the concept by emphasizing collaboration with customers and other stakeholders. It involves actively involving them in the value generation process, often leading to more personalized and innovative solutions.
5) What is the difference between value creation and value capture?
Value Creation and Value Capture, hold distinct roles in determining an organization’s success. These concepts may seem closely related, but they serve different purposes and strategies within the business realm.
- Value Creation: Value creation is the process of generating additional value, whether through innovation, efficient operations, or customer-centric approaches. It is about expanding the overall value pool.
- Value Capture: Value capture involves retaining a portion of the value created as profit or return on investment. It focuses on the organization’s ability to capture a share of the value it contributes to, often through pricing strategies, cost management, or market positioning.



























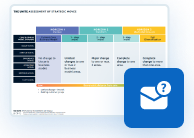

 Book How to Create Innovation
Book How to Create Innovation