Table of Contents
A market opportunity functions as a brief document that delineates a distinct prospect within a market, offering essential insights to aid decision-makers in gauging the viability of pursuing a specific venture or strategy. The imperative for businesses to thrive necessitates the proactive identification of market opportunities. The effectiveness of your innovation endeavors hinges greatly on the prevailing market demand. Undertaking a thorough examination of market opportunities is vital for making well-informed investments to draw in new customers.
Although recognizing these opportunities can pose a challenge, it remains a critical task. Small businesses aiming to navigate and explore fresh avenues for growth can benefit from adopting methodologies like Jobs to be Done (JTBD) and other customer analysis approaches, which offer valuable insights and guidance in the pursuit of sustainable expansion.
Digital leadership specialists have invested considerable effort in exploring the applications of Jobs to be Done (JTBD) for enhancing customer satisfaction, conducting market opportunity analyses, and developing target markets. Our expertise lies in delivering innovation consulting services, and supporting organizations in revealing unmet needs and undiscovered opportunities within the market. As an initial step to assist businesses in selecting tailored services that align with their specific needs and objectives for innovation, we offer an Innovation Blueprint to evaluate current innovation practices.
What is Market Opportunity
A market opportunity refers to a prospect for sales that the sales team thoroughly assesses and recognizes as an individual with potential interest in a product or service.
For market needs, understanding the foundational aspects becomes paramount for identifying opportunities. It emphasizes the role of innovative jobs in shaping market landscapes. As businesses navigate the quest for growth, the discussion extends to discovering new market opportunities and staying ahead in a competitive environment. Hidden markets emphasise strategies to unearth opportunities beyond the surface and tap into unconventional sources of business potential encouraging businesses to look beyond traditional boundaries for sustained success.
Market Opportunities Identification Importance
The pivotal process of recognizing and assessing market opportunities stands as a fundamental element for any business. This undertaking empowers companies to pinpoint potential revenue streams, enhance their comprehension of the target customer base, and formulate effective strategies for acquiring and retaining these customers.
The importance of market opportunity identification extends beyond immediate gains, shaping the long-term success and relevance of businesses in today’s dynamic and competitive business landscape.
- Strategic Growth: Identifying market opportunities provides businesses with a strategic pathway for sustainable growth. It allows organizations to expand their offerings, enter new markets, and diversify their revenue streams, contributing to long-term success.
- Competitive Edge: In a competitive business environment, being the first to identify and act on market opportunities provides a distinct competitive advantage. Early movers can establish themselves as industry leaders and capture market share ahead of competitors.
- Meeting Unmet Needs: Market opportunities often arise from unmet or underserved Customer needs. Recognizing and addressing these needs positions businesses as valuable problem-solvers, fostering customer loyalty and trust.
- Innovation Catalyst: The identification of market opportunities fuels innovation within organizations. It encourages a proactive approach to understanding customer behaviours, preferences, and emerging trends, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation.
- Adaptability to Trends: Markets are dynamic, with trends and consumer preferences evolving rapidly. Identifying opportunities allows businesses to stay ahead of these changes, adapt their strategies, and align their offerings with current market demands.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Understanding market opportunities requires a deep understanding of customer needs and pain points. This customer-centric approach not only aids in opportunity identification but also enhances overall customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Diversification of Revenue: Recognizing diverse market opportunities enables businesses to diversify their revenue streams. This diversification provides a buffer against market fluctuations and economic uncertainties, contributing to financial resilience.
- Exploration of Hidden Potential: Markets often conceal untapped potential beyond the surface. Identification of hidden opportunities involves exploring unconventional sources and niche markets, and uncovering new avenues for business growth.
- Strategic Positioning: Businesses that actively identify and capitalize on market opportunities can strategically position themselves in the marketplace. This positioning involves aligning offerings with consumer needs and establishing a unique value proposition.
- Utilization of Innovative Frameworks: Leveraging innovative frameworks such as Jobs To Be Done (JTBD) enhances the ability to identify market opportunities. These frameworks provide structured approaches to understanding customer motivations and aligning products or services accordingly.
Jobs to be done Benefits in Market Opportunities Identification
Transitioning to the concept of Jobs To Be Done (JTBD), a powerful framework is introduced for comprehending market dynamics. By framing jobs and mapping them, organizations gain valuable insights into customer needs and behaviors, ultimately driving evolution in the market.
The Business Model Canvas holds immense importance in the context of Jobs to Be Done (JTBD) as it serves as a valuable framework for visualizing and structuring business strategies. When integrated with JTBD, the canvas becomes a dynamic tool for not only analyzing and aligning business activities with the identified jobs that customers aim to accomplish but also for market opportunity identification. It provides a holistic view of key components like customer segments, value propositions, distribution channels, and revenue streams, enhancing the overall understanding of how the business can effectively meet customer needs and enhance value creation, and pinpointing potential market opportunities for growth and development.
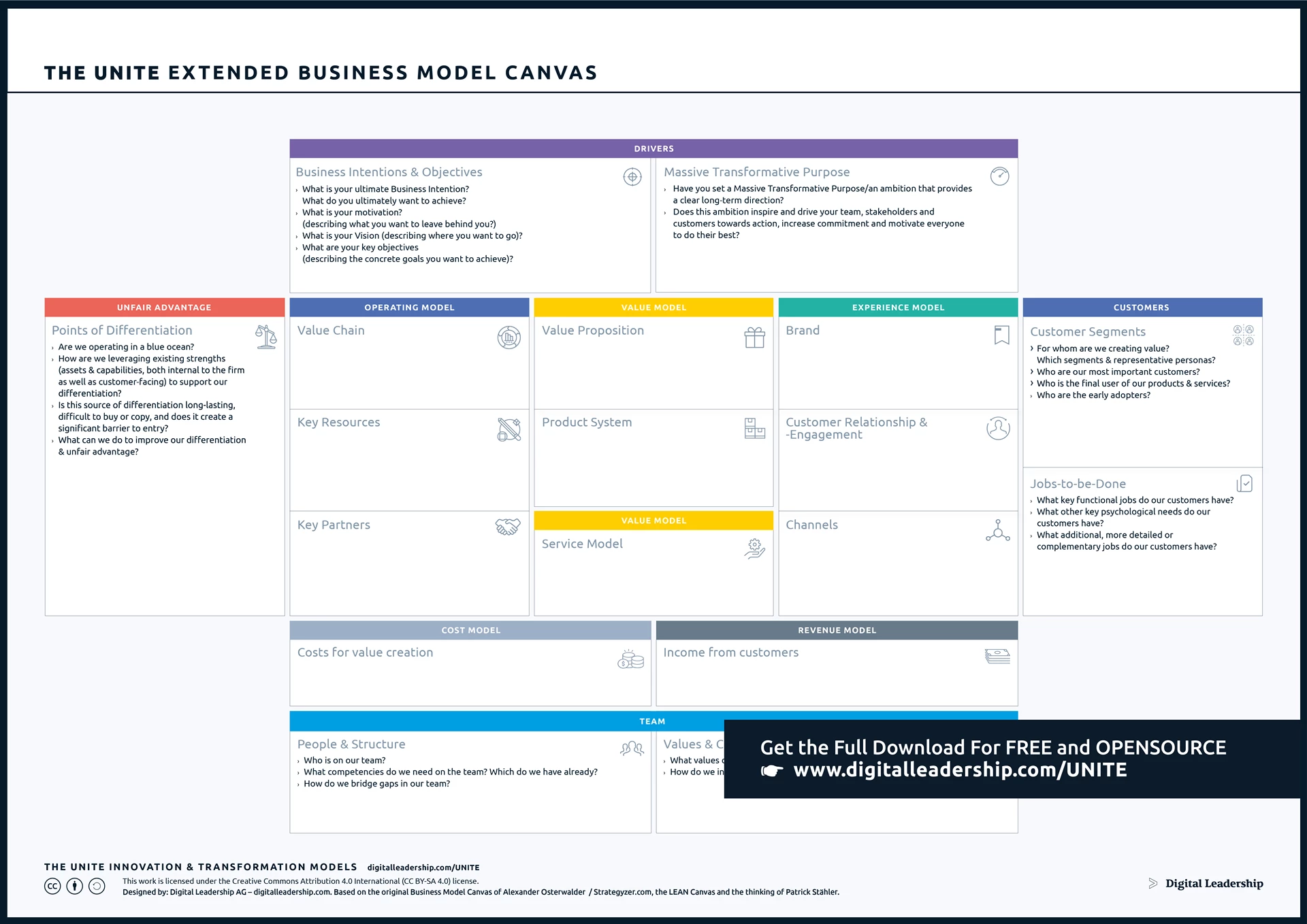
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Based on the Original Business Model Canvas of Alexander Osterwald, the Lean Canvas & the Thinking of Patrick Stahler
Download the Complete eXtended Business Model Canvas Package, including instructions for putting it to work for you today.
The utilization of the “Jobs to Be Done” (JTBD) framework offers several noteworthy advantages in the identification of market opportunities:
1- Customer-Centric Approach
The “Jobs to Be Done” (JTBD) framework adopts a customer-centric approach that delves into understanding the intricate needs and motivations of customers by focusing on the jobs they aim to accomplish. This strategic perspective ensures that market opportunities are intricately aligned with genuine customer needs, fostering a more meaningful connection between businesses and their target audience.
2- Insights into Customer Behavior
Through the meticulous mapping of the jobs customers seek to fulfill, businesses gain profound insights into customer behavior. This comprehensive understanding proves invaluable in not only foreseeing market trends and preferences but also in pinpointing areas for improvement. By grasping the nuances of customer actions, businesses can strategically enhance their offerings and services.
3- Innovation Catalyst for Innovation Strategy Alignment in Innovation Process
Jobs to be done serves as a potent catalyst for innovation, illuminating unmet needs and areas where existing solutions fall short. This unique insight propels the development of innovative products or services precisely tailored to the intricate requirements of customers. It acts as a guiding beacon for businesses to stay ahead of the innovation curve.
The Jobs to be done framework seamlessly integrates into the innovation process within organizations, instilling a systematic and structured approach to innovation. Insights gleaned from customer needs to drive every stage of the iterative and customer-centric innovation process, becoming a cornerstone of sustained success and growth. Aligned with a robust innovation strategy, JTBD becomes a linchpin for businesses seeking to remain at the forefront of market dynamics. It provides a strategic roadmap to identify and capitalize on emerging trends, fostering an environment where innovation aligns seamlessly with overarching business goals. Integrated into the broader innovation strategy, JTBD ensures that the pursuit of market opportunities is not just reactive but a proactive and strategic endeavour.
4- Effective Opportunity Mapping
The framework’s structured approach serves as an effective tool for opportunity mapping. By systematically breaking down the customer journey into specific job steps, businesses can identify and analyze areas ripe for improvement and innovation. This methodical mapping facilitates a strategic understanding of where opportunities lie within the market landscape.
5- Competitive Edge
Organizations that embrace the JTBD framework gain a distinctive competitive edge by finely tuning themselves to customer needs. This heightened awareness empowers businesses to craft unique value propositions that resonate deeply with customers, setting them apart in the fiercely competitive market arena.
The Value Proposition Canvas plays a pivotal role in the Jobs to Be Done (JTBD) methodology, offering crucial importance in understanding and enhancing customer experiences as well as market opportunity identification. It serves as a visual tool that enables organizations to meticulously map out customer profiles, including their pains, gains, and jobs to be done. This canvas becomes instrumental in aligning product or service offerings with customer needs, ensuring a compelling and customer-centric value proposition. You can download it now.
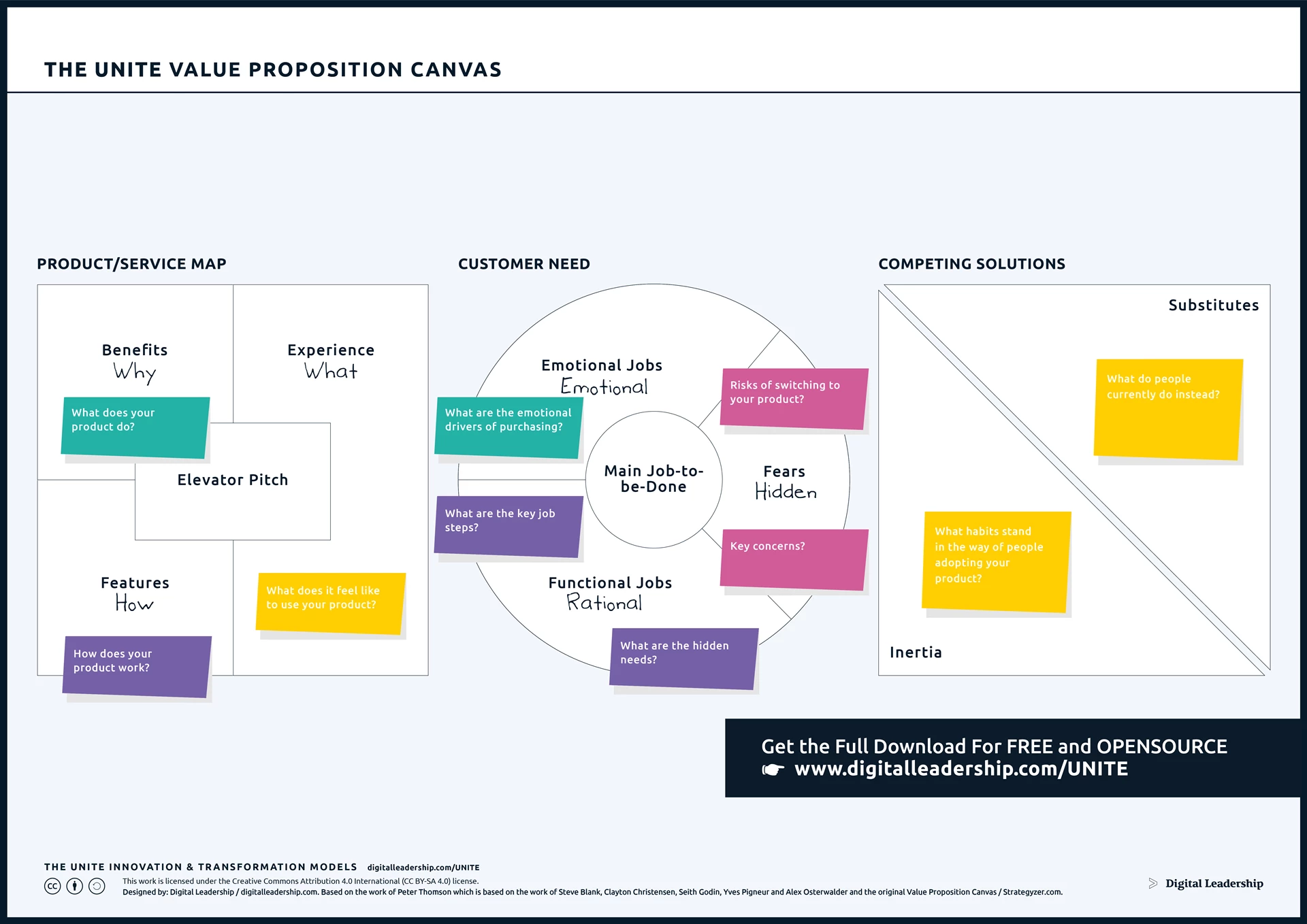
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Based on the work of Peter Thomson which is based on the work of Steve Blank, Clayton Christensen, Seith Godin, Yves Pigneur and Alex Osterwalder and the original Value Proposition Canvas
Download the complete Value Proposition Canvas Package, including instructions for putting it to work for you today.
6- Adaptability to Market Changes
JTBD provides a dynamic and adaptable methodology that equips businesses to navigate the ever-evolving business landscape. This flexibility allows organizations to adjust their strategies based on shifting customer needs and emerging market opportunities, ensuring a proactive and responsive stance in the market.
7- Customer-Driven Decision Making
JTBD actively promotes customer-driven decision-making processes. By comprehending the specific jobs customers are hiring products or services to accomplish, businesses can make informed decisions that prioritize customer satisfaction and loyalty. This customer-centric approach forms the bedrock of strategic decision-making within organizations.
Jobs to be done Framework in Market Opportunities Identification
The JTBD framework emerges as a powerful strategic tool for conducting market opportunity analysis. Its effectiveness stems from its ability to comprehend customer needs and motivations, offering a comprehensive perspective on market dynamics. By focusing on the fundamental jobs customers are trying to accomplish, JTBD becomes a guiding force in unraveling opportunities that align closely with genuine customer requirements. This holistic approach ensures that businesses gain nuanced insights into the intricate interplay of customer needs, driving informed decisions in the pursuit of market opportunities.
Jobs to be done Framework Steps for Identifying Market Opportunities
1- Introduction to jobs to be done JTBD
In introducing the Jobs to be Done (JTBD) framework, it is crucial to lay the groundwork for a comprehensive understanding of its application in market analysis. JTBD posits that customers essentially “hire” products or services to fulfill specific tasks or objectives. Recognizing and comprehending these underlying jobs is paramount for achieving success in the market. Unlike traditional approaches that focus solely on features or demographics, JTBD shifts the perspective to the functional and emotional needs that customers are seeking to address.
By delving into the reasons why customers “hire” a particular solution, businesses gain valuable insights into designing products or services that precisely meet those needs, ultimately enhancing their competitive edge and market positioning. This foundational understanding sets the stage for a more nuanced and customer-centric approach to market analysis and strategy development.
2- Customer-Centric Approach:
Embrace a customer-centric approach by delving into the needs and motivations of customers through the lens of the jobs they aim to accomplish. This involves empathizing with customers, understanding their pain points, and recognizing the aspirations driving their choices.
3- Opportunity Mapping with JTBD:
Leverage the structured approach of JTBD to map out customer journeys, systematically identifying areas for improvement and innovation. This step involves breaking down the customer journey into specific job steps, and creating a visual representation that helps identify pain points and opportunities.
4- Realizing Opportunities Through Examples:
Gain insights into practical applications by exploring real-world examples of how JTBD has been instrumental in realizing market opportunities. This includes studying successful cases where companies effectively identified and capitalized on market opportunities using JTBD.
5- Strategic Decision-Making with Opportunity Maps:
Implement the Identify, Predict, Decide, Execute (IPDE) approach within the JTBD framework for effective decision-making and strategy execution. This step involves using opportunity maps to systematically identify, predict the outcome of decisions, make informed choices, and execute strategies.
6- Qualitative Interviews and Job Statements:
Initiate qualitative interviews to delve into customer experiences and extract valuable insights. Understand customers’ needs, preferences, and pain points by engaging in conversations. Craft concise Job Statements using the customer’s voice, articulating their needs, aspirations, and struggles. Dive deeper into customer criteria, exploring functional, emotional, and social aspects related to the job. Use this information to validate and enrich the insights gained through qualitative interviews.
The UNITE Jobs to Be Done Customer’s Job Statement Model emphasizes creating clear, concise statements that capture the essence of customer needs, forming the foundation for the Jobs to Be Done Framework and serving as a crucial component in identifying market opportunities.
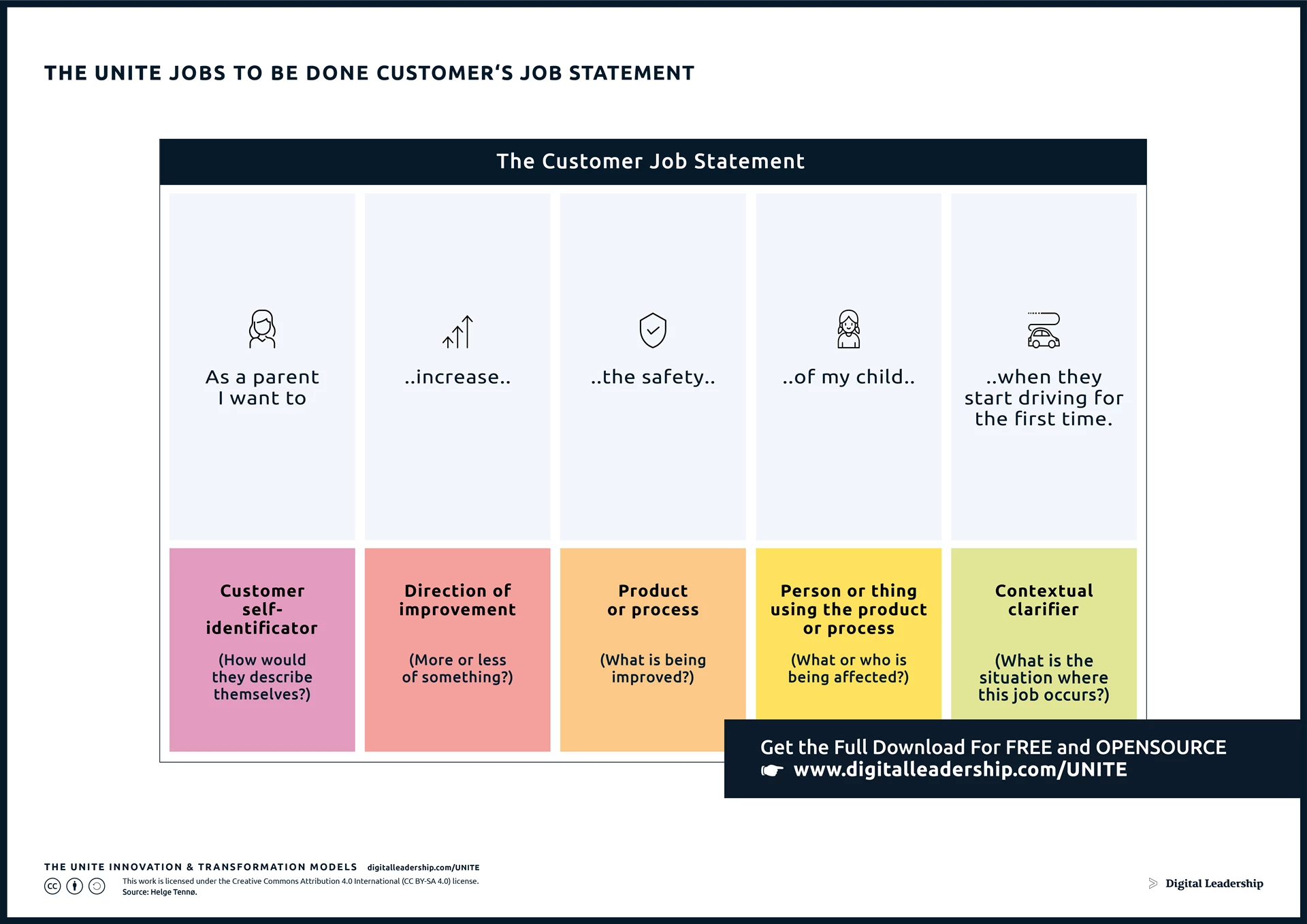
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Source: Helge Tennø.
Your download is now available!
You can now access the complete JTBD Customer’s Job Statement Package, including a full presentation, related models and instructions for use.
7- Job Map Creation:
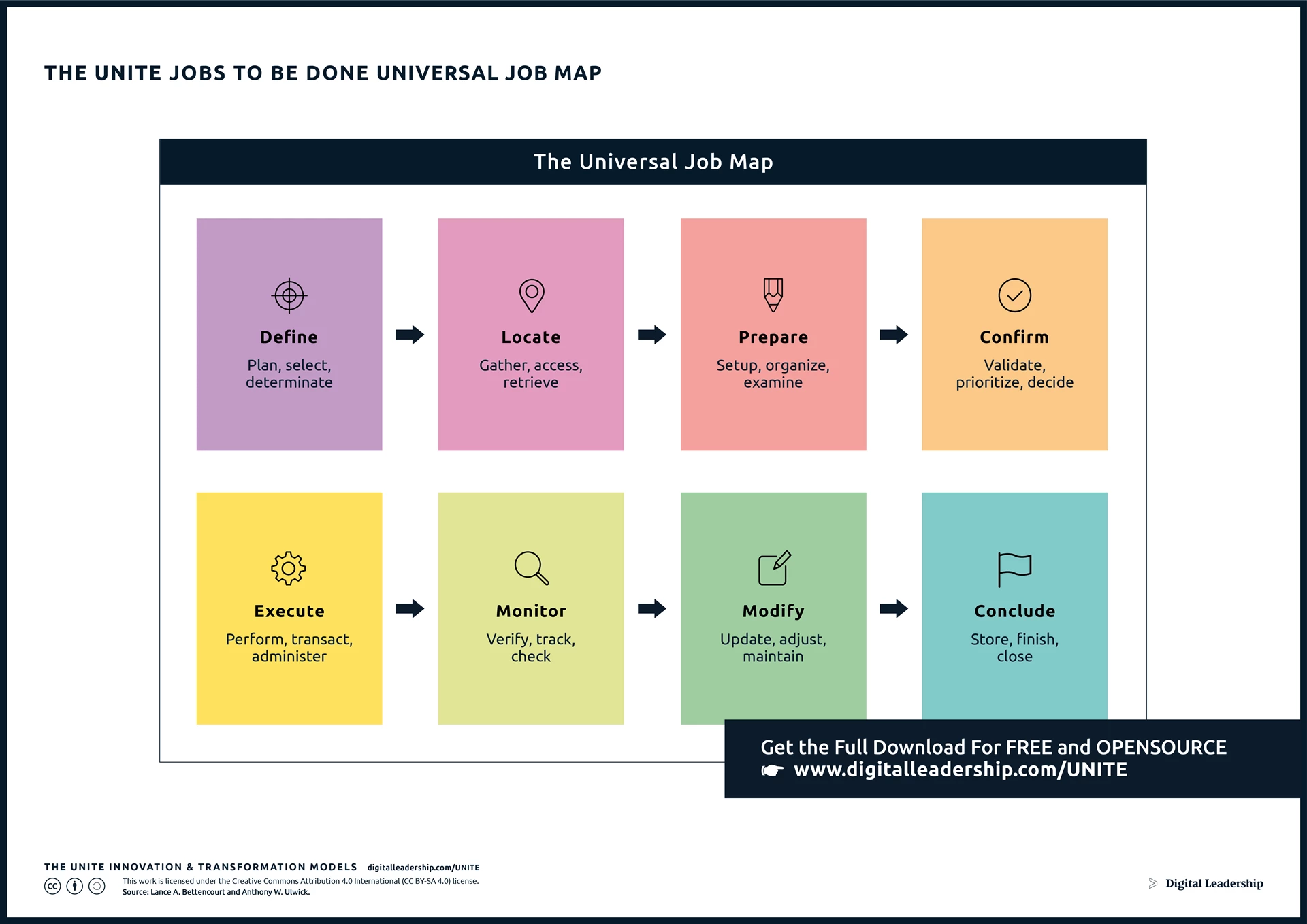
Develop a Job Map using the eight essential steps, outlining the tasks and activities customers perform to accomplish a specific job. Understand the customer’s journey from defining and planning to concluding the job, identifying critical touchpoints and areas for improvement.
Incorporating “The UNITE Jobs to Be Done Universal Map” Model enhances this step by providing a visual representation, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the customer journey, and helping businesses align strategies with identified jobs effectively, thereby optimizing the pursuit of market opportunities.
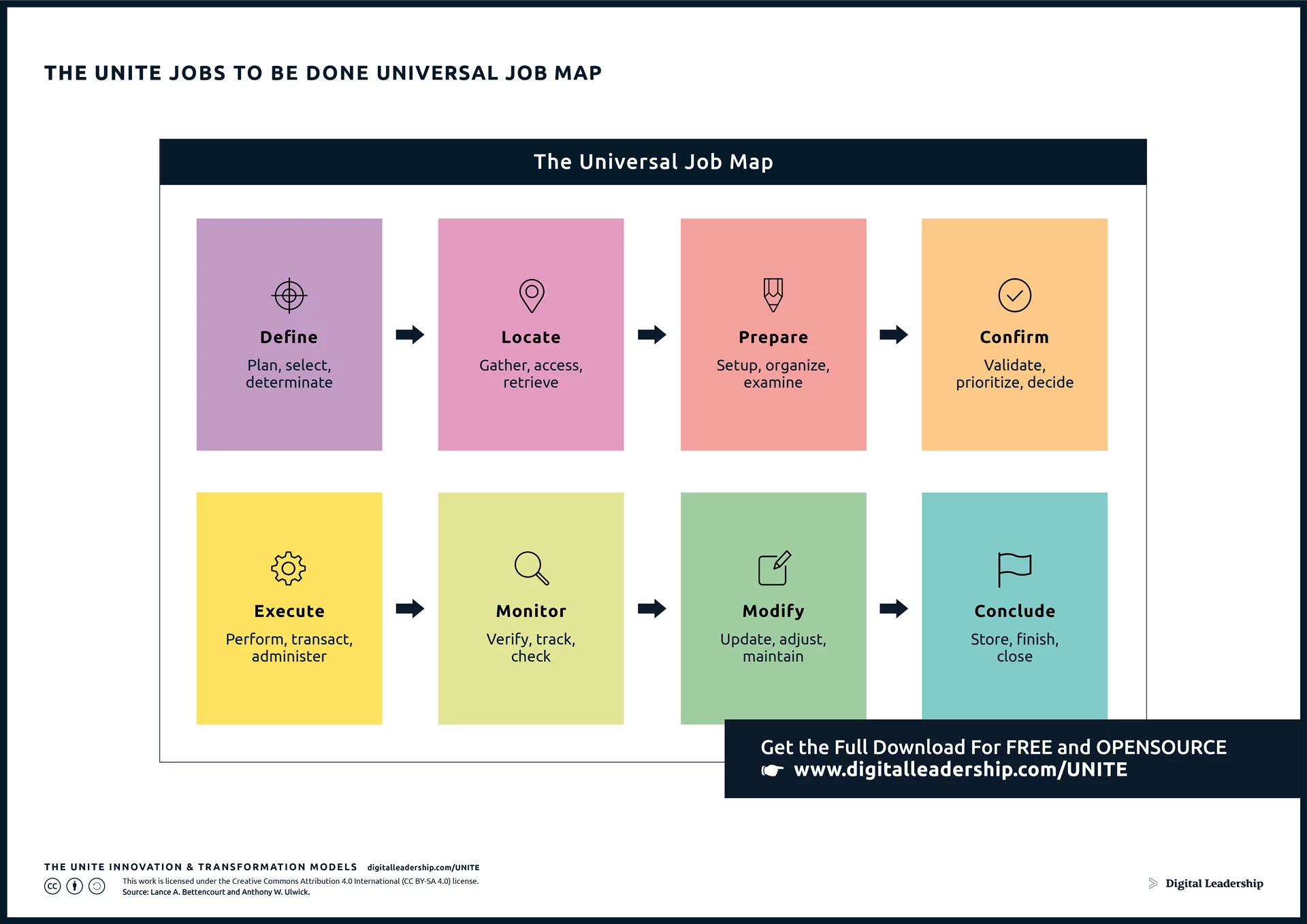
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Source: Lance A. Bettencourt and Anthony W. Ulwick.
Your download is now available!
You can now access the complete Jobs to be Done Universal Map Package, including a full presentation, related models and instructions for use.
The Job Map involves outlining the smaller tasks and activities that customers undertake to accomplish their job. This is a collaborative process where the team gathers to brainstorm and categorize tasks into eight steps. The Universal Job Map comprises the following steps:
- Define and plan: The customer consciously or subconsciously creates an initial plan for their approach.
- Locate the input needed: Identifying and locating information necessary for decision-making.
- Prepare: Organizing information, filtering, qualifying, and making decisions.
- Confirm and validate: Making decisions and validating them.
- Execute: Performing the action or procedure resulting from the decision.
- Monitor: Monitoring the effects and outcomes of the decision.
- Modify: Assessing the decision based on new information and continuously monitoring or improving.
- Conclude: Concluding the journey, taking stock, and learning from the experience.
8- Validate with Data:
Undertake a large-scale quantitative survey covering identified Customer Criteria to validate their importance and satisfaction levels. Collaborate with a specialized research institute to ensure statistical significance and accuracy. This step ensures that insights gained from qualitative methods are validated on a broader scale.
The UNITE Jobs-to-be-Done template is recommended for defining Customer Criteria, providing a structured approach to gathering essential information for the product development process. The methodology encourages a holistic understanding of customer needs and preferences, ensuring that products align closely with the jobs customers are trying to get done.
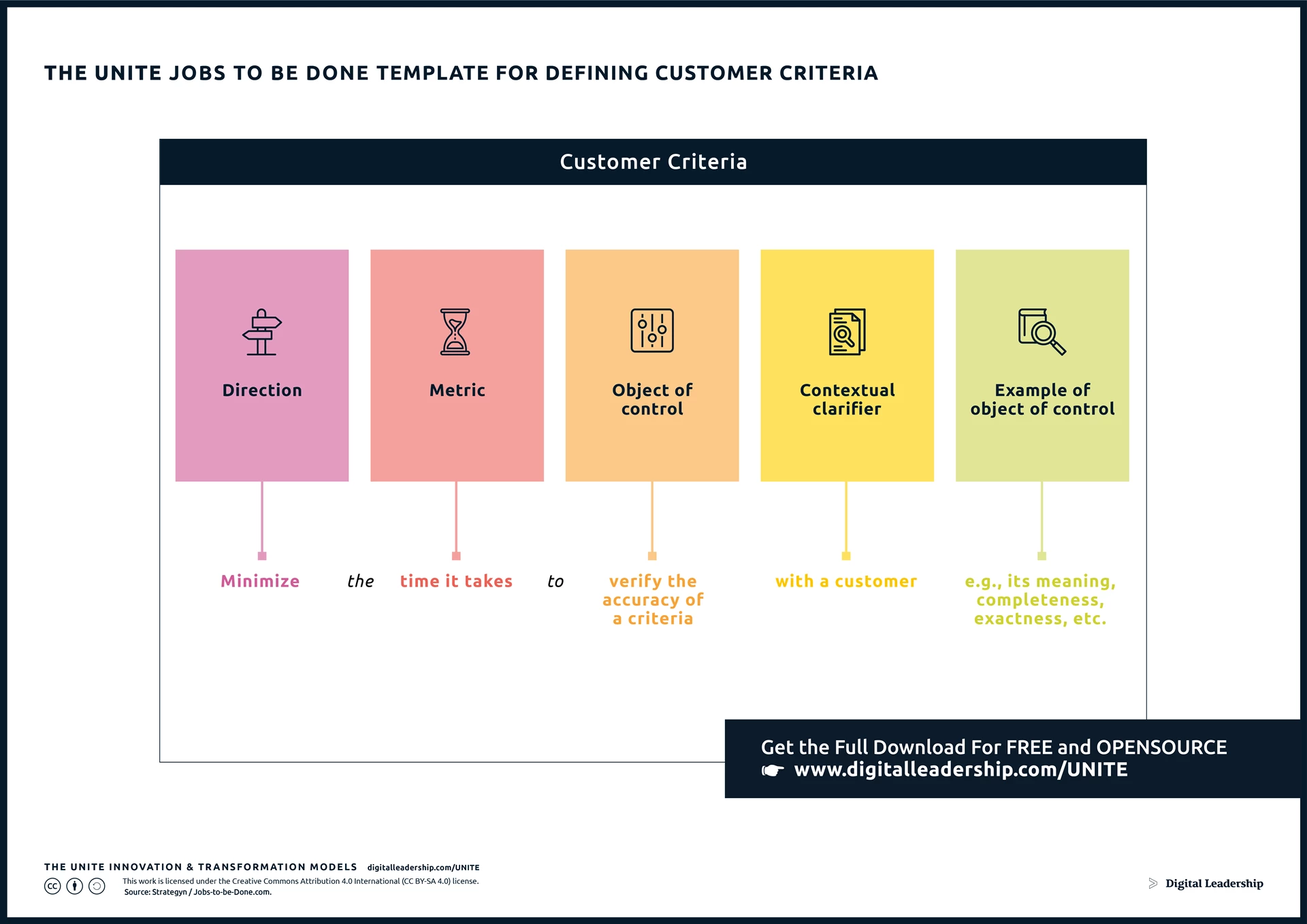
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Source: Strategyn
Your download is now available!
You can now access the complete Jobs to Be Done Template for Defining Customer Criteria Package, including a full presentation, related models and instructions for use.
9- Identify Big Opportunities:
Visualize survey results using tools like the Job Journey Navigator, identifying gaps where customer importance is high, but satisfaction is low. Group opportunities into logical categories, considering different customer segments and preferences. Connect identified needs to business opportunities by articulating promises to customers based on unmet needs.
The “Jobs to be dine job journey navigator” help businesses navigate the intricacies of the customer journey, gaining valuable insights into the various stages and touchpoints where specific jobs need to be accomplished and facilitates the identification of key pain points, unmet needs, and areas of improvement along the customer journey, laying the groundwork for the discovery of significant market opportunities.
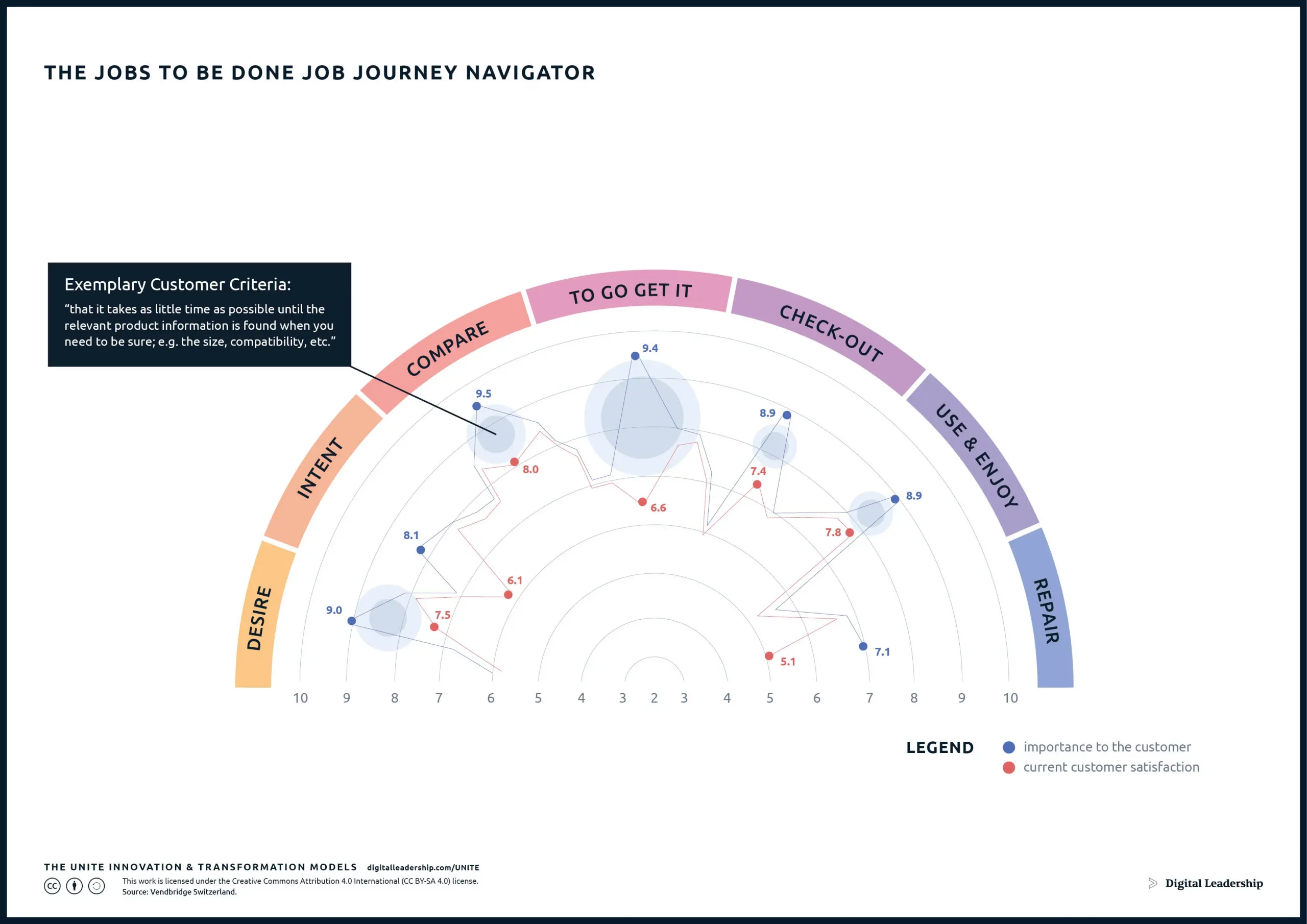
Designed by: Digital Leadership AG – Source: Vendbridge Switzerland.
Your download is now available!
You can now access the complete Jobs to Be Done Journey Navigator Package, including a full presentation, related models and instructions for use.
10- Comparative Analysis and Consumer-Centric Approaches:
Conduct a thorough comparative analysis with competitors to determine distinctive market positioning. Engage with both current and former customers to regain insights, fostering success through approaches centered around consumers. Understand how competitors position themselves and pinpoint opportunities for setting oneself apart.
11- Environmental Analysis and Global Opportunities:
Widen the perspective by undertaking an environmental analysis, exploring global markets, and uncovering opportunities beyond traditional boundaries. Examine foreign markets and explore cross-industry opportunities for a comprehensive market exploration. This step involves grasping the broader business landscape to identify potential opportunities outside the immediate market.
Jobs to Be Done Market Opportunity Examples
In market opportunity analysis, the Jobs to Be Done (JTBD) framework stands out as a strategic ally for businesses. The following examples illustrate how astute marketing, guided by jobs to be done examples insights, can unlock and maximize market potential. Enhancing user experiences to drive industry transformations, these instances underscore the pivotal role of marketing in tandem with JTBD principles.
- Enhancing User Experience Through JTBD:
- Scenario: A leading tech company, such as Apple, employs JTBD to identify unmet needs in user experience related to device integration.
- Opportunity: Tailored marketing campaigns emphasizing seamless integration not only improve product adoption but also solidify Apple’s position as an industry leader in user-centric design.
- Example: Apple’s introduction of AirPods, aligning with the need for hassle-free wireless audio connectivity, exemplifies how JTBD-driven innovations can reshape and dominate markets.
- Transformation through Marketing Using JTBD:
- Scenario: Tesla, the electric car manufacturer, integrates jobs to be done insights into its marketing strategy.
- Opportunity: By aligning marketing messages with innovative features addressing customer jobs, Tesla attracts new customers and positions itself as an industry innovator.
- Example: Tesla’s emphasis on electric vehicles meeting environmental needs and providing a unique driving experience exemplifies the successful integration of JTBD into marketing, transforming the automotive industry.
- Improving Product Management with JTBD:
- Scenario: Product management firm Atlassian applies JTBD principles to understand client needs.
- Opportunity: By incorporating JTBD insights into product development, the firm enhances its offerings, creating a competitive edge and opening avenues for new market opportunities.
- Example: Atlassian’s Jira software, developed with a focus on streamlining project management tasks, reflects how JTBD insights can lead to products that redefine industry standards.
- Health and Wellness Innovation:
- Scenario: Nike, a fitness brand, embraces jobs to be done analysis to understand customer aspirations in the health and wellness sector.
- Opportunity: Strategic marketing messages tailored to JTBD insights result in successful product launches, establishing the brand as a leader in the health and wellness market.
- Example: Nike’s use of JTBD in launching personalized training apps addresses individual fitness goals, showcasing the brand’s commitment to customer-centric solutions.
- Streamlining Business Processes:
- Scenario: Salesforce, a B2B company, strategically incorporates JTBD into its marketing communication.
- Opportunity: By showcasing how its services address specific jobs for corporate clients, Salesforce strengthens existing client relationships and attracts new business opportunities.
- Example: Salesforce’s emphasis on simplifying customer relationship management aligns with jobs to be done, showcasing its value in streamlining business processes for enhanced efficiency.
- Personal Finance Revolution:
- Scenario: A financial institution, like PayPal, revolutionizes its marketing approach with JTBD insights.
- Opportunity: Crafting campaigns positioning its services as solutions to customer financial aspirations, the institution enhances brand visibility, fostering customer trust and loyalty.
- Example: PayPal’s adoption of JTBD in marketing highlights its role in providing secure and convenient financial solutions, revolutionizing the digital payment landscape.
Strategic Approach to Identifying and Navigating Market Opportunities
In the pursuit of market opportunities, strategic decision-making becomes paramount, and the IPDE (Identify, Predict, Decide, Execute) approach emerges as a guiding methodology.
A tangible outcome of this strategic approach is the creation of opportunity maps and crafting these maps is integral to the Jobs to Be Done framework, and here, businesses find templates and guidelines to ensure the clarity and actionable insights of their opportunity maps. The focus shifts to methods for identifying market opportunities, starting with a detailed analysis of direct competitors.
Understanding the competitive landscape is supplemented by insights from indirect competitor analysis, a method that looks beyond traditional industry boundaries to spot gaps and potential areas for innovation. The exploration expands globally, guiding businesses in analyzing foreign markets and navigating international complexities for new opportunities.
Types of Market Opportunities
Market opportunities come in various forms, each presenting unique avenues for growth and success. Understanding the different types of market opportunities is essential for businesses seeking to diversify, innovate, and thrive in dynamic landscapes. Here are key categories:
New Market Opportunities:
Venturing into untapped markets or demographic segments can provide significant growth potential. Identify emerging markets or demographics with unmet needs and tailor offerings to capture these opportunities.
Low-End Market Opportunities:
Addressing the needs of cost-conscious consumers by providing budget-friendly alternatives or streamlined solutions. Low-end market opportunities require efficiency and a keen understanding of essential features that resonate with value-driven customers.
Innovation-driven Opportunities:
Leveraging technological advancements or unique approaches to address existing challenges. Innovations may involve introducing groundbreaking products, services, or processes that redefine industry standards and captivate consumers.
Niche Market Opportunities:
Focusing on specific, specialized market segments can lead to success. Niche opportunities involve catering to the distinct needs of a targeted audience, fostering brand loyalty and differentiation.
International Market Opportunities:
Exploring global markets provides avenues for expansion. Identify regions with compatible cultural contexts, regulatory environments, and unmet needs, tailoring strategies for successful international market entry.
Partnership Opportunities:
Collaborating with other businesses or forming strategic partnerships can unlock new possibilities. Joint ventures, alliances, or collaborations can lead to shared resources, expanded networks, and mutually beneficial growth.
Conclusion
Success hinges on the adept identification and utilization of market opportunities. The Jobs to Be Done (JTBD) framework serves as a strategic tool, offering a comprehensive approach to analyzing market opportunities. Delving into the nuances of market needs, uncovering both new and latent opportunities, and harmonizing strategies with customer-centric approaches are crucial facets of this process. By embracing the potency of JTBD, businesses not only pinpoint market opportunities but also foster an environment conducive to innovation, guaranteeing sustained growth in a dynamic business landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
1- What is a Market Need?
A market need is a specific demand or requirement within a target market that businesses aim to fulfill. It represents an opportunity for products or services to address gaps or solve problems. Identifying and meeting market needs is essential in business strategy to enhance value creation and gain a competitive edge. From defining market needs to recognizing the nuances of unmet needs, we explore the fundamental elements that drive businesses to innovate and cater to evolving customer demands.
2- What is Unmet Need Meaning?
An unmet need is a requirement or desire that remains unsatisfied, indicating a gap in the provision of goods, services, or solutions within various contexts such as healthcare, business, technology, and social services. Recognizing unmet needs is essential for fostering innovation and problem-solving, as it reveals opportunities for enhancing existing products or developing new ones to better meet the demands of individuals or markets. Understanding unmet needs is a crucial component of market research and strategic planning, enabling businesses and organizations to customize their offerings to address specific gaps or deficiencies in the current landscape.
3- What is an Opportunity, and Why Are They Important?
Opportunities are pivotal moments that offer the chance for growth and positive change. Whether in personal or professional realms, they provide avenues for learning, innovation, and career advancement. Embracing opportunities is key to overcoming challenges and adapting to change. Seizing opportunities is synonymous with success, driving innovation and strategic development. Recognizing and capitalizing on opportunities require awareness, a willingness to take calculated risks, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Ultimately, these moments shape individual destinies and organizational trajectories, serving as catalysts for achieving goals and navigating the evolving landscapes of life and work.
























 Book How to Create Innovation
Book How to Create Innovation